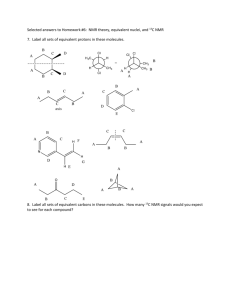
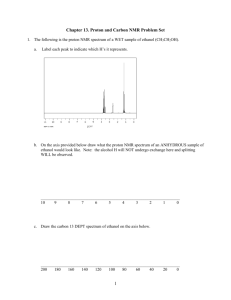
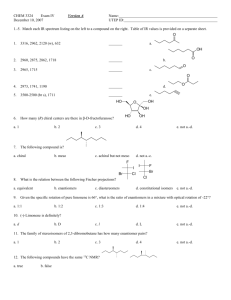
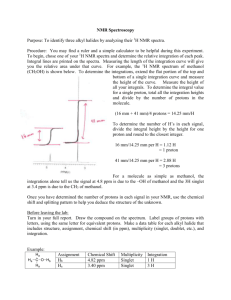
H-NMR and CMR
advertisement

Today: • Brief Review of Mass Spectroscopy • Discussion/Review of H-NMR, CMR Next time (our last lab lecture): Your questions Final Exam at 2:10 pm in your Lab! •Exam covers the material of the second half of the semester(only): “Unknowns”. •Study/ review lab lectures, your labs, practice questions, sample final (in eres file). •Same rules as for Midterm. No calculator needed. •Spectral correlation charts will be provided. Mass Spectrometry Summary (Examine your Unknown #3 Mass spectrum!) Molecular weight: • Molecular ion peak M+ ? • odd-numbered (N ...) ? • isotope peaks (Cl, Br)? • Alcohols … Recognize typical fragments: H2O, alkyl, acyl, tropylium ion … Weights of common fragments or neutral losses O 15 = CH3 18 = H2O 29 = C2H5 43 = C3H7 or O 31 = CH3O O 57 = C4H9 or 71 = C5H11 or 45 = CH3CH2O O 79Br 81Br 85 = C6H13 or 35Cl 77 = O C CH2 91 = 105 = 37Cl phenetole 3-methoxytoluene Salicylaldehyde Benzoic acid M+ = 122 This is the mass spectrum for which compound? 91 77 107 NMR Basic Information from Proton NMR (Examine your Unknown #3 H-NMR spectrum!) Number of signals Number of different types of protons Chemical shifts Type of environment for protons Integration Ratios of numbers of protons Splitting of Signals Information about neighboring protons Solvent peaks ….. Proton NMR Chemical Shifts () For 1H NMR, the scale generally extends from 0-12 ppm (TMS standard) • Simple hydrocarbon protons absorb in the region 0.5-1.5 • Protons on a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl are shifted to 2 ppm (acetone!) • Electronegative atoms (O, halogens) move protons to 3-4 • Alkene protons are shifted to 5-6 • Aromatic protons to 7-8 (Amide CONH is also found here) • Aldehydic protons to 10 • Most highly shifted protons are generally those of carboxylic acids, with values of 12 • Can also be far downfield: phenol OH, enol Proton NMR Chemical Shifts for Common Functional Groups For 1H NMR, the scale generally extends from 0-12 ppm Proton NMR Common Splitting Patterns A J’s (Hz)! B Practice Proton NMR Practice Proton NMR http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS/cgi-bin/cre_index.cgi 13C NMR Chemical Shifts for Common Functional Groups Range 0-220 ppm (TMS standard) Proton noise-decoupled Integration not useful (Examine your Unknown #3 CMR spectrum!) •Simple methyl carbons tend to absorb in the region 15-30, simple methylene carbons are shifted to 20-65 • Electronegative atoms (O, halogens) move attached carbons to 40-80 • Alkyne carbons are shifted to 70-90, • alkene carbons to 100-150, • aromatic carbons to 120-170 • Most highly shifted carbons are generally those of carbonyls, with values of 180-220. 13C NMR Chemical Shifts for Common Functional Groups 13C NMR Practice How many types of C ? Indicated by how many signals there are in the spectra (solvent peaks ….) What types of C ? Indicated by the chemical shift of each signal 13C Symmetry! NMR Practice 13C NMR Practice How many signals would you expect in the 13C spectrum of • o-xylene • m-xylene • p-xylene? Next time (our last class): • Your questions • Final Exam at 2:10 pm in your Lab (Begin studying early!) Exam covers the material of the second half of the semester: “Unknowns”. Study/ review lab lectures, your labs, practice questions, sample final. Same rules as for Midterm. No calculator needed. Spectral correlation charts will be provided. How your C336 class grade is calculated ….