File
advertisement

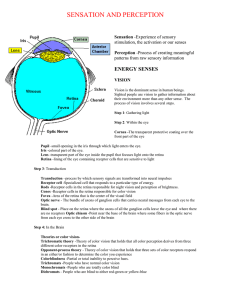
Unit 4 Sensation and Perception Lecture List the 5 senses below: Perception is important because: It is the key mediator between ______________________________________________ It is the source of most knowledge that humans acquire Definitions Sensation Define below: Perception Define below: enables us to recognize meaningful objects and events Sensation Bottom-Up Processing Information processing beginning “at the bottom” with raw sensory data that are sent “up” to the brain for higher level analysis _________________________ processing that moves from the parts to the whole Give an example: Top-Down Processing Information processing starting “at the top” with higher level cognitive processes (such as expectations and knowledge) and then “working down” ________________________________ processing that moves from the whole to the parts Give an example: Sensation- Basic Principals Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological experience of them Light: ________________________ Sound: _______________________ Pressure: _____________________ Taste: ________________________ Sensation- Thresholds Absolute Threshold ____________________________ needed to detect a particular stimulus usually defined as the stimulus needed for detection ________ of the time Give an example: Difference Threshold minimum ___________________________________ that a subject can detect 50% of the time just noticeable difference (JND) increases with magnitude Give an example: Signal Detection Theory predicts how and when we detect the presence of a faint ____________ (signal) amid background _______________ (noise) assumes that there is __________________________________________ detection depends partly on person’s -experience -motivation -expectations -level of fatigue Weber’s Law________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ light intensity- 8% weight- 2% tone frequency- 0.3% Sensory Adaptation: diminished ______________________________________ - receptors higher up in sensory system get tired and fire less frequently Examples: Vision Transduction: _____________________________________________________ Wavelength: the distance from the peak of one wave to the peak of the next Hue: dimension of color determined by __________________________ Intensity: amount of energy in a wave determined by amplitude __________________________ __________________________ Vision: Physical Properties of Waves Draw examples of the waves below: Short wavelength=high frequency (bluish colors, high-pitched Great amplitude (bright colors, loud sounds) sounds) Long wavelength=low frequency (reddish colors, low-pitched sounds) Small amplitude (dull colors, soft sounds) Vision: Parts of the Eye ________________-: transparent covering on the front of the eye _____________: central point of focus on the back of the eye _____________: adjustable opening in the center of the eye _______: a ring of muscle the forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening _________: transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape to focus images on the retina Accommodation: change in shape of lens focus near objects __________________ Layers of neurons on inner surface of eye light sensitive contains rods and cones beginning of visual information processing Blind Spot: area of retina where optic nerve leaves back of eye Retina’s Reaction to Light Receptors Cones – near center of ___________________ – _____________________________ – daylight or well-lit conditions Rods • Located in periphery of _______________ • detect __________________________________________ • twilight or low light Vision Acuity: _______________________________ Nearsightedness _______________ objects seen more _____________ lens focuses image of distant objects in front of retina Farsightedness _____________ objects seen more _____________ lens focuses near objects behind retina Color-Deficient Vision People who suffer ________________ blindness have trouble perceiving the number within the design Visual Information Processing Feature Detectors ____________________________________________________ to specific features shape angle movement Parallel Processing simultaneous processing of __________________________________________________________ color motion form depth Visual Information Processing _________________________________________________ Young and Helmholtz The eye contains _____________ different types of cones capable of responding to various _________________________ red green blue Opponent-Process Theory: ___________________________________________________________ Draw a Necker Cube below: Visual Perception: Gestalt • Gestalt Principles (gestalt = an organized whole. We tend to integrate pieces of info. into meaningful wholes) – _______________________ – _________________ (law of good form) – _______________________________ – ________________________ – Continuity – Similarity – Phi Phenom Visual Perception: Depth Depth Perception: The Visual Cliff Binocular Cues: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Retinal Disparity: the fact that the right and left eyes see slightly different views of the object Convergence: the degree to which the two eyes must converge to focus on the object Monocular Cues: _____________________________________________ Linear Perspective: parallel lines converge in the distance Relative Size: if two objects are the same, the larger one is seen as closer Interposition: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ Texture Gradient: textures are coarser the closer they are Light and shadow Height in plane Visual Perception: Constancies Perceptual Constancies: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Color: an object will be perceived as the same color even if the color reflected on the retina changes Example: Size: an object will be perceived as the same size even if the size reflected on the retina changes Example: Shape: an object will be perceived as the same shape even if the shape reflected on the retina changes Example: Audition (Hearing) – Audition – the sense of ______________________ – Frequency – the _____________________________________ that pass a point in a given time – Pitch – a tone’s ____________________________ – depends on frequency – The Stimulus – Vibrations of ______________________ – Amplitude: __________________ – Wavelength: pitch – Purity: timbre Audition: The Ear Outer Ear - Auditory Canal ___________________________ Middle Ear - ________________________ _________________________ stirrup Inner Ear - oval window cochlea basilar membrane _____________________________ Audition: Pitch Perception Place Theory the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated Frequency Theory ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ How we locate sounds ________________________________________________ Sound is heard in the nearest ear first Sound is heard loudest in the nearest ear Audition: Loss Conduction Hearing Loss hearing loss caused by _______________ to the mechanical system that conducts _________________________________ Nerve Hearing Loss hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea’s receptor cells or to the auditory nerve Touch • Skin Sensations – _____________________ • only skin sensation with identifiable receptors – ______________________ – ______________________ – ______________________ • Gate-Control Theory – Theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological “____________” that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain – “gate” opened by the activity of pain signals ____________________________________ – “gate” closed by activity in larger fibers or by ___________________________________ Taste • Taste Sensations (List below) • Sensory Interaction – the principle that one sense may influence another – as when the smell of food influences its taste • The Stimuli: ____________________________________________ • • The Anatomy: taste buds act as the receptors for taste (about every ______________________) Perception of taste & flavor – Numerous factors can impact the flavor of food (Ex: temperature of the food, texture, prior condition of the mouth, health state of the organism, smell) Smell (Olfaction) • • • • The Stimuli: chemical substances that are soluble The Anatomy: receptors are olfactory cilia which ______________________________________ and sinus Sense ______________________ get filtered by thalamus _____________________________ interact to produce _______________ Body Position and Movement • • Kinesthesis o the system for sensing the ______________________________________ of individual body parts Vestibular Sense o the sense of body movement and body’s position relative to gravity o including the _________________________________ o Semicircular canals in ears Touch • Numerous types of receptors lie in varying depths in the skin • Four Basic Skin Senses (List Below)