BIOLOGYUnit_3_PPT
advertisement
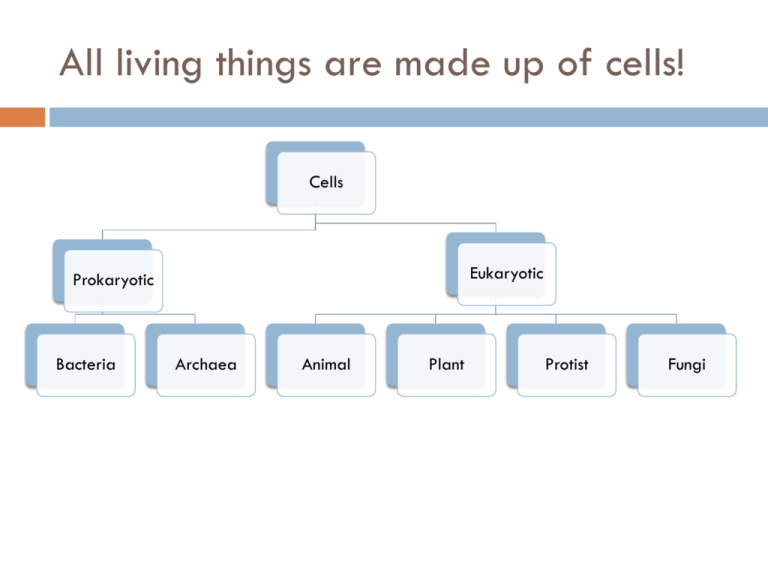
All living things are made up of cells! Cells Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Bacteria Archaea Animal Plant Protist Fungi All cells are made up of structures & organelles. Structures provide support to the cell & its organelles Organelles each have a specific “function” (job) within the cell EX: the function of the nucleus is to control all cell activities ALL CELLS HAVE THESE 5 THINGS: Cytoplasm Genetic Material (DNA) Cell/Plasma Membrane Ribosomes Cytoskeleton Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells PROKARYOTIC Simple Small Have: Capsule Cell Wall Genetic Material in a Nucleoid 5 things in all cells Structure for movement (pili, cilia, or flagella) EUKARYOTIC Large Complex 4 different types Have: Cell wall (Plants) 5 things in all cells Organelles Genetic material in a real nucleus Structure for movement (cilia or flagella) Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Review ?s: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Which type of cell is simple and small? Which type of cell has organelles? Which type of cell has a true nucleus that stores genetic information? Which type of cell has a nucleoid (scattered DNA)? Which type of cell is protected by a capsule in addition to a cell wall & cell membrane? Which type of cell does not have organelles? What are the 5 things in ALL CELLS??? All living things are made up of cells! Cells Prokaryotic Bacteria Archaea Eukaryotic Animal Plant Protist Fungi Eukaryotic Cells are large & complex. PLANT CELLS Square 5 things in all cells Structure for movement Same organelles as an animal cell PLUS… Chloroplast Cell Wall Large Vacuole ANIMAL CELLS Round 5 things in all cells Structure for movement Same organelles as a plant cell except… NO CELL WALL ONLY have a cell/plasma membrane NO CHLOROPLAST Small vacuoles Review Questions: Animal vs. Plant Which type of eukaryotic cell only has a cell membrane? Which type of eukaryotic cell has a large, centrally located vacuole? Which type of eukaryotic cell is round? Which type of eukaryotic cell uses a chloroplast for photosynthesis? Which type of eukaryotic cell is square? Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Cells Cell Structures & Organelles Things in the cell that do work – they each are VITAL to the cell because they have a specific function! Structures Around the Cell Capsule Prokaryotic cells Extra layer of protection outside of the cell wall & cell membrane Cell Wall Protective, outer layer surrounding cells. Only in PLANT & PROKARYOTIC cells. Cell Membrane In ALL CELLS Made up of a phospholipid bilayer (REMEMBER: lipids make up membranes!) Selectively permeable --- lets things in & out! A Closer Look @ the Cell/Plasma Membrane Lines ALL cells Made up of a phospholipid bilayer Hydrophobic (water fearing) tail Hydrohphilic (water loving) head Most of the cell membrane is hydrophobic Selectively Permeable = ONLY lets things in that it NEEDS!!! The cell membrane is selectively permeable. Hydrophilic Head 3 Ways that Cells Move! Cilia 1. • • Most common Tiny hair-like structures surrounding the cell Flagella 2. • • Tail on the cell Shown in both prokaryotic & eukaryotic cells Pseudopodia 3. • • LEAST COMMON Cytoplasm extends out of the cell, sticks to surface, & pulls cell forward Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Nucleus Controls ALL cell activities Brain of the cell Located in the center of eukaryotic cells NOTE: prokaryotic cells DO NOT have a nucleus Nucleolus Center of the nucleus Important in protein synthesis (creation of proteins) Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Lysosome The “trash can” of the cell Throughout the cytoplasm Larger than ribosomes Remove waste & dying organelles Ribosome Protein factories of the cell RNA Studded on Rough E.R. Throughout the cytoplasm Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum After the Rough E.R. (which is next to the nucleus) Lipid synthesis Steroid storage Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Closer to the nucleus Ribosomes studded all over it Vital in protein synthesis… sends proteins to the Golgi Apparatus, which then go through the membrane to leave the cell Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Golgi Apparatus (Body) Organize, package, & distribute molecules to the rest of the cell Like a post office Cytoplasm Protective gel that surrounds the entire cell Supports the organelles