Human Muscle Fiber Types
advertisement

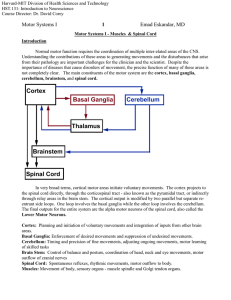
Human Muscle Fiber Types Classification and Properties Muscle Fiber Classification Classification Basis Contractile Properties slow fast Metabolic Properties oxidative glycolytic Color Properties red white Staining Properties enzymes pH Contractile Properties Contractile Properties • Slow twitch (I) fibers innervated by alpha 2 motor neurons, smaller of the two α motor neurons • Fast twitch (II) fibers innervated by alpha 1 motor neurons, larger of the two α motor neurons • Fast twitch (II) fibers have higher excitation threshold and faster conduction velocity Contractile Properties Motor Unit Recruitment • Motor neurons recruited in order of size: Size Principle • Smallest alpha motor neurons, α2, which belong to slow twitch recruited first • Largest alpha motor neurons, α1, which belong to fast twitch recruited last Motor Unit Recruitment • Slow twitch with low • Fast twitch with threshold nerves (α2) higher threshold recruited during nerves (α1) activated light-to-moderate as force effort. requirements • Sustained increase. submaximal jogging, • Sprint running or cycling, lifting a light weight at a swimming or cyclist slow speed. ascends hill. Metabolic Properties • All muscle fibers can produce energy both aerobically and anaerobically • One or the other may predominate or production may be balanced • SO (I) fibers rely mainly on oxidative pathways • FG (IIb) fibers rely mainly on glycolytic pathways • FOG (IIa) possess characteristics like SO and FG Metabolic Properties • FOG (IIa) and FG (IIb) have higher glycogen stores than SO (I). • SO (I) has more triglyceride than either FG or FOG. Color Properties • Myoglobin contains heme (Fe) which carries O2 in muscle makes it RED. • Myoglobin cooked turns tan color. • Dark turkey meat (thigh) was once oxidative. • WHITE turkey meat (pectoralis) had no myoglobin, was not oxidative. • So turkeys walk all day and flap occasionally but rarely fly. Color Properties Pheasants fly far to survive. Pheasant pectoralis muscle has myoglobin which is red or dark. Staining Properties • Slow twitch (type I) have myosin isoforms with low ATPase activity. • Fast twitch (type II) have myosin isoforms with high ATPase activity that promotes rapid breakdown of ATP for energy of highspeed muscle shortening. Muscle Fiber Types Diameter (neuron & fiber) Force Capacity Myosin ATPase Activity Myoglobin Content Metabolic Properties Fatigue Resistance Type I Red Medium Type IIa Red Large Type IIb White Large Low (5g) Moderate (20 g) High (50 g) Low High High High High Low Oxidative Oxidative/ Glycolytic Intermediate Glycolytic High Low Distribution of Fiber Types • All muscle composed of ST & FT fibers • Distribution varies from muscle to muscle within an individual • Most individuals possess between 45 and 55% ST Distribution of Fiber Types • Vastus lateralis on average 52% SO, 33% FOG, 14% FG. Same for deltoid, biceps brachii. • Soleus may have as much as 85% SO. • Triceps brachii may have as few as 30% SO. Distribution of Fiber Types • Great variation between individuals • Vastus lateralis of elite distance runners had 79% ST, untrained had 58% • Available evidence indicates that the distribution of slow and fast twitch fibers is genetically determined and not altered by training Illustration References • McArdle, William D., Frank I. Katch, and Victor L. Katch. 2000. Essentials of Exercise Physiology 2nd ed. Image Collection. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. • Plowman, Sharon A. and Denise L. Smith. 1998. Digital Image Archive for Exercise Physiology. Allyn & Bacon.