Business Academy & Dual Enrollment
advertisement

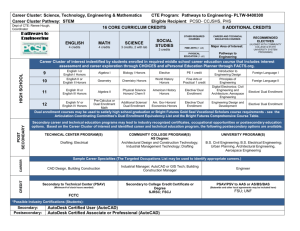
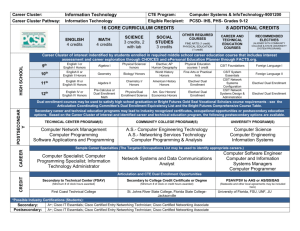
Rob Robison Robert.Robison@mywccc.org Warren County Career Center August 1, 2014 Outline Introduction Myself Business Academy Business Academy History and Course Offerings Degree Statistics (U.S. and Ohio) Dual Enrollment Difference in Credit Awards Cost Comparison Scholarships Speakers, Programs, and Activities 2 Credentials/Experience Degrees/Licensures Business & Accounting Major – Malone College Masters in Business Administration – Webster University Career Technical Licensure – Ohio State University Masters in Education – Xavier University Principals Licensure – Xavier University Nine years with numerous companies such as Daimler Chrysler, Givaudan Flavors, Lexis Nexis, NanYa Plastics… Spent time as an international accountant, controller, project manager, consultant, sales, and financial manager Began teaching Business as a satellite instructor at Kings High School through the Warren County Career Center Assistant Director of Secondary Education 3 Questions to Consider Why offer a Business Academy? What courses should you offer? What are the benefits to the students? How do you get students excited about the courses? How do you retain students in the program? Why offer dual enrollment courses in high school? How do you get approved for dual enrollment? What credits will transfer and which ones will not? Is the course rigor the same in high school as in college? 4 History of Business Academy Started the Business Academy in 2009 One of four CTE programs at Kings offered through WCCC Classroom has 30 desktop computers, 30 iPads, Promethean board, mobile laptop & projector cart, video conferencing equipment, and podcast equipment First years enrollment was 160 students, 2013-14 enrollment was 245 5 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th Introduction to Business & Ethics (3 transcipted credit hours) 11th &12th Honors Financial Accounting (3 T.A.G. credit hours) (fulfills graduation Personal Finance requirement) Introduction to Sales & Logistics Honors Business Law (3 T.A.G. credit hours) Fundamentals of Leadership & Supervision Honors Sports & Business Management (3 transcipted credit hours) Money Management & Investing (3 transcipted credit hours) (fulfills graduation Personal Finance requirement) Why should you take these business classes in high school? Sports & • Eliminates you from taking certain courses in college Entertainment • Significantly more time to learn the subject than in college Marketing • Looks good on a college application and financial scholarships (3 T.A.G. credit • Computer simulation programs to enhance learning hours) [2015-2016] • Business Academy scholarship opportunities • Class field trips (NYC/Philly) and “real world” guest speakers • Compete in Business Professionals of America in Columbus, OH and Anaheim, CA Honors Financial Accounting Honors Financial Accounting is a yearlong, junior/senior level honors course that will provide students with the background and understanding to read financial reports, assess company’s financial positions, and make managerial decisions when relating to Accounting. This course will also provide basic knowledge in preparing, processing, and interpreting the data pertaining to business transactions from different types of external, as well as internal investors, management, and other accounting information users. By the end of the course, students will be expected to be able to apply a set of accounting concepts to read annual financial report of a corporation and financial ratios to assess its position. Successful completion of this course could substitute Financial Accounting for colleges or universities in the state of Ohio. 7 Honors Business Law In this honors level course, students will explore the legal environment in which businesses operate and study the interaction between business and the legal system. Students examine various areas of the law which are integral to operating a business enterprise. Topics include contracts, torts, agency, Uniform Commercial Code, ethical and criminal implications of business actions, property laws, and the legal aspects of different business entities. In addition, we will study how laws were formed, procedures in civil and criminal cases, responsibilities of minors, being a consumer, purchasing power, purchasing insurance, personal and real property rights, starting a business and leadership skills. Successful completion of this course could substitute Business Law I for colleges or universities in the state of Ohio. 8 International Business International Business is a yearlong, junior/senior level course that will give students the understanding of global business needs and will help them solidify their ideas around exploration of international and domestic business needs. This course will put emphasis on history, geography, psychology, wars, culture, and customs that have varied in all nations and guide international business trade and transactions. Students will acquaint themselves with the growing opportunities and potential risks in doing business across international boundaries. Particular emphasis will be placed on the management of people and resources involved in the successful designing of products, channels of distribution, promotion, and pricing of goods or services in the global marketplace. 