File
advertisement

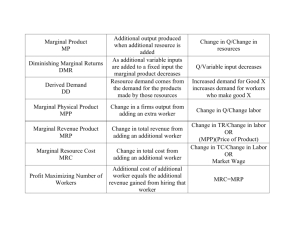
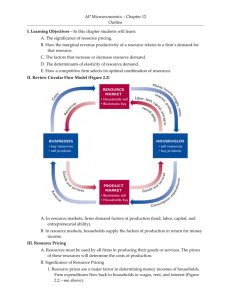
AP Economics December 8, 2014 1. Review Unit 3 Exam: Theory of the Firm 2. Begin Unit 4: Factor Markets 3. Unit 4 Exam NEW DATE: Monday, December 22 and Tuesday, December 23. Factor/Resource Market: Firm is a Seller and a Buyer The Demand for Resources • Factor of production is something (an input) that is used to produce output. • Examples: buildings, machinery, land, labor, raw materials • Derived Demand: The demand for an input is derived from the demand for the output that the input helps produce. MRP & MRC • Marginal Revenue Product (MRP): change in Total Revenue that results from the employment of an additional worker. • MRP = DTR / DL • Marginal Resource Cost (MRC): change in Total Cost that results from employment of an additional worker. • MRC = DTC / DL • A firm maximizes its total profit by using: • MRP=MRC Rule MRC in a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market • Each time a firm hires another worker, its cost increases by the price of the labor (PL) • For a firm in a perfectly competitive labor market, MRC = PL (MRC=Wage) • (If a firm is not in a perfectly competitive labor market, this is not true.) The Supply Curve of Labor to a Firm that is a Perfect Competitor in the Labor Market (Firm is a Wage-Taker) Price of Labor PL S Labor AP Economics December 9, 2014 1. Continue Lesson 4-1: MRP as Resource Demand 2. HW: Activity 4-1 3. Return Work MRP as Resource Demand Perfectly Competitive Product Market (1) (2) Units of Total Product Resource (Output) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (3) Marginal Product (MP) (4) Product Price 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 $2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 0] 7] 13 ] 18 ] 22 ] 25 ] 27 ] 28 (5) Total Revenue, (2) X (4) $0 14 26 36 44 50 54 56 ] ] ] ] ] ] ] (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) $14 12 10 8 6 4 2 $18 Purely Competitive Firm’s Demand for a Resource Resource Wage (Wage Rate) 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 D=MRP 2 0 -2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Quantity of Resource Demanded LO1 12-8 MRP as Resource Demand Imperfectly Competitive (1) (2) Units of Total Product Resource (Output) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (3) Marginal Product (MP) 0] 7] 13 ] 18 ] 22 ] 25 ] 27 ] 28 (4) Product Price (5) Total Revenue, (2) X (4) $2.80 2.60 2.40 2.20 2.00 1.87 1.75 1.65 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 $ 0.00 18.20 31.20 39.60 44.00 46.25 47.25 46.20 ] ] ] ] ] ] ] (6) Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) $18.20 13.00 8.40 4.40 2.25 1.00 -1.05 $18 Imperfectly Competitive Firm’s Demand for A Resource Resource Wage (Wage Rate) 16 14 D=MRP (Pure Competition) 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 D=MRP (Imperfect Competition) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -2 Downward sloping at steeper rate due to (1) Diminishing Marginal Productivity (2) Product price drop Quantity of Resource Demanded LO1 12-9 AP Economics December 10, 2014 1. Review Activity 4-1 2. Lesson 4-2: Optimal Combination of Resources 3. HW: Activities 4-2, 4-3, 4-4 Lesson 4-2 The Optimal Combination of Resources • In our Yo-Yo activity, we assumed the firm was operating in the Short Run with fixed capital and labor as its variable resource. • Long Run: Firm can change its capital (K) and it labor (L) • Q: What combination of L & K should the firm employ? • We can Minimize Cost or Maximize Profit… The Least Cost Combination • If a firm wants to produce the most output on a given budget…or…if it wants to produce a given level of output at lowest cost, it uses… Marginal Product Of Capital (MPK) Marginal Product Of Labor (MPL) = Price of Labor (PL) (MRCL) LO3 Price of Capital (PK) (MRCK) 12-12 Profit Maximizing Rule • Least Cost Rule is necessary but not efficient… MRPL MRPK = 1 = LO3 PL PK (MRCL) (MRCK) 12-13 Suppose a firm's marginal product of capital and marginal product of labor schedules are as shown in the table below. The firm hires both capital and labor competitively for $4 and $8, respectively. Its output is sold in a competitive market for $.50 per unit. 1.Suppose the firm is currently using 4 units of capital and 4 units of labor. Is the corresponding output being produced at least cost? How do you know? 2.What combination of labor and capital should the firm use to maximize its profit? Capital MP of Capital Labor MP of Labor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 --10 9 8 7 6 5 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 --28 30 24 20 16 12 8