Final, Fall 2014
advertisement
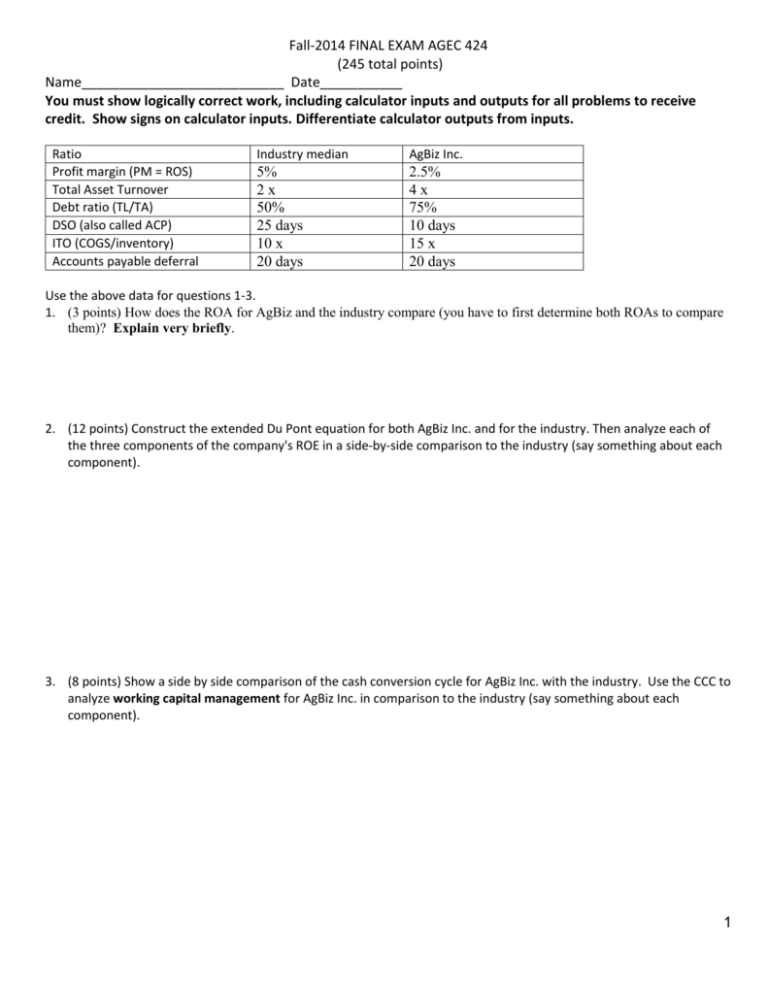
Fall-2014 FINAL EXAM AGEC 424 (245 total points) Name___________________________ Date___________ You must show logically correct work, including calculator inputs and outputs for all problems to receive credit. Show signs on calculator inputs. Differentiate calculator outputs from inputs. Ratio Profit margin (PM = ROS) Total Asset Turnover Debt ratio (TL/TA) DSO (also called ACP) ITO (COGS/inventory) Accounts payable deferral Industry median AgBiz Inc. 5% 2x 50% 25 days 10 x 20 days 2.5% 4x 75% 10 days 15 x 20 days Use the above data for questions 1-3. 1. (3 points) How does the ROA for AgBiz and the industry compare (you have to first determine both ROAs to compare them)? Explain very briefly. 2. (12 points) Construct the extended Du Pont equation for both AgBiz Inc. and for the industry. Then analyze each of the three components of the company's ROE in a side-by-side comparison to the industry (say something about each component). 3. (8 points) Show a side by side comparison of the cash conversion cycle for AgBiz Inc. with the industry. Use the CCC to analyze working capital management for AgBiz Inc. in comparison to the industry (say something about each component). 1 4. Critically evaluate the following statements made over the years by groups during AGEC 424 term project presentations. Explain in one or two sentences. a. (2 points) My company has a debt ratio (TL/TA) of 1.08. b. (2 points) The industry has an equity multiplier of 0.73. c. (2 points) My company has poor earnings from interest because TIE is only 2 compared to the industry median of 8. d. (2 points) I need to present both ITO and inventory conversion period because they show different information. 5. The risk free rate and MRP were given to you as 3% and 5%, respectively, for the term project. a. (4 points) What are the required rates of returns for equity investors in company A with a beta of 0.5 and company B with a beta of 1.5? Show work b. (2 points) Based on the data given, implicitly what is KM, the expected return on the market? Show work c. (2 points) What is the economic factor making the required returns for companies A & B different than the market? 6. (6 points) The Paragon Company has sales of $2,000 with a cost ratio of 60%, current ratio of 1.5, inventory turnover ratio (based on cost) of 3.0, and average collection period (ACP) of 45 days. Complete the following current section of the firm's balance sheet. Clearly show/label the calculation of each component. Cash Accts Rec Inventory Current Assets $ $ Accts Payable $ Accruals Current Liabs 60 $ 750 2 7. a. (7 points) What is the monthly payment (to the penny) on a 5-year car loan of $30,000 at 3.5% interest compounded monthly? Show work b. (13 points) Construct an amortization table below for the first 2 months of the loan. Show work for the interest calculation Month Beg. Bal. Payment Interest Prin. Reduction End. Bal. 8. (6 points) Smith Blarney is trying to sell my grandmother a semiannual, 10% coupon, $1000 face value bond with 12 years to maturity. Currently the market requires a 8% rate of return on bonds of this risk. What is this bond worth? Show work 9. Thompson Tires Inc. has an outstanding semiannual, 12% coupon, $1000 face value bond that is selling for $1185 and has 10 years to maturity. a. (6 points) What is the yield to maturity of this bond? Show work b. (6 points) What are the current yield and capital gains yield of this bond? Show work 10. (6 