Alkali Metals: Properties, Reactions, and Reactivity
advertisement

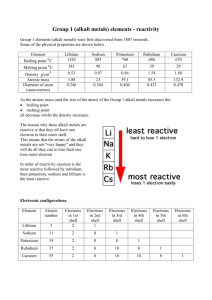
Alkali Metals Learning Objectives: • BRONZE: Identify the location of alkali metals in the periodic table and describe alkali metals as: a) soft metals b) metals with comparatively low melting points (E-C) • SILVER: Describe the reactions of lithium, sodium and potassium with water to form hydroxides which are alkaline, and hydrogen gas (C-B) • GOLD: Describe the pattern in reactivity of the alkali metals lithium, sodium and potassium with water and use this pattern to predict the reactivity of other alkali metals H and explain the pattern. (B-A*) Periodic Table Group 1 Alkali Metals Why are they called the ‘alkali metals’? The alkali metals are so reactive that they have to be stored in oil. Why do we need to do this? Alkali metals are different to most other metals. Alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife, and the most common alkali metals, lithium, sodium and potassium, all float on water. The elements in group 1 also react with water and form alkaline compounds. This is why they are called alkali metals. Reaction of metals with water metal metal hydroxide water hydrogen Reaction of metals with water Sodium water Sodium _______ hydroxide hydrogen Symbol Equations Sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen gas Na H2O NaOH H2 Is this equation balanced? 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2 What is the electron structure of alkali metals? How many electrons are in the outer shell of alkali metals? This means that: They are found in group 1 of the periodic table. They have similar physical and chemical properties. They can readily lose the outer shell electron to form positive ions with a +1 charge and a full outer shell. lithium 2,1 sodium 2,8,1 potassium 2,8,8,1 Lithium Li Reactivity Series Sodium Na Potassium K Rubidium Rb Caesium Cs Francium Fr As you go down the group the elements get more reactive! They get more reactive but why??? Explanation • The greater the number of electron shells will mean that the one electron on the outer shell will be further from the nucleus. • The force between the positive and negative charges will decrease the further away the outer electron is, so the outer electron in a caesium atom is not held as strongly as the outer electron in a sodium atom, so this is why it is more reactive. • The more shells there are between the outer electron and the nucleus the more shielding there is, this also makes the electron easier to remove.