Short Story Analysis Worksheet: Plot, Character, Theme
advertisement

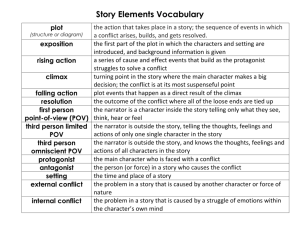
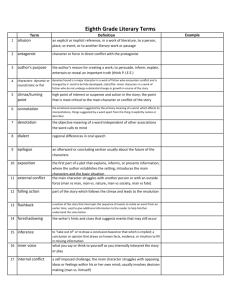
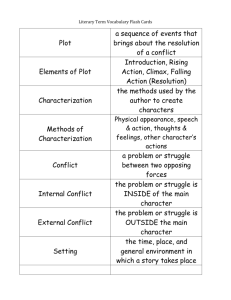
Name: _______________________________________ Mods:______________ Date:_______________ Short Stories Applied Notes Story Title:___KEY______________________________ Author:______________________________ GENRE – type of literature Short story – fictional, prose narrative of 12,000 words or less fictional – not true prose – told in sentences & paragraphs narrative – story I.PLOT – sequence of events A. Plotline Exposition – introduces setting and characters Complication – the first problem is revealed Rising Action – additional problems & events Climax – most interesting or exciting part of the story Denoument (Falling Action/Resolution) – events after the climax B. Plot related terms & concepts Reconstructed Past – events from before the story began that are necessary for reader’s understanding Flashback – plot sequence that has gone back in time Foreshadowing – hint of what is yet to happen Epiphany – sudden realization of important issue Turning point – (self explanatory) Projected future – events likely to happen after story’s end C. Conflict Character vs. Character Character vs. Nature Character vs. Society Character vs. Self II. CHARACTER A. Character terms protagonist – character we want to succeed; major force in the story antagonist – character who goes against the protagonist flat – one-dimensional character; may be a stereotype round – multi-sided, complex character dynamic – character who changes over the course of the story static – character who remains the same throughout the story foil – 2 characters who are opposites. The author uses one to highlight traits of the other. B. Characterization Direct – narrator tells the characteristics Indirect – reader surmises the characteristics from the story’s events and dialogue List main characters. Identify major traits. Character Traits/Notes III. SETTING Time Place Atmosphere “I” Narrator is a character. Narrator knows all. IV. POINT OF VIEW _____ 1st Person _____ 3rd Person Limited _____ 3rd Person Omniscient Narrator sees only what one character sees. V. THEME Literary devices Simile – comparison using “like” or “as” Metaphor – comparison not using “like” or “as” Imagery – author creates a vivid picture in reader’s mind; sensory words Irony – the unexpected happens, or a significant coincidence occurs Allusion – a reference to another major or classic literary work Personification – assigning human qualities to non-living things Symbolism – using an object to signify something abstract, such as an idea Alliteration – repetition of initial consonant sounds Onomatopoeia – words or phrases that have the sounds that they name Hyperbole – using exaggeration to explain or state an extreme degree Symbol – Established – a symbol which is universally recognized in a given culture or subculture Created – a symbol which the author creates for the purpose of this particular story