The Respiratory System
advertisement

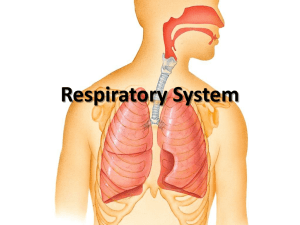
The Respiratory System Organ System Connections The cardiovascular system and the respiratory system are responsible for supplying the body of oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide Respiratory system deals the gas exchange Cardiovascular system deals with transportation Functional Anatomy Organs of the respiratory system (in order of air passage) Nose/Mouth Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi and their smaller branches Lungs and alveoli Nose Air enters the nose by passing through the nostrils Separated by a nasal septum The interior of the nose is called the nasal cavity Lined with respiratory mucosa Rests on a rich network of thin-walled veins that function to warm the air as it flows past These are what cause nosebleeds Pharynx Review True or false: This organ is a part of the digestive system and the respiratory system TRUE! Remember: the pharynx is for PHood, PHluids, AND air Larynx “Voicebox” Formed by 8 rigid hyaline cartilage rings The epiglottis is also located in this organ and separates the larynx from the esophagus What was the epiglottis again? Flap of cartilage that prevents food from “going down the wrong tube” Trachea “Windpipe” Walls are reinforced with Cshaped rings of hyaline cartilage Dual functions The open part of the C allows the esophagus to expand anteriorly when we swallow The solid portions keep it open during the pressure changes that occur during breathing Bronchi There are 2 main bronchi plus many pairs of shorter branching bronchioles Lungs Flank the heart Lungs are covered with serous membrane Visceral pleura Parietal pleura Pleural fluid in between (basically plain old serous fluid) Sound familiar? This is JUST like how the heart is set up! Lungs The primary bronchi (the two main branches) enter the lungs and then subdivide into smaller and smaller branches Called bronchioles The terminal set of bronchioles lead into respiratory zone structures Eventually terminate into alveoli, small air sacs Lungs: Alveoli The walls of the alveoli are composed of a single, thin layer of squamous epithelial cells External surface of the alveoli are covered with a “cobweb” of pulmonary capillaries Alveoli + capillary walls = respiratory membrane Air (containing gases) flows past on one side and blood flows on the other side This is also known as the air-blood barrier Gases Gas exchange Oxygen passes from the alveolar air into the capillary blood Carbon dioxide leaves the blood to enter the gasfilled alveoli Zones Respiratory zone Includes respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs Conducting zone All other respiratory zone structures Zones List the organs that are considered to be in each zone Respiratory zone: Bonchioles, alveoli Conducting zone: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi Accessory Organ Diaphragm: muscle that helps to inflate the lungs