plot the sequence of events in a story exposition in the plot structure
advertisement

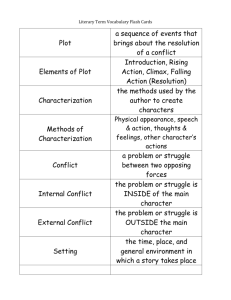
