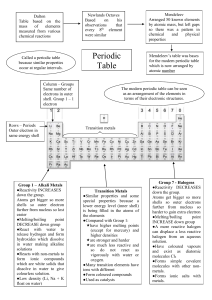
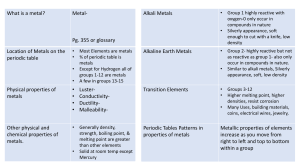
Comparison of groups in the periodic table
advertisement

The periodic Table Groups A group or family is a vertical column in the periodic table. Groups are considered the most important method of classifying the elements. In some groups, the elements have very similar properties and exhibit a clear trend in properties down the group. These groups tend to be given names, e.g., the alkali metals, alkaline metals, halogens and noble gases. Periods A period is a horizontal row in the periodic table. Although groups are the most common way of classifying elements, there are some regions of the periodic table where the horizontal trends and similarities in properties are more significant than vertical group trends. This can be true in the transition metals. Comparison of groups in the periodic table Alkali Metals Transition Metals Halogens Noble gasses Low (Li, K and Na float in water). Soft (can be cut with a knife) High; usually hard and tough; can be hammered or bent into shape Low (brittle when solid) Low Ability to conduct heat and electricity Good Good (metalloids semiconductors) Poor Poor Melting point Low High (mercury is exception) Low Very low React quickly with water producing hydrogen gas Less reactive than alkali metals such as Li, Na, K. Highly reactive Stable/unreactive Become softer, denser and more reactive; melting point decreases Not significant Become darker and less reactive; melting point increases Density increases Density Reactivity Trends in the Periodic table (Going down)