independent section.
advertisement

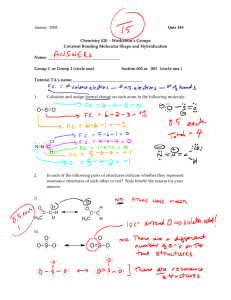
NAME________________________________ TEST: BONDING AND NOMENCLATURE Multiple Choice Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1-5 refer to the following molecules. (A) CO2 (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. This molecule has exactly one double bond. This molecule contains the most polar bond. This molecule has an atom with trigonal pyramidal geometry. This molecule is commonly known as methane. This molecule contains an atom with a hybridization of sp. Questions 6-8 (A) F (B) N (C) Mg (D) Cr (E) Mn 6. Only forms monatomic ions with 2+ charge in solutions. 7. Forms a compound having the formula K2XO4 8. Forms oxides that are common air pollutants and that yield acidic solution in water. Questions 9-12 (A) SO32(B) NO31(C) PO43(D) SCN1(E) H3O+ 9. This molecule forms a trigonal planar geometry. 10. This molecule does not require resonance to accurately describe its bonding. 11. When this molecule bonds with hydrogen, it forms an acid which is named phosphoric acid. 12. The central atom of this molecule has sp type hybridization. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or compilations. Select the one that is best in each case and then blacken the corresponding space on the answer sheet. 13. Which of the following correctly identifies the formula for copper (II) dichromate (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Cu2Cr2O7 Cu(CrO4)2 CoCr2O7 CuCr2O7 Co2(CrO4)2 14. Of the following compounds, which is the most ionic? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) SiCl4 BrCl PCl3 Cl2O CaCl2 15. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is best accounted for by the (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) increasing strength of the bonds. decreasing size of the central atom. increasing electronegativity of the central atom. increasing number of unshared pairs of electrons. decreasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms. 16. Types of hybridization exhibited by the C atoms in propene, CH3CHCH2, include which of the following? I. sp II. sp2 III. sp3 (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 17. The SbCl5 molecule has trigonal bipyramid structure. Therefore, the hybridization of Sb orbitals should be (A) sp2 (C) sp2d (E) sp3d2 (B) sp3 (D) sp3d 18. CCl4, CO2, PCl3, PCl5, SF6 Which of the following does NOT describe any of the molecules above? (A) Linear (D) Tetrahedral (B) Octahedral (E) Trigonal pyramidal (C) Square planar 19. Which of the following compounds is ionic and contains both sigma and pi covalent bonds? (A) Fe(OH)3 (C) H2S (E) NaCN (B) HClO (D) NO2 20. The most correct name for FeSO3 is: (A) Iron sulfate (C) Iron sulfite (B) Iron (II) sulfate (D) Iron (III) sulfite (E) Iron (II) sulfite 21. The geometry of the SO3 molecule is best described as (A) trigonal planar (D) bent (B) trigonal pyramidal (E) tetrahedral (C) square pyramidal 22. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? (A) N2 (C) Cl2 (E) I2 (B) O2 (D) Br2 23. Pi (π) bonding occurs in each of the following species EXCEPT. (A) CO2 (C) CN(E) CH4 (B) C2H4 (D) C6H6 24. Which of the following has a zero dipole moment? (A) HCN (C) SO2 (E) PF5 (B) NH3 (D) NO2 25. For which of the following molecules are resonance structures necessary to describe the bonding satisfactorily? (A) H2S (C) CO2 (E) PF3 (B) SO2 (D) OF2 Free Response: Directions: Using the paper provided, answer each of the following questions clearly showing the methods you use and the steps involved at arriving at the answers. 1. Answer the following questions using principles of chemical bonding and molecular structure. a. Consider the carbon dioxide molecule, CO2, and the carbonate ion, CO32–. i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each species. ii. Account for the fact at the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO32– is greater than the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO2. b. Now consider the sulfate ion SO42- and the iodine trifluoride molecule IF3. i. Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each ion/molecule. ii. In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the SO42- ion is nonpolar, whereas the IF3 molecule is polar. 2. Using dot structures and words completely compare and contrast ionic bonds and covalent bonds. 3. Completely fill in the table below. (Hint: For Ca(SCN)2 do not include the Ca when considering the shape, hybridization or polarity.) Name Chemical formula Lewis structure Hybridization Ammonia Ca(SCN)2 Nitrous Acid ClBr3 sp3d2 Molecular shape Polar?