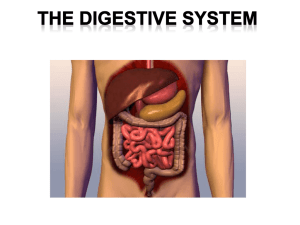
Digestive System Sunny Wang - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement

1 Good morning! Welcome to Duodenum Ad Agency. I am Sunny Wang, your tourist guide during this 5 days tour 2 of human digestive system. Enjoy your time! Brief In Introduction P4 Alimentary Canal P5 Tongue P7 Teeth P8 Salivary Glands P9 Pharynx P10 Epiglottis P11 Esophagus P12 Cardiac Sphincter P13 Stomach P15 Pyloric Sphincter P16 Duodenum P17 Pancreas P18 Gall Bladder P19 Liver P20 Small Intestine P22 Villi P23 Appendix P24 Large Intestine P25 Rectum P26 Anus P27 Physical and Chemical Digestion P30 Digestive Enzymes P31 Chemical Digestion of Carb P32 Chemical Digestion of Protein P33 Chemical Digestion of Fat P34 Importance of Liver and Pancreas P36 Mesentery P37 Mucus P38 pH Level P39 E Coli P40 Heartburn P42 Reference P43 3 Human digestive system is a complex processes. In order to use the food we eat, our body has to break the food down into smaller molecules that it can process; it also has to excrete waste. 4 The alimentary canal means the whole digestive tract from the mouth to the anus. 5 6 Tongue moves food to the pharynx and keeps food in the mouth. 7 Teeth start the process of physical digestion and pushes chewed food to the pharynx. With our teeth, food become pieces so that convenient for swallowing. 8 The salivary glands produce saliva which moisten food and use amylase to digest carbohydrate. There are three different salivary glands: sublingual gland which beneath the tongue, submaxillary gland which under the mouth and partoid gland which in front of ears. 9 The pharynx is at back of the throat and it is the place that swallowing occurs. 10 It is located at the back of the throat where oral and nasal cavities join. Also it is where swallowing occurs. 11 The esophagus is the tube which leads from the pharynx to the stomach. Food moves down in the esophagus by peristalsis. 12 Cardiac sphincter is muscle which close off the top of the stomach. It’s function is to keep stomach acid from entering the esophagus. 13 14 The stomach is a J-shaped organ which stores and churns food. There are both chemical and physical digestions in the stomach . Chruning is physical digestion and results “acid chyme”. Chemical digestion of protein is start in stomach. 15 Pyloric sphincter is located at the bottom of the stomach. It ‘s function is to let a small amount of chyme to enter the intestine. 16 The duodenum is first 1o inches of the small intestine. In the duodenum, bile enters and emulsifies fat. Thus, pancreas help to digest carbohydrate, protein and fats. 17 The role of the pancreas is to make insulin, glacagon, and pancreatic juices, including sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acid chyme. 18 The gallbladder acts as a storage for bile. Bile can emulsifies fats which means break down fat into small fat droplets. Bile is not an enzyme. 19 The liver has 6 different functions. 1 to produce bile. 2 to destroy old red blood cell and replace hemoglobin to a product in bile. 3 Stores and then breaks down glycogen to glucose between eating to help maintain glucose level of blood. 4 produces urea by deamination 5 Uses amino acid to make blood proteins. 6 Detoxification. 20 21 The first 25cm of the small intestine is duodenum. Small intestine receives bile and pancreas juice through the duct. Nutrients are absorbed into the vessels of villi. Small intestine has a large surface area to absorb carbohydrate, protein and fats. 22 Villi is the singular of villus, are finger-like projections in the small intestine that help absorb food more efficiently in the body. 23 The appendix has no function. 24 The large intestine is also known as the colon. It is divided into ascending, transverse, sigmoid and descending colons. The colon's functions are to absorb water and to eliminate The matter remaining after water is known as feces. 25 The rectum at the end of the large intestine. It stores undigested waste temporally. 26 Anus is bands of muscle that allows waste to exit from body. 27 28 29 Mechanical digestion is simply breaks down food into pieces. Chemical digestion using enzymes 30 Amylase: Acts on starch to break it into many molecules of moltose. Then moltose is broken down into glucose. Protease: Breaks down proteins to peptides and later become amino acid. There are two types of proteases: Pepsin and trypsin. Lipase: Produced by pancreas. Breaks down fat droplets. Nuclease: Breaks down RNA and DNA into nucleotides. Both small intestine and pancreas produce nuclease. 31 Hydrolysis is the result of chemical digestion of carbohydrate. There are three parts that enzymes take place. Salivary amylase is in saliva, pancreatic amylase occurs in duodenum but produced by pancreas. And moltase is produced in the small intestine. 32 There are two types of protein, pepsin is produced by gastric gland and trypsin is produced by the pancreas. There are two steps to break down proteins. Firstly, protease breaks down proteins to peptides. Then, peptidase breaks down peptides into amino acid. 33 Bile is an important substance during the digestion of fat. Bile is not an enzyme. It is produced by liver but stores in the gall bladder. It emulsifies fat into small fat droplets so that droplets can disperse water. Thus, lipase can break down fat droplets into glycerol and 3 fatty acid. 34 35 The pancreas serves two roles in the human body. One function is to produce enzymes that break our food down small enough to be absorbed into our body. The second function is to produce the hormones insulin and glucagon. The pancreas can develop disorders and diseases that effect both functions. It manufactures and secretes digestive enzymes such as amylase, which digests starch. It also produces lipase, which breaks down fats, and trypsin, a protein processor. The pancreas creates and secretes insulin, glucagon and other hormones. Insulin and glucagon are especially important for the maintenance of blood sugar, as insulin lowers the blood sugar and glucagon increases the blood sugar according to the body's needs. 36 Sheets of membrane that are attached to organs and prevent your intestines from twisting during digestive movements. 37 Mucus creates a barrier that prevents infection. 38 The overall pH level is about 7.40. However, acid in body is lower than that. 39 The E. Coli offers vital service to us and helps metabolize our bodies. 40 41 Heartburn — stomach feels an uncomfortable (burning and warmth) due to acid backs up into the esophagus. 42 43 Good bye! Wish you learn something useful and take photos during this trip! 44