points) Assume the Thompson Tires bond above is callable in 5 years with a $70 call premium. What is the YTC? Show work 11. (6 points) Smith Blarney is back trying to sell Grandma a 10 year, callable, semiannual, $1000 face value, 12% coupon bond. It is callable in 1 year with a $80 call premium. If comparable bonds of this risk yield 5% and you expect this bond to be called, what is its value? Show work 12. (6 points) Frazier Manufacturing paid a dividend last year of $2, which is expected to grow at a constant rate of 5%. Frazier has a beta of 1.3. If the market is returning 11% and the risk-free rate is 4%, calculate the value of Frazier’s stock. Show work 3 13. (15 points) Forecast AFN with a 50 % sales increase; at 80% of capacity last year; any additional funds will come from Notes payable, or a surplus will reduce notes payable. The interest rate is 10%. Round to the nearest whole dollar. Show sales factor ____________ Show capacity factor____________ Last Factor 1st Pass Feedback 2nd Pass Sales -VC -FC EBIT -interest EBT -Taxes (40%) NI -Div (45%) Add. RE Cash AR Inv CA NFA TA AP Accr. Notes CL Bonds Stock RE TL+E 36,000 -17,440 -15,000 3,560 -560 3,000 -1,200 1,800 -810 990 1,080 6,480 9,000 16,560 12,600 29,160 4,320 2,880 2,100 9,300 3,500 3,500 12,860 29,160 Show clearly your interest calculations, the AFN for each pass, and total AFN after two passes: 4 14. (4 points) Nu-Mode Fashions Inc. manufactures quality women’s wear, and needs to borrow money to get through a brief cash shortage. Unfortunately, sales are down, and lenders consider the firm risky. The CFO has asked you to estimate the interest rate Nu-Mode should expect to pay on a one year loan. She’s told you to assume a 3% default risk premium even though the loan is relatively short, and to assume the liquidity and maturity risk premiums are each ½%. Inflation is expected to be 4% over the next twelve months. Economists believe the pure interest rate is currently about 3½%. 15. (15 points) Long Life Insurance Inc. just paid a dividend of $1.50, and projects supernormal growth at of 12% for the next three years. After that growth is expected to slow down to a normal 4% and go on at that rate for the foreseeable future. Stocks of similar risk are earning a return of 10%. How much would you pay for a share of Long Live today? 16. (2 points) What is the market price per share of Whopie, Inc. if the firm had net income of $200,000, earnings per share of $2.70, total equity of $800,000, and a market to book value ratio of 1.5? Show worka. a. $16.20 b. $10.80 c. $7.20 d. None of the above 17. (2 points) Which of the following is not a short-term debt instrument? a. Commercial paper b. Common stock c. Money market securities d. Treasury bills 18. (2 points) Which of the following is a characteristic(s) of initial public offerings (IPOs)? a. Very stable b. General public can get involved right away c. Institutions are the largest investors in IPOs d. Secondary market transaction 19. (2 points) The term “red herring” relates to the: a. SEC’s approval of a stock offering from a company whose future is questionable. b. circulation of the company’s prospectus prior to approval by the SEC. c. document distributed to potential investors that is stamped “incomplete information.” d. SEC’s conditional approval of the prospectus. 5 20. (2 points) Interest rates are set by: a. the forces of supply and demand in the market for debt. b. the Federal Reserve, the nation’s central bank which regulates the banking industry. c. senior banking executives on the basis of the funds banks have available to lend. d. the president and his council of economic advisors. 