Respiratory System Notes
advertisement
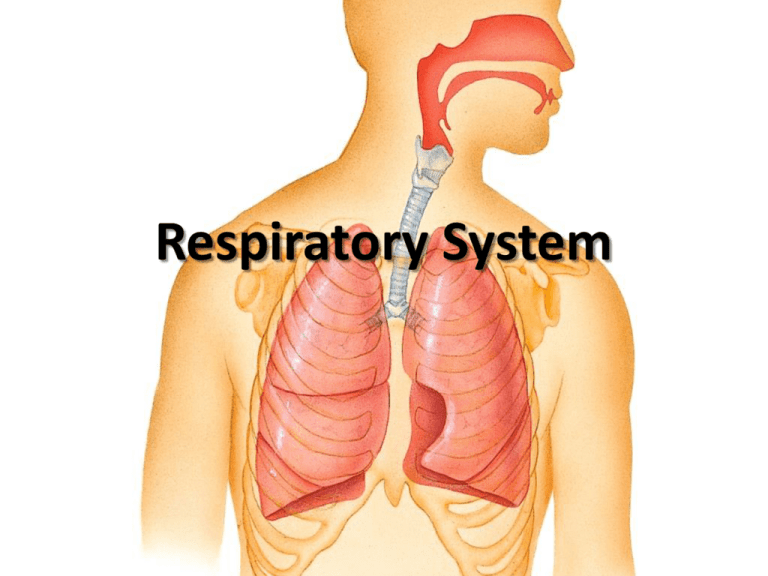
Respiratory System INTRODUCTION Functions • • • • • • • • Provide for gas exchange Intake of O2 Removal of CO2 Regulate blood pH Sense of smell Produces sounds Filters, warms, moistens air Water, heat balance 3 Major Steps Pulmonary Ventilation • Moving air in and out of lungs External Respiration • Gas exchange between alveoli and blood Internal Respiration • Gas exchange between blood and body cells STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Upper Respiratory Nose (nares) • Warm, humidify, filter dust • Olfactory stimuli • Modify vocal sounds Pharynx • 3 regions • Tonsils, adenoids here • Eustachian tubes Lower Respiratory Larynx • “Voice box” • Thyroid cartilage • Epiglottis • Cricoid cartilage Lower Respiratory Trachea • Windpipe • Lined with ciliated mucous membrane; traps dust and moves it upward • C-shaped rings of cartilage keep airway open Lower Respiratory Bronchi, Bronchioles • Bronchi contain cartilage rings • Primary (1° ) bronchi enter lungs • Secondary bronchi branch from 1°, one for each lobe (3R, 2L) • Tertiary bronchi →→ terminal bronchi • Smaller airways have less cartilage, more smooth muscle Lower Respiratory Lungs • Right lung has 3 lobes, left has 2 • Surrounded by pleural membrane • Tertiary bronchioles divide into terminal bronchioles • These lead to respiratory bronchioles, which lead to the alveoli Lower Respiratory Alveoli • This is where gas exchange takes place • Surfactant cells secretes a substance that keeps the alveoli from collapsing • Macrophages help fight infection Pulmonary Ventilation Volume and pressure are inversely related Inhalation: • Contraction of diaphragm lowers the muscle and lung volume ↑ • Alveolar pressure ↓ • Air enters lungs to equalize pressure Pulmonary Ventilation Exhalation: • Relaxation of the diaphragm raises the muscle and lung volume ↓ • Alveolar pressure ↑ • Air rushes out Air Flow Frequency (f): Breaths/min; normal = 12 Tidal Volume (TV): volume moved in one normal breath • Normal = approx. 500ml • About 70% reaches alveoli • 30% remains in airway Minute Ventilation (MV): f x TV = 6000 ml/min Air Flow Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV): volume of air that can be inhaled beyond TV Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV): volume of air that can be exhaled beyond TV Residual Volume (RV): air remaining in lungs after ERV Nature of Air Mixture of gases – N2, O2, CO2, H2O, etc. Each gas exerts a partial pressure Sum of partial pressures = atmospheric pressure Each gas diffuses down its pressure gradient • Example: O2 • In air, P = 105 mm Hg • In blood, P = 40 mm Hg Breathing Control Brain Centers: • Medullary rhythmicity area • 2 areas in the pons Factors: • Voluntary adjustment (cortical) • Chemoreceptors • Limbic system; emotion, anticipation • Body temperature • Pain, airway irritation (cough, sneeze)