LITERARY TERMS
advertisement

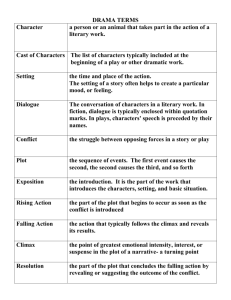
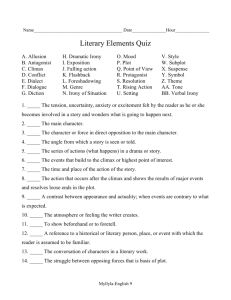
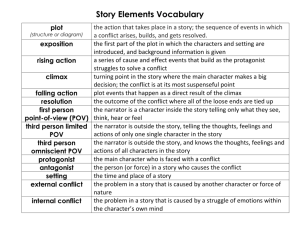
LITERARY ELEMENTS A tell-all guide about the major elements of literature SETTING The time in which the story takes place Present day The future The year 1984 The place where the story occurs Dallastown, Pa Planet Mars Mr. Wingard’s classroom PLOT LINE CLIMAX RISING ACTION RESOLUTION EXPOSITION PLOT: EXPOSITION It is the background information about the characters, setting, and situations. It introduces the author’s essential parts of the story to the reader. It is at the beginning of the plot. PLOT: RISING ACTION The part of the story in which the tension rises. The events or *CONFLICTS* build up to the story’s climax. The majority of the plot is in this part. PLOT: CLIMAX This is the moment when the action comes to its highest point. The protagonist decides how to deal with the main conflict. It’s the moment the reader has awaited. Usually, there is little excitement after this point. PLOT: FALLING ACTION The protagonist carries out the decision he or she made in the climax. There is a sharp decline in dramatic tension. PLOT: RESOLUTION The conflict is resolved. Life goes back to “normal” for the characters. Authors use this to “wrap up” the story to give the readers a feeling of relief or to leave them with something to ponder. CONFLICT The source of tension and drama in the story The conflict is the “story’s problem”. Takes place in the rising action Keeps the readers interested TYPES 1. Character versus character 2. Character versus self 3. Character versus nature 4. Character versus supernatural 5. Character versus society 6. Character versus technology 7. Character versus machine THEME The “message” that the author intends to communicate by telling the story Often universal truths, which are general statements about life or people Just ask yourself, “WHAT IS THIS ALL ABOUT?” Examples– Love conquers all. – The truth will prevail. – The “good guy” always wins. – Don’t judge a book by its cover. – Be careful what you wish for… CHARACTERS One main character in the story is the protagonist. Usually the protagonist is the positive force in the story. Another main character may be the antagonist who opposes the protagonist. CHARACTERIZATION Character can be revealed through the character’s – Actions – Dialogue – Appearance It also can be revealed by the comments of other characters and of the narrator. LITERARY DEVICES The techniques the author uses to develop his/her style Literary Elements VS. Literary Devices Elements – Plot – Characters – Setting – Conflict – Theme The basic needs to create a story Devices (partial list) – Point of view – Dialogue – Flashback – Foreshadowing – Mood – Tone – Imagery – Irony – Symbolism The devices used to make a story truly unique. Reflects the author’s style. AUTHOR’S STYLE The ways that an author uses language including… Word choice Length and complexity of sentences Use of imagery and symbols Use of literary devices Class Connection* Does this seem familiar? It should! Remember the Domain Scoring Rubric’s explanation of a writer’s style? POINT OF VIEW The perspective from which the story is told – Ask: Who is telling the story? FIRST PERSON – Story is told from the perspective of one of the characters; uses first person pronouns (I, me, we, us) “When I walked in the room, all eyes were on me.” Commonly used by authors- why? THIRD-PERSON LIMITED – Told from the perspective of a narrator; using third person pronouns (he, she) Only knows limited characters’ thoughts. An observer watching the characters- just like the reader! THIRD-PERSON OMNISCIENT – Narrator knows what ALL the characters’ are thinking, feeling, and doing FORESHADOWING Gives readers clues about events that will happen later in the story. Hints at what is going to happen! Think about scary music during a movie or when you say outloud, “NO! Don’t open the door! The killer is probably hiding in there!” MOOD overall feeling that is created by an author’s choice of words. Does the author make the story seem scary, creepy, and eerie or happy, warm, and fuzzy? The TONE author’s attitude toward his readers and his subject The IRONY The contrast between what is expected and what happens in reality – When the unexpected happens… An old man has played the lotto every day since the age of 14 and has yet to win a cent. On his 87th birthday he bought his usual lotto ticket, deciding it was his last, after years of defeat. As he strapped his seat belt, he listened to the newscaster spit out the winning lotto numbers “710-43”. His birthday. His lotto numbers. “Finally, I’ve won!” he shouted in disbelief. As he jumped up and down in his seat excitedly, he felt a sharp pain in his left arm. His body went numb and his mind went blank. The old man collapsed onto the steering wheel; his heart slowly stopped beating. As he died, he clutched the winning lotto ticket to his chest and closed his eyes. DIALOGUE The actual words that characters speak Uses “quotation marks” Dialogue dramatizes conflict and helps to portray (describe) the characters of the story Adds to characterization! FLASHBACK Is a scene that interrupts the story in order to relate events that occurred in the past to the present story line Takes the reader into the past SYMBOLISM Symbolism is achieved by the use of a symbol which is something-- an image, object, person, situation, or action--that stands for an idea beyond its literal meaning. *An engagement ring is a real object, but it is also a SYMBOL stands for the love between the engaged couple IMAGERY The use of words that appeal to one or more of the five senses – Sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch – This gives the reader additional meaning and feeling THAT’S ALL FOLKS!