21. (2 points) The underlying principles of portfolio theory include: a. diversifying business-specific risk away. b. basing decisions on stocks’ risk/return characteristics in a portfolio context rather than on a stand-alone basis. c. getting the highest available return for the amount of risk the investor is comfortable with. d. all of the above 22. (2 points) Which of the following statements is false? a. Beta is meaningful only if an investor holds a well-diversified portfolio. b. You can completely eliminate risk if you hold a well diversified portfolio. c. A portfolio composed of only one stock will not be well diversified. d. A wise investor diversifies to capture the high average return of stocks while avoiding as much risk as possible. e. All of the above statements are correct. 23. (2 points) A statistic known as a stock’s beta coefficient measures: a. total risk. b. systematic or market risk. c. unsystematic or business-specific risk. d. none of the above 24. (2 points) The only component of the CAPM equation that relates specifically to a company is: a. βX b. kM c. kRF d. (kM – kRF) 25. (2 points) If you invest 30% of your funds in AT&T stock with an expected rate of return of 10% and the remainder in GM stock with an expected rate of return of 15%, the expected return on your portfolio is: Show work a. 12.5%. b. 13.0%. c. 13.5%. d. 14.5%. e. none of the above (2 points) 26. (2 points) The yield curve is: a. inverted when short-term rates are higher than long-term rates. b. normal when it slopes upward to the right c. a plot of interest rates versus term, also called the term structure of interest rates. d. all of the above 27. (3 points) A firm has EBIT of $3.6M and debt of $15M on which it pays 8% interest. What is its Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)? Show work a. 1.0 b. 1.4 c. 1.5 d. 1.6 6 28. (6 points) ) Mr. Moore is 35 years old today and is beginning to plan for his retirement. He wants to set aside an equal amount at the end of each of the next 25 years so that he can retire at age 60. He expects to live to about 80, and wants to be able to withdraw $25,000 per year from the account on his 61st through 80th birthdays. The account is expected to earn 10 percent per annum for the entire period of time. Determine the size of the annual deposits that must be made by Mr. Moore. Include a timeline in your answer. Show work 29. a. b. c. d. (3 points) How much must be invested today to have $1,000 in two years if the interest rate is 5%? Show work $909.09 $900.00 $907.00 $950.00 30. (3 points) Find the present value of $100 to be received at the end of two years if the discount rate is 12% compounded monthly. Show work. a. $66.50 b. $78.76 c. $68.80 d. $91.80 e. $79.75 31. (3 points) What is the rate of return on an investment if you lend $1,000 and are repaid $1,254.70 two years later? Show work a. 12% b. 25% c. 6% d. 18% e. 4% 32. (4 points) Designs Now is opening a showcase office to display and sell its computer designed poster art. Designs expects cash flows to be $120,000 in the first year, $180,000 in the second year, $240,000 in the third year. If Designs uses 11 percent as its discount rate, what is the present value of the cash flows? Show work a. $429,720 b. $457,620 c. $456,000 d. $424,820 33. (6 points) Assume the following facts about a firm that sells just one product: Selling price per unit = $24.00 Variable costs per unit = $18.00 a. 417 units Total monthly fixed costs = $2,500 b. 1,250 units What is the firm’s monthly breakeven volume in units? c. 5,000 units Show work d. 1,667 units 7 34. (2 points) Kermit’s Hardware’s (KH) fixed operating costs are $20.8 million and its variable cost ratio is 0.30. The firm has $10 million in bonds outstanding with a coupon interest rate of 9%. KH has 200,000 shares of common stock outstanding. The firm has revenues of $32.2 million and its marginal tax rate is 40%. Compute KH’s degree of total leverage. Show work a. 26.8 b. 5.5 c. 29.1 d. 4.7 35. (2 points) A firm’s degree of financial leverage is 2 and the degree of operating leverage is 2.5. What is their degree of total leverage? Show work a. 6.0 b. 4.5 c. 5.0 d. none of the above 36. (2 points) Stocks that have high financial rewards are generally accompanied by: a. high dividend payments. b. low dividend payments because of internally generated growth. c. high risk. d. all of the above 37. (4 points) Phoenix Company common stock is currently selling for $20 per share. Security analysts at Smith Blarney have assigned the following probability distribution to the price of (and rate of return on) Phoenix stock one year from now: Price Rate of Return Probability $16 –20% 0.25 20 0% 0.30 24 +20% 0.25 28 +40% 0.20 Assuming that Phoenix is not expected to pay any dividends during the coming year, determine the expected rate of return on Phoenix Stock. a. 8% b. 0% c. 10% d. 40% 38. (10 points) Projected cash flows for two mutually exclusive projects are as follows (again, identify all calculator inputs and outputs – don’t assume they are already identified): Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Project A ($150,000) 80,000 60,000 50,000 Project B ($200,000) 40,000 50,000 50,000 60,000 50,000 53,000 If the firm’s cost of capital is 10% and the equivalent annual annuity method is used to eliminate the disparity between the projects’ lives, which project should be undertaken? Why? 8 39. (40 points) Replacement Problem: Atlantic Control Company purchased a machine two years ago at a cost of $70,000. At that time, the machine’s expected economic life was six years and its salvage value at the end of its life was thought to be $10,000. It is being depreciated using the straight line method so that its book value at the end of six years is $10,000. The old machine can be sold today for $20,000. In three years, however, the old machine will have a market value of only $9000. A new machine can be purchased for $100,000, including shipping and installation costs. The new machine has an economic life estimated to be three years, at which time it would be sold for $20,000. Three-year MACRS depreciation will be used (with percentages 33, 45, 15 and 7). During its three-year life, the new machine will reduce cash operating expenses by $40,000 per year. Sales are not expected to change. But the new machine will require net working capital to be increased by $4,000. The firm’s marginal tax rate is 40 percent. The appropriate required rate of return is 10 percent. On the attached form identify the relevant cash flows for this project, NPV, IRR, Payback, and should the company make this replacement investment (state why)? 9 Worksheet for the capital budgeting question Initial Outlay Depreciation [initial basis = ] Work space Operating Cash flow minus deprec. EBT less taxes EAT Dep. addback OCF Terminal CF Calculator inputs/outputs and investment decision TCF workspace 10








