Respiratory System Notes
advertisement
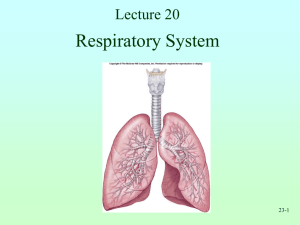
Respiratory System Structures & Functions • The organs of the respiratory system include – Nose – Pharynx – Larynx – Trachea – Bronchi – Lungs • Accessory organs – Diaphragm – Thorax Structures & Functions • The process of respiration involves the inspiration of air that contains O2 for use by the cells of the body and the expiration of CO2, which is a waste product from the cells of the body. • The respiratory system relies on the circulatory system to complete the respiratory cycle. Structures & Functions • O2 is inhaled into the lungs and transported by the blood. • The blood then transports waste products back to the lungs to be exhaled. Nose • Naso or rhino mean nose • Acts as an entrance for air and exit for CO2. • Mucous membrane lines the nose. ▫ Acts as a filter for dust and other foreign matter • The nose also warms and moistens the entering air. • Contains olfactory receptors. • Bloodhound Nose • The nostrils are paired external openings to the airways. ▫ Very in pliability and expandability Horse – expandable nostrils Pig – rigid nostrils Importance of Concha • Responsible for bringing air temperature to an acceptable level. • Bulldog Pharynx • AKA the throat • The upper portion of the pharynx is attached to the base ok the skull and the lower portion unites with the esophagus. • Divided into three parts – Nasopharynx • Opening into the back of nasal chambers – Oropharynx • Opening into the back of the mouth – Laryngopharynx • Opening into the larynx and esophagus Pharynx • The pharynx is used by both the respiratory and the digestive tracts as a passageway for air and food • Depending on the species, it may also have a role in vocalization. Larynx • The larynx is commonly called the voice box and is located just below the pharynx. (Adams apple) • Firm cartilage structure at the opening to major airways. ▫ Epiglottis a lid like cartilage structure that prevents food from entering the airway during swallowing Main sound organ in mammals Larynx • The larynx contains the vocal folds • Opening between the vocal folds is the glottis. Trachea • Series of cartilage rings joined by connective tissues. ▫ Rings are C shaped, not complete circles Why? • Supports a rigid airway, allows for movement. Trachea • Lined with epithelium containing cilia. ▫ Particles that get past the nasal membranes are caught in the cilia. ▫ Worked toward pharynx where it is swallowed. Trachea • Trachea branches into 2 bronchi. ▫ Right and left lung • Trachea ▫ Bronchus Bronchioles Alveolar Sacs ▫ Aveoli RESPIRATORY RATES OF VARIOUS ANIMALS HORSE: 10-14 BPM MEAN 12 DAIRY COW: 26-35 BPM MEAN 29 PIG: 32-58 BPM MEAN 40 DOG: 18-34 BPM MEAN 24 CAT: 20-40 BPM MEAN 31 SHEEP: 20-34 BPM MEAN 25