Diffusion and Osmosis - White Plains Public Schools
advertisement

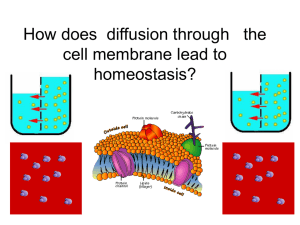
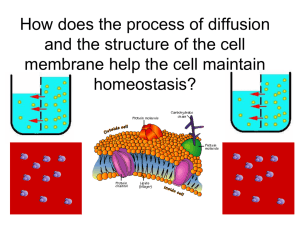
Diffusion and Osmosis Movement of particles and water along concentration gradients Diffusion: motion of particles in a liquid • Particles will move along a concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to low concentration. • Once equilibrium is reached there is no longer a concentration gradient so diffusion stops. • How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion? Diffusion across a membrane • Most biological membranes (cell membrane, nuclear membrane, membranes around organelles) are selectively permeable or semipermeable. • Some substances can pass through easily, some pass slower, others cannot pass at all Substances such as water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and glucose pass easily through cell membranes. Proteins, carbohydrates and lipids pass more slowly or not at all. What will happen to the concentrations of O2 and CO2 assuming both are permeable to the cell membrane? Osmosis: the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane • Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from high concentration to low concentration • What will the water levels and concentration of water look like after equilibrium is reached? Thistle Tube Experiment • Thistle tube is filled with a concentrated solution of sugar water covered with a semipermeable membrane which sugar cannot pass through. What will happen if it is placed in a beaker of water?