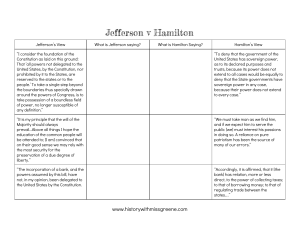
Early Republic Cheat Sheet George Washington Set many
advertisement

Early Republic Cheat Sheet George Washington Set many precedents as 1st President Unwritten Constitution – Things our government does out of custom and tradition even though there is no mention of them in the Constitution – examples - Political Parties, President’s Cabinet 1st Political Parties created because of differences in his cabinet Hamilton vs. Jefferson Hamilton’s Financial Plan – Excise tax (on Whiskey caused Whiskey Rebellion), National Bank, high tariff Jefferson opposes National Bank arguing it is unconstitutional Strict vs loose interpretation of Constitution Strict (Jefferson) – Govt can ONLY do what the Constitution says it can do Loose (Hamilton) – Govt can do a lot more because of the elastic (or necessary and proper) clause Hamilton Wins – National bank will help stabilize the American economy and lead to prosperity Washington’s Foreign Policy NEUTRALITY – All the early presidents favored a policy of neutrality in order to preserve newly won independence Thomas Jefferson Also remained NEUTRAL in European conflicts/crisis Biggest achievement was purchase of Louisiana. However, this purchase requires a loose interpretation of the Constitution Louisiana was important because it allowed the U.S. to use the Port of New Orleans and the Mississippi river to transport U.S. agricultural products Monroe Doctrine – issued to prevent European nations from future colonization in Latin America. Court Cases Judicial Review – Power of the Supreme Court to declare a law unconstitutional. First used in Marbury v. Madison Gibbons v Ogden – based on the federal governments right to regulate interstate commerce Andrew Jackson Greatly expanded the power of the Presidency (even given nickname King Andrew) – examples: used veto power often, replaces government workers with his supporters (spoils system), removed Native Americans from South to West of the Mississippi River (Trail of Tears)