Digestion Core 2015
advertisement

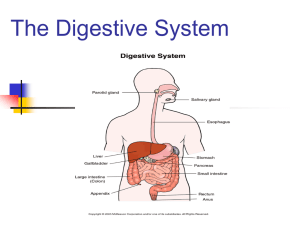
Topic 6.1 Digestion TOPIC 6.1 DIGESTION The structure of the wall of the small intestine allows it to move, digest and absorb food. Slide taken from Digestion power point by Stephen Taylor You might try drawing a digestive system that looks something like this. • Clearly show how and where accessory organs connect. Skill 2: Plan Diagram of the small intestine Slide taken from Absorption of Digestion power point by Stephen Taylor Contraction of circular and longitudinal muscle of the small intestine mixes the food with enzymes and moves it along the gut Epithelium Submucosa Mucosa Circular Muscle Smooth muscle layers Longitudinal Muscle Serosa Small Intestine: Contains different regions • Duodenum • Jejunum • ileum • Chyme enters duodenum • The pancreas secretes enzymes into the duodenum. • Pancreatic amylase & lipase • Endopeptidases like trypsin (break peptide bonds in the center of polypeptide molecules) • Pancreas also secretes sodium bicarbonate which neutralizes the stomach acid. • Pancreatic juice also contains water Does this look familiar? This is the internal structure of a pancreas cell. Rat Pancreas Slide taken from Digestion power point by Stephen Taylor Enzymes of the pancreas tend to act on larger macromolecules to break them into smaller monomers. See your chart Membrane bound enzymes: • The epithelial lining of the small intestine also secretes enzymes • Disaccharidases like maltase • Dipeptidases • The digestive enzymes in the epithelial cells of villi of the duodenum are are attached to the cell membrane. • They are peripheral proteins in the membrane • They anchored in the membrane so NOT swept along in the digestive process. • If the whole cell detached the enzyme will continue to work in the lumen of the GI tract. Advantages: • Products are released close to the membrane & easily absorbed by blood • Digestion of disaccharides takes place early in the small intestine. Villi of the Small Intestine: small projections that cover the inner lining of the small intestine. • INCREASE surface area for the absorption of digested food. Campbell Reese 9th edition, p887 Villi of the Small Intestine: • Majority of digestion occurs in the duodenum while much of the absorption occurs in the ileum. Each villus contains: • blood capillaries • lymph capillaries (the LACTEAL). Amino acids & glucose are absorbed into the blood glycerol and fatty acids absorbed into the lacteal. Campbell Reese 9th edition, p887 Specific molecules absorbed by the epithelium cells of the villi • • • • • Glucose, fructose, galactose, Amino acids Fatty acids, monoglycerides & glycerol Bases from nucleotides Mineral ions (Calcium, potassium, sodium) • Vitamins (vitamin c) Absorption of Lipids through epithelial cells PASSIVE DIFFUSION: Water, fats, fat soluble vitamins, Oxygen, CO2 & alcohol Copy the link below into your browser to see a video reviewing passive diffusion http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animations.cfm?id=5&debug=0 Campbell Reese 9th edition p888 Fructose absorption through the epithelium by Faciliated Diffusion • Fructose and other water-soluble molecules (such as vitamins) move down the concentration gradient into the epithelial cells. • Integral protein channels allow them to pass through the hydrophobic phospholipid bilayer Copy link below to your browser to see the video on facilitated diffusion http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animations.cfm?id=2&deb ug=0 Absorption of Monosaccharides through the epithelium (glucose & galactose) Copy the link below into your browser to see a video http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/animations.cfm?id =3&debug=0 http://nutrition.jbpub.com/resources/ani mations.cfm?id=4&debug=0 Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide found in plant foods Cellulose is digested by cellulase (humans can’t produce this) Most cellulose is egested in the feces and not broken down