9 Sports Entertainment & Marketing Sports Entertainment and Marketing is a yearlong, junior/senior level course that will explore and focus on the fundamental principles and strategies associated with the sports and entertainment industry. Furthermore, this course will provide students with an overview of the different facets and career opportunities that are available in these fields. This course will teach the students how to formulate strategies and understand implementation issues when dealing with sports marketing. Students will look at, dissect, and understand contracts, opportunity costs, return on investments, etc. 10 Honors Sports & Business Management This course outlines the definition and evolution of sport management and will provide student with an overview of the structures within the sport industry and the management techniques that are applied. Students will explore various careers in professional, collegiate, high school and other areas of sport management. In addition, the student will define professional goals based on personal strengths and weaknesses in light of skills and competencies of sport leaders. Included in the curriculum, students will get a breadth of knowledge as it pertains to business management in general. Key focus will be on environmental awareness, personnel and risk management, policy making, and all other facets that are included in everyday business operations. 11 How to Get and Keep Students “Industrial Strength Teachers” – Get the right person in front of the students (easier said than done) Extra incentives for CTE programs Classroom environment Case Studies Simulations Real World Examples Do your due diligence, get students to buy in Connect with the customers, find out what they want New Coke vs. Classic Coke U.S. Statistics Business Degrees Business was the most popular degree in 2007-2008, according to the 2010 Digest of Education Statistics from the U.S. Department of Education Of the 1,601,368 bachelor's degrees awarded by degree-granting institutions, 346,972 or 22% were for degrees in business, management, marketing and related support services The next closest degree awarded was Social Sciences with 133,789 or 8% A bachelor's degree is often adequate for entry-level jobs, but you may need a higher degree for advancement and more technical positions Job prospects: Employment is expected to increase approximately 28% from 2008-2018 in the field of business SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. (2010) Digest of Education Statistics, 2009 (NCES 2010-2013.) 13 Employment by major occupational group, 2012 and projected 2022 (Bureau of Labor & Statistics) Ohio Statistics More than 60% of the fast-growing occupations require at least a bachelor’s degree in Ohio. Service and professional occupations, particularly in the fields of health, business, and education, dominate the list of occupations gaining the most employment or growing the fastest. The top fifty occupations pay an average annual earnings of more than $59,600 in Ohio. 15 16 17 Dual Enrollment Video 18 What is Dual Enrollment? The Warren County Career Center offers students the opportunity to begin post-secondary education through multiple agreements with local colleges and universities prior to high school graduation. The dual enrollment means that students may take selected high school courses through WCCC and earn credit towards high school graduation as well as, simultaneously, earn college credit. Students participating in a dual enrollment course are enrolled in a course which satisfies both high school and college requirements. This program was developed to allow students to begin working on their college degree earlier in their academic careers and thus complete their degree in a shorter period of time. 19 Dual Enrollment Offered through Cincinnati State Technical & Community College Dual enrollment courses offered by WCCC: Financial Accounting (3 semester credits) Business Law (3 semester credits) Marketing (3 semester credits) (n/a) Business Management (2 semester credits) Each semester hour credit costs is currently waived These classes are Transfer Assurance Guide (T.A.G.) courses and have been approved by the Ohio Board of Regents Curriculum and content is exactly the same as it would be at CST&CC Students have twice the amount of time to receive the curriculum in high school than at CST&CC 20 Advantages of Dual Enrollment Dual enrollment programs benefit a wide range of students Enhances