1/24
advertisement

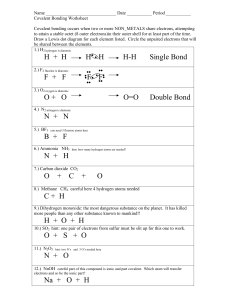
What is the world made of, and how is it all held together? Nothing… …if the earth is the nucleus of an atom, the electrons are twice as far away as pluto CB 2.4 Atoms are made of: protons neutrons electrons CB 2.8 Each element is defined by the number of protons, has an equal number of electrons, the number of neutrons may vary. The Periodic Table of the Elements Atoms can be combined together to make molecules How do atoms form molecules? An atom’s chemical characteristics are determined by the number of electrons it has. Bonds holding atoms together: • Covalent – Strong – Sharing Electrons – When broken = chemical reaction • energy consumed or released • Ionic – Weak – Positive and Negative atoms attracted to each other CB 2.13 Ionic bonds- electrons donated/accepted then atoms attracted by opposite charge CB 3.6 Ionic bonds are easily broken Bonds holding atoms together: • Covalent – Strong – Sharing Electrons – When broken = chemical reaction • energy consumed or released • Ionic – Weak – Positive and Negative atoms attracted to each other CB 2.11 Covalent bondsatoms share electrons CB 8.14 a chemical reaction makes or breaks covalent bonds Electron sharing in a covalent bond is not CB 2.12 always equal water + + CB 2.12 polar versus non-polar molecules + H + + + water H H C + + H methane Bonds holding atoms together: • Covalent – Strong – Sharing Electrons – When broken = chemical reaction • energy consumed or released • Ionic – Weak – Positive and Negative atoms attracted to each other Four types of molecules that are primarily found in living systems (biomolecules): •Carbohydrates/ Sugars •Nucleotides- DNA/RNA •Amino Acids- Proteins •Lipids- fats/phospholipids Videos: http://www.microscopyu.com/moviegaller y/livecellimaging/a549/index.html http://sunflower.bio.indiana.edu/~rhangart/ plantmotion/starthere.html CB 6.2