Factor Markets - Cobb Learning
advertisement

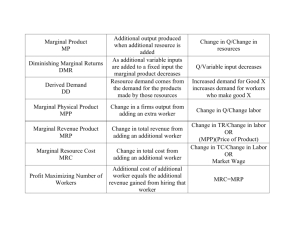
Factor Markets Unit IV Basic concepts • Similar to those of: – supply and demand – And product markets – Same concepts with new application Circular Flow (review) • Shows the difference and interaction between factor and product markets • The real flow and money flow • Households supply the factor market • Business supply the product market • Households are demand in the product market • Business is the demand in the factor market Factor, or resource markets ( inputs) • What is the difference between factor markets and product markets? • A firm is both a seller in the product market and a buyer in the factor market • Factor markets may be perfectly competitive or imperfectly competitive. • MRP=MRC rule • Basically the same as the MR=MC rule Big Ideas about Factor, or Resource, Markets 1. Economic concepts are similar to those for product markets. 2. The demand for a factor of production is derived from the demand for the good or service produced from this resource. 3. A firm tries to hire additional units of a resources up to the point where the resource’s marginal revenue product (MRP) is equal to its marginal resource cost (MRC). 4. In hiring labor, a perfectly competitive firm will do best if it hires up to the point where MRP= the wage rate. Wages are the marginal resource cost of labor. More Big Ideas about Factor, or Resource, Markets 5. If you want a high wage: A. Make something people will pay a lot for. B. Work for a highly productive firm. C. Be in relatively short supply. D. Invest in your human capital. 6. Real wages depend on productivity. 7. Productivity depends on real or physical capital, human capital, labor quality and technology Important terms • • • • • Derived demand Marginal revenue product Marginal physical product Marginal resource cost Profit maximizing rule for employing resources Factor Markets day 2 • Journal: Explain the profit maximizing rule for factor markets. Don’t just state it. Make sure you understand how and why it works. • Why is the MRP or demand downward sloping? Diminishing marginal returns Changes in demand • What are factors that can shift demand for a resource? • Remember that the product market and factor market are interrelated: derived demand • Factors that can shift demand for a resource: 1. change in product price 2. change in productivity 3. changes in the price of substitutes or complementary resources depending on the substitution effect and the output effect Determinants of the elasticity of resource demand: • Rate of MRP decline ( remember that MRP is the D curve) • Elasticity of product demand • Ease of resource substitutability • The proportion of total costs that the resource represents Complete Activity 46 in class • Things to keep in mind: – A monopoly firm will hire fewer workers than a perfectly competitive firm. – The examples in # 46 compare monopoly and perfectly competitive firms in the product markets, even though the analysis is for the factor markets. They are interrelated. – Activity #47 for homework