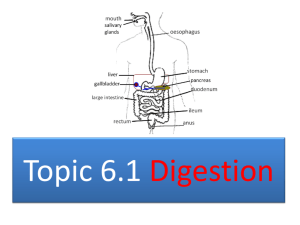
SBI3U TGT - Organ Systems & Digestion (Ch. 6)
advertisement

ORGAN SYSTEMS & DIGESTION - Review Questions 1. Which organ system involves the: pancreas, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland? 2. Which organ system involves the: kidney, bladder, ureter, urethra? 3. What are the 4 components of digestion? 4. Describe digestion in an Amoeba. 5. What are 2 advantages to having an alimentary canal vs. having a gastrovascular cavity? 6. How is physical digestion accomplished in an earthworm or a bird? 7. In humans, physical digestion occurs in 2 different places along the alimentary canal. Describe the 2 instances of physical digestion. 8. What causes the food to move along the alimentary canal? 9. What are the 3 major nutrients.macromolecules that we consume in our food? 10. What type of teeth are well adapted to grinding or crushing? 11. Name all of the organs that food passes through (in order) in the human digestive system, starting with the mouth. 12. Name 3 accessory organs to the digestive system. 13. Name the 2 muscles that allow food into and out of the stomach. 14. What are the 3 components of gastric juices in the stomach and what do they do? 15. What is an ulcer? 16. What device can be inserted into the digestive tract, enabling a doctor to look inside it without performing surgery? 17. The presence of acid in the duodenum (small intestine) causes a chemical signal to be sent to the pancreas. What does the pancreas release that neutralizes the acid? 18. Name 3 substances that are secreted by the cells of the small intestine. 19. What are the average dimensions (length and diameter) of an adult small intestine? What length of it is the duodenum? 20. The 3 sections of the small intestine are: the duodenum, the _______ and the _______. What part of digestion occurs in the last 2 sections? 21. Where is bile produced and where is it stored? What happens when bile crystalizes in the body? ORGAN SYSTEMS & DIGESTION - Answers 1. endocrine (hormonal) system 2. excretory (urinary) system 3. ingestion, digestion, absorption, egestion 4. ingestion: Amoeba engulfs food with pseudopods digestion: food vacuole fuses with lysosome, and enzymes digest absorption: nutrients are abosorbed into the cell egestion: wastes are eliminated in vacuoles 5. -cells in the alimentary call can be organized into highly specialized organs for digestion -more efficient at digesting foods & absorbing nutrients 6. sand/rocks in the gizzard help to break down large food particles 7. -mouth: teeth chew food -small intestine: bile emulsifies fat 8. rhythmic contractions of muscles (peristalsis) 9. carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (fats) 10. molars (and premolars) 11. mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus 12. liver, pancreas, gall bladder, salivary glands... 13. cardiac sphincter and pyloric sphincter 14. mucus: protects the lining of the stomach from acid & enzymes hydrocholoric acid: kills pathogens, activates pepsinogen pepsinogen: when activated, digests proteins 15. condition where there is an area of the stomach where mucus is not protecting it...cells are damaged due to the acid and enzymes 16. endoscope 17. bicarbonate ions 18. -prosecretin (is converted into secretin and signals the pancreas) -enterokinase (converts trypsinogen to trypsin) -erepsins (protein-digesting enzymes) -disaccaharidases such as maltase (break down disaccharides into monosaccharides) -pancreatic lipases (break down fats) 19. about 7 metres long and 2.5 cm in diameter duodenum is about 25-30 cm long 20. jejenum and ileum are for absorption of nutrients 21. bile is produced in the liver, stored in the gall bladder; if it crystallizes, it causes gall stones