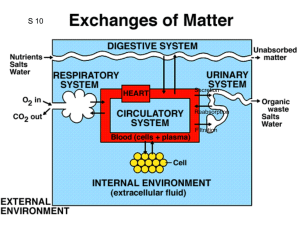
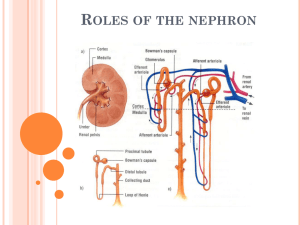
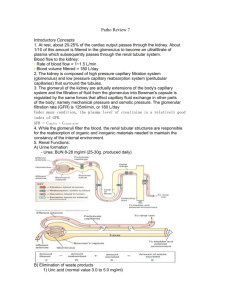
Renal3
advertisement
2 December 2011 Renal Physiology Test # 3 Monday Dec 5th Lab Next Week: Urinalysis Options: 800 ml tap water 800 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl 80 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl None of the above Urinalysis Lab Day Drink plenty of water the day of lab; Avoid coffee, caffeine, salty foods 60 min 1 Hr before Lab Empty bladder; note time Drink Test Beverage 30 min 800 ml tap water 800 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl 80 ml tap water + 7 g NaCl 30 min 30 min 30 min At 30 min intervals, collect urine measure V and [NaCl] Beginning of Lab: Collect Urine, measure Volume and titrate for [NaCl] 30 min 1QQ 33 for 8:30 1. How does the composition of the ultrafiltrate in Bowman’s space differ from plasma? If glucose concentration in the plasma is 70 mg/ml, what will the glucose concentration be in the ultrafiltrate in Bowman’s space? 2. What is the location and role of macula densa cells? 3. Which segments of the nephron are found in the medulla? 4. What are two ways by which GFR can be increased? 1QQ 33 for 9:30 1. How does the composition of the ultrafiltrate in Bowman’s space differ from plasma? If glucose concentration in the plasma is 100 mg/ml, what will the glucose concentration be in the ultrafiltrate in Bowman’s space? 2. What is the location and role of macula densa cells? 3. Which segments of the nephron are found in the medulla? 4. What are two ways by which GFR can be decreased? Membrane proteins are segregated into apical (luminal) and basolateral membranes. Figure 14.10 reabsorption secretion Amino acid metabolism glucose Filtration is controlled by aa and ea diameters! Consider a substance that in filtered only, no reabsorption, no secretion. Excretion of this substance = GFR Clearance of this substance = GFR • Clearance = volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed (cleared) by the kidneys per unit time. • Two substances that are only filtered: Inulin and Creatinine • Cinulin or Ccreatinine = Glomerular Filtration Rate • Clearance of Inulin is 120 ml/min Renal Handling of Substances Filtration + complete Secretion Ex: Para AminoHippurate (PAH) Measure Renal Plasma Flow Filtration + partial reabsorption Filtration + 100 Reabsorption Ex: Sodium Ex: Water Ex: Glucose Ex: Amino Acids • Clearance allows us to determine how the kidneys are handling a substance (net secretion or net reabsorption.) • Clearance of Inulin is 120 ml/min • Cinulin or Ccreatinine = Glomerular Filtration Rate • If C x is greater than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR SECRETION • If C x is less than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR REABSORPTION Renal Handling of Substances Filtration + complete Secretion Ex: Para AminoHippurate (PAH) Measure Renal Plasma Flow Filtration + partial reabsorption Filtration + 100 Reabsorption Ex: Sodium Ex: Water Ex: Glucose Ex: Amino Acids A little more on Clearance: Clearance of glucose = 0 ml/min which means…. Clearance of X = 120 ml/min which means…. Clearance of antibiotic XXX = 500 ml/min which means… Calculating clearance Clearance of s = Urine concentration of s X Urine Volume Plasma concentration of s “24 hour urine catch” + blood sample Special cases: Clearance of • Inulin and creatinine (filtered only; use to measure Glomerular Filtration Rate.) • Para Amino Hippurate (filtered and completely secreted, use to measure Renal Plasma Flow) Who Cares? S 17 Sonogram showing fluid-fill cavities within the kidney Dr. Davis’s lovely bride of 30+ years S 18 Fluid-filled cysts Polycystic Kidney Disease Symptoms? Genetics? Prognosis & Treament? Fig. 14.04 PKD is an autosomal dominant: pp X P? Measure Ccreatinine To chart the progress of the disease. End of Material for Test # 3 Reabsorption and secretion in proximal tubule is NOT under hormonal control. Primary active transport of Na+ establishes a gradient for reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, etc. Reabsorption and secretion in DCT & CD is under hormonal control. Hormones that act here: ANH, ADH, Aldosterone. Here, reabsorption of Na+ is linked to the secretion of K+.