Muscle Fibre Types - Broughton Hall Catholic High School
advertisement

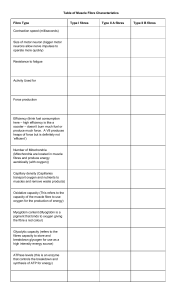
Muscle Fibre Types The athlete’s ability to excel at endurance or speed work will depend largely on their muscles’ ability to produce a certain speed and strength of contraction, aided by the type of training that they undertake. Slow twitch fibres (SO) function predominately during submaximal exercise, whereas fast twitch fibres are recruited as the exercise intensity increases. Fast oxidative glycolytic fibres (FOG) are recruited during medium intensity work and fast glycolytic fibres (FG) high intensity work. Slow twitch fibres – also known as slow oxidative (SO) or type l fibres – designed for aerobic work. It uses oxygen to produce a small amount of force over a long time. Marathon runners have a high percentage in their leg muscles. Fast twitch fibres – two types known as fast oxidative glycolytic (FOG) or type lla and fast glycolytic (FG) or type llb – designed for anaerobic work. It produces a large amount of force in a very short time. Shot putters have a high percentage in their arm muscles. Slow glycolytic fibres Myelin sheath of the motor neurone stimulating the muscle fibre is thinner than that of the fast twitch unit. Contain more mitochondria and myoglobin. They are supplied by more blood capillaries than fast twitch fibres. Have the enzymes for aerobic respiration. They are able to break down fat and carbohydrate to CO2 and H2O which does not produce any fatiguing by-products. They are designed for long bouts of aerobic exercise Fast oxidative glycolytic Thicker myelin sheath than slow twitch fibres. They can contract more quickly and exert more force. They can release energy very quickly. However, the rapid build-up of lactic acid lowers the pH and has a negative effect on enzyme action causing the muscle fibre to fatigue quickly. Fast glycolytic They have a greater CP content than slow twitch fibres. They have a small number of mitochondria and low myoglobin content. They have a relatively small capillary network. They are quick to contract and can exert a large amount of force, but while energy is rapidly released the muscle fibre is quick to fatigue.