The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system
advertisement

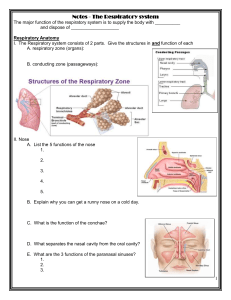
ANATOMY OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM BMS 231: 2015/2016 DR SOBIA IKRAM DR AQEELA BANO Objectives At the end of the lecture you should be able to 1. Describe the anatomical organization of the respiratory system. 2. Describe the basic anatomy of all the organs present in respiratory system. The Respiratory System • Basic functions of the respiratory system – Supplies body with oxygen – Removal of carbon dioxide Respiratory System • Respiratory organs – Nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses – Pharynx, larynx, and trachea – Bronchi and smaller branches – Lungs and alveoli Organs of the Respiratory System Figure 21.1 The Nose • Provides an airway for respiration • Moistens and warms air • Filters inhaled air • Resonating chamber for speech • Olfaction (smell) Anatomy of nose • Anatomically nose is divided into • External nose and internal nose 1. External nose External nose is shaped like a pyramid with a tip directed upward and base directed downwards. - upper 1/3 is made up of bone - lower 2/3 is made up of cartilage Internal nose 2. Internal nose Is also called nasal cavity or vestibule. Divided by nasal septum into right ant left halves. External openings are called nostrils or external nares Posteriorly it is continuous with nasopharynx. Para-nasal Air Sinuses Definition: - They are air-filled spaces in certain bones of skull. - They open into the lateral wall of the nose. Para-nasal Air Sinuses Types: 1. Maxillary sinus 2. Frontal sinus 3. Sphenoid sinus 4. Ethmoid sinus Para-nasal Air Sinuses The Pharynx Pharynx is the cavity behind the nose and mouth and connect them to the esophagus. Anatomically it is the part of the conducting zone of the respiratory system • Divided into three sections by location – Nasopharynx – Oropharynx – Laryngopharynx Seen from lateral • Nasopharynx • Oropharynx • Laryngopharynx The Larynx • larynx is an organ ,present between the trachea and the root of the tongue. • It is also called voice box as it contains vocal cord that are responsible for voice production • It is made up of various cartilages membranes and ligaments. The Larynx Functions – Voice production – Provides an open airway – Routes air and food into the proper channels • Superior opening , which is guarded by epiglottis , is – Closed during swallowing – Open during breathing The Larynx Cartilages of the larynx 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Epiglottis Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Arytenoid cartilage (2) Corniculate cartilage (2) Cuniform cartilage (2) The Larynx Anterior view of the larynx The Larynx Posterior view of the larynx THE TRACHEA • Tube shaped structure that extend from lower border of layrnx • It end by dividing into right and left main bronchi. • It provides the passage for air. TRACHEA AND BRONCHI • Anatomy of trachea and bronchi THE TRACHEA Anatomically trachea is made up of c shaped tracheal cartilages. On the back these cartilages are completed by the muscle called trachealis muscle The Pleura Definition • A double-layered serous membrane surrounding each lung is called Pleura – Parietal pleura – Visceral pleura • Pleural cavity – Space between the visceral and parietal pleura is called Pleural cavity. The Pleura Anatomy of the Lungs • Each lung has – Apex, a pointed upper end – Base, lower or diaphragmatic surface – Hilum, depression on the medial surface of each lung. APEX BASE HILUM Anatomy of the Lungs LEFT LUNG Left lung have following anatomical terms. • Superior and inferior lobes separated by oblique fissure . • Space for the heart called cardiac notch. CARDIAC NOTCH SUPERIOR LOBE OBLIQUE FISSURE INFERIOR LOBE Anatomy of the Lungs RIGHT LUNG Right lung has following anatomical terms • Superior, middle and inferior lobes. • Transverse and oblique fissures Superior lobe Middle lobe Inferior lobe Transverse fissure Oblique fissure LOBES OF LUNGS ANY QUESTIONS????????????????????????????