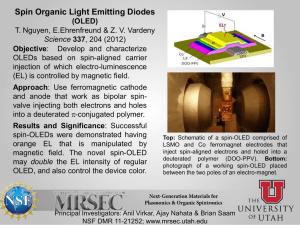
3Flat-panel-displays..
advertisement

The Science of DigitalSeminar Media Display Technologies Flat Panel Displays 7May 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 1 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Agenda • • • • • • • Introduction FPD in general FED OLED PLED SED Conclusions 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 2 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Flat Panel Displays Volatile • Pixels are periodically refreshed to retain their state • Refresh many times a second • Otherwise image will fade from the screen • Plasma, LCD, OLED, LED, ELD, SED and FED-displays 17 March 2010 Static • Material with bistable color states • No energy to maintain image needed, only to change • Slow refresh state • Deployment in limited applications • Cholesteric displays, outdoor advertising, e-book products Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 3 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Field Emission Display • Developed by Motorola and others during the 1990s • Very similar to a CRT • Utilizes an electron emitter which activates phosphors on a screen • In CRT an electron gun scatters the charged particles • Each FED pixel has its own corresponding electron source • At first conical electron emitters (known as a "Spindt tip") – nowdays carbon nanotubes • Electrons in a FED are not produced by heat 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 4 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel FED 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 5 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel FED Advantages • More power efficient than LCD • Less weight that same size LCD • Fewer total components and processes involved 17 March 2010 Disadvantages • Erosion of the emitters • Extremely high vacuum required in order to operate • Hard to manufacture for commercial use • Production difficulties Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 6 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel FED First models 2007 •19.2-inches. •1,280 x 960 resolution •brightness of 400cd/m2 •20,000:1 contrast ratio •Sony’sField Emission Technologies, whose purpose was to develop the displays closed it doors in 2009. •Reason mainly due to difficulty in raising funds for manufacturing. 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 7 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Organic Light-emitting Diode • Developed by Eastman-Kodak • Two types: small molecule OLED and polymer OLED • A Layer of organic material is sandwiched between two conductors (an anode and a cathode) which are between seal and subsrate • Electro-luminescent bright light is produced from the organic material when current is applied to the conductors 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 8 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel OLED color • Only pure colors expressed when an electric current stimulates the relevant pixels • Primary color matrix arranged in red, green, and blue pixels, mounted directly to a printed circuit board • Ambient light interference reduced with "micro-cavity” structure -> improves overall color contrast • Organic layer adjusted for each color for strongest light • Colors purified with color filter without the need for polarizer -> outstanding color purity. 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 9 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel OLED Source: http://www.oled-display.net/how-works-the-oled-technology 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 10 The Science of Digital Media How OLED is built OLED production VS. LCD production Source: http://www.oled-display.net/how-works-the-oled-technology The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel PLED Source: http://www.educypedia.be/electronics/pled.htm 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 12 The Science of Digital Media Different OLED technologies • • • • • • • • • • • AM OLED = Active Matrix OLED device FOLED = Flexible Organic Light Emitting Diode (UDC) OLED = Organic Light Emitting Diode/Device/Display PhOLED = Phosphorescent Oragnic Light Emitting Diode (UDC) PLED = Polymer Light Emitting Diode (CDT) PM OLED = Passive Matrix OLED device POLED = Polymer Oragnic Light Emitting Diode (CDT) RCOLED = Resonant Coloe Oragnic Light Emitting Diode SmOLED = Small Molecule Ogranic Light Emitting Diode (Kodak) SOLED = Stacked Oragnic Light Emitting Diode (UDC) TOLED = Transparent Oragnic Light Emitting Diode (UDC) The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel OLED Advantages • Can be printed onto any suitable substrate with inkjet (PLED) • Flexible displays • Great artificial contrast ratio and color potential • No need for a backlight • Great viewing angle • Fast response times 17 March 2010 Disadvantages • Lifespan (especially blue) • Color balance issues (due lifespan issues) • Water damage • Outdoor performance • Power consumption • Possible screen burn-in Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 14 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel OLED • Samsung SDI exhibited a 40-inch OLED panel at the FPD International 2008 • full HD resolution of 1920 x 1080 • contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1 • color gamut of 107% NTSC • luminance of 200cd/m2 (peak luminance of 600cd/m2) • Samsung shows 3D Panels at CES-2010. • Sony shows 24.5-inch prototype OLED 3D television during the Consumer Electronics Show in January 2010. 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 15 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel OLED Source: DisplaySearch Q2,09 Quarterly OLED Shipment and Forecast Report 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 16 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Surface-conduction Electron-emitter Display • Co-developed by Canon and Toshiba Corporation • Very similar to a CRT • Utilizes an electron emitter which activates phosphors on a screen • The electron emission element is made from few nanometers thick electron emission film • No electron beam deflector required • Separate emitter for each color phosphor, 3/pixel or 1/sub-pixel 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 17 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel SED Source: http://www.oled-display.info/what-means-sed-tv 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 18 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel SED vs. FED • The significant differences between SED (a) and FED (b) is in the electron source plate and the drive electronics Source: http://www.oled-display.info/structure-and-manufacturing-of-an-sed-tv-andfed-tv-partii 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 19 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel SED Advantages •The overall power efficiency about ten times better than a LCD of the same size •Less complex than LCD •Fast response time and high contrast ratio •Wide viewing angle •advantages over the FED in manufacturing state 17 March 2010 Disadvantages •Potential screen burn-in •Mass production difficulties Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 20 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel SED Prototype 2006 • 1080p 55-inch models • 450 nits of brightness • 50,000:1 contrast ratio • 1ms response time •Mass production delayed due to lawsuits between Canon and NanoProprietary Inc concerning SED panel patent license agreement 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 21 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Future • Some of the technologies have faded after the prototype phase • OLEDs are the most promising • Flexible displays • Printing technology • Printed vs non printed • Rigid vs flexible • Inorganic vs organic, • Cost of materials vs process • New technologies still in development 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 22 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Future Samsung Wave (SuperAMOLED) vs. Nokia X6 (TFT LCD capacitive touchscreen) 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 23 The Science of Displays Digital Media Flat Panel Questions? Thank you! 17 March 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences 24