academic profile when applying to postsecondary institutions Rigor and academic content is exactly as it would be if taught at the postsecondary institution Students have more time to learn and saves money Makes transition to college easier, students know what to expect Taking a dual enrollment class as a high school student can help students find their area of interest before the pressure is on to declare a major Students can start accumulating college credits, helping them graduate on time or even early from college Student/Parent Cost Benefit Business Academy has awarded 1,465 T.A.G. credit hours In total, Kings has awarded 1,893 T.A.G. credit hours and 330 articulated/transcripted credit hours. The total cost, to date, for our students has been $43,610 (tuition not waived first three years for Cincinnati State, Engineering @ $110 per credit hour) Tuition cost for taking these courses on the following campuses: Cincinnati State $323,002 University of Cincinnati $1,000,350 (Clifton campus) The Ohio State University $1,456,065 (Columbus campus) Studies show that students who enter an institution with college credit will have an 80% chance of graduating with a degree compared to 37% entering with no college credit What is a Transfer Assurance Guide (T.A.G.) credit? Students are guaranteed the transfer of applicable credits among Ohio’s public colleges and universities and equitable treatment in the application of credits to admissions and degree requirements. The Ohio Board of Regents established policies and procedures applicable to all state institutions of higher education to ensure that students can begin higher education at any state institution of higher education and transfer coursework and degrees to any other state institution of higher education without unnecessary duplication or institutional barriers. 23 Articulated and Transcripted Credit What is articulated credit? Articulated college credit is awarded to students who successfully complete a course/program while in high school and/or complete coursework that meets the requirements of the articulation agreement for the course/program in which the student was enrolled. These credits can be used at the institution in which the articulation agreement is for. Courses are designed to provide the same skills and competencies you would gain by taking a similar course at the local higher learning institution. Articulation agreements help avoid coursework duplication and allow students to move towards more advanced classes in their specific program. Each course/program has different requirements for awarding articulated credit, so have students check with their guidance counselor for more information. What is transcripted credit? Graded credit is posted on your college transcript when you complete the coursework or enroll in college. The transcripted, graded credit is generally based on an end-of-course test, either developed or approved by the college faculty in the discipline area. The course could be taught in the college or high school setting. If the instruction is delivered by your high school teacher, this teacher must meet the credentialing requirements of the college. Ideally, the instructor is designated as a college adjunct instructor. Transcripted ungraded credit is posted on your college transcript when you enroll in college or complete a set number of college courses. Colleges use various codes to identify ungraded credit. This non-grade transcripted credit, most typically referred to as articulated credit, is based on secondary teacher certification or college test-out procedures. 24 Scholarships 2010-2011 was the first year that the Business Academy gave away two scholarships. $600.00 Tuition Scholarship Essay Topic: “How can I tie this article into the things I learned within the Business Academy and how can I take this learning and apply it to my future?” IBM Laptop Scholarship Essay Topic: “Why college is important to me and what will I gain by furthering my education?” Over 60 essays were submitted for the scholarships Winners picked by the Business Academy Advisory Committee 25 Guest Speakers/Programs Sarah Quick, Assistant Director of Public Relations – Green Bay Packers Real Money, Real World Simulation 26 Student Activities Kings Bookstore Sports Media Guide Business Professionals of America 27 Field Trips International Business in NYC Sports Management at Cyclones Sports Marketing at GABP Accounting at Fifth Third MOC 28 References Educational Article: http://msn.careerbuilder.com/Article/MSN-2567-CollegeInternships-First-Jobs-Is-Your-MajorMarketable/?SiteId=cbmsnhp42567&sc_extcmp=JS_2567_home1&gt1=23000 Transfer Assurance Guides: http://regents.ohio.gov/transfer/tags/index.php U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://www.bls.gov/ Ohio Department of Job and Family Services: http://jfs.ohio.gov/ Ohio’s High-Wage Occupations in Demand: http://ohiolmi.com/proj/projections/ohio/Buckeye50.pdf 29