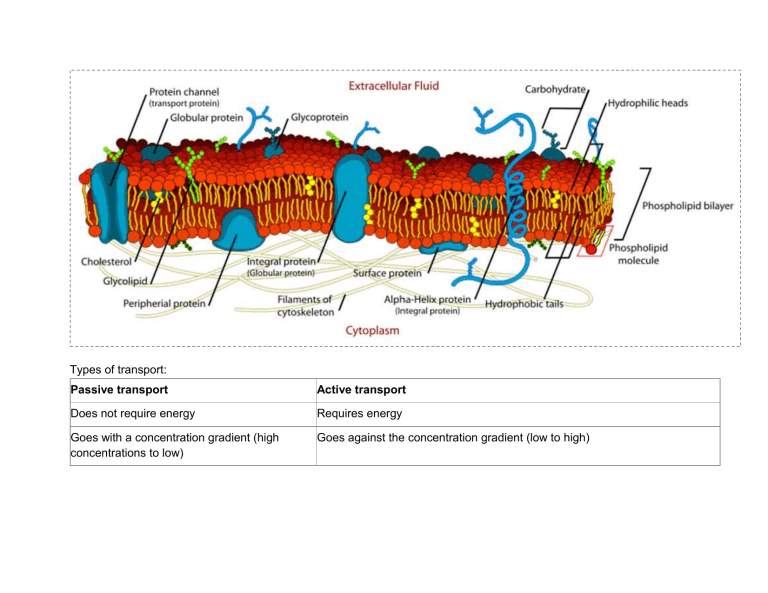
Types of transport: Passive transport Active transport Does not require energy Requires energy Goes with a concentration gradient (high concentrations to low) Goes against the concentration gradient (low to high) Examples: Example: Diffusion - movement of particles/substance across a membrane, down a concentration gradient Protein pumps- proteins in the membrane that use energy to transport particles/substance against the concentration gradient Osmosis - movement of water across a membrane Vesicle mediated transport - piece of the cell membrane that is 'breaking off' or 'joining to' in order to let things in and out of the cell. Typically with large molecules ***Think of a plant cell lab! - Exocytosis - outside ***think of hypo, hyper, and isotonic - Endocytosis - inside - pinocytosis - drinking Facilitated diffusion - diffusion using a channel protein - phagocytosis - eating