Ribosomes live in this Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Chloroplast ONLY in plant cells Home of Photosynthesis Chlorphyll (green pigment) Vacuole Food & water storage in the cell PLANTS: Large & centrally located ANIMALS: Small & all throughout the cytoplasm Cell Organelles perform specific functions! Mitochondria Power house of the cell Converts glucose into chemical energy (ATP) through cellular respiration Cytoskeleton Network of filaments all over the cell that provide structure Like the bones in a human body Cell Organelle Flash Cards! Make flashcards for the following organelles using your notes! Remember put the name of the organelle/structure on 1 side & the definition/description on the other Make a flashcard for the following: Nucleus Cell membrane Cell wall Capsule Cytoplasm Nucleolus Lysosome Smooth E.R. Rough E.R. Golgi Apparatus Ribosome Mitochondria Vacuole Chloroplast Cell Movement (cilia, flagella, pseudopodia) Cytoskeleton Molecules move in/out cells through the Cell/Plasma Membrane REMEMBER: the cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, that has a hydrophobic tail & hydrophilic head. Hydrophobic = Water-fearing Hydrophilic = Water-loving The majority of the cell membrane is hydrophobic, so hydrophobic molecules will pass through more easily. EX: a lipid molecule will pass more easily than an H2O molecule Cellular Transport through the Cell Membrane can happen in a couple ways… Cellular Transport Passive Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Osmosis Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Passive Cellular Transport Simple Diffusion 1. Facilitated Diffusion 2. 3. Movement from high concentration to low concentration Easiest form of transport – hydrophobic molecules use this!!! Movement from high concentration to low concentration through a protein channel Hydrophilic molecules use this form of transport – protein channels are special passage ways that let them in Osmosis: Movement of water through a membrane from area of high concentration to area of low concentration Passive Transport Examples Active Cellular Transport Active Transport 1. Moves against the concentration gradient by going from low concentration to high concentration Requires ATP (ATP: stands for adenosine triphosphate energy bearing molecule found in all living cells.) to do this! Endocytosis 2. The process that allows macromolecules to enter the cell (bulk transport) Requires ATP (energy) Exocytosis 3. The process that allow macromolecules to leave the cell (bulk transport) Requires ATP (energy) So what’s the difference? ENERGY Passive Transport Active Transport Osmosis Solutions are a mixture of a solvent & solute Solute = solid item in a solution (EX: salt) Solvent = liquid solute is dissolved in (EX: water) Solution EX: salt water The movement of water in the direction of the greater amount of solute concentration EX: if a cell was in a cup full of salt water, the water in the cell will move out of the cell to the solution, making the cell shrivel Type of passive cellular transport BUT ONLY INVOLVES WATER! Why does cellular transport happen? Cells NEED molecules in order to stay alive & healthy (EX: cells need oxygen) Cells sometimes have too much of a molecule & will burst if they don’t get rid of it If the cell & the outside environment are in equilibrium, cellular transport will not happen Chemical Reactions in the Cell There are major chemical processes that happen in the cell that allow cells & organisms to function. (1) Photosynthesis (2) Cellular Respiration How do organisms get energy? EATING & DRINKING! In the food web of life there are producers & consumers Plants = Producers Producers Animals, use photosynthesis to make their own food! humans, etc = Consumers Consumers eat producers or eat other consumers who eat producers…so consumers need photosynthesis to happen! Photosynthesis Reactants (inputs) = Air (CO2), H2O, Light Energy Products (outputs) = Carbohydrate (Glucose) & Oxygen (O2) Chloroplasts, location of photosynthesis, in plant cells absorb energy from the sunlight Purpose: convert solar energy into sugar (energy) Photosynthesis (continued…) Cellular Respiration allows consumers to use the energy from Photosynthesis! Reactants (inputs) = Glucose & Oxygen Products (outputs) = H2O, CO2, ATP (energy) Purpose = convert glucose produced from Photosynthesis into energy that our cells can use (ATP) Takes place in the mitochondria Cellular Respiration (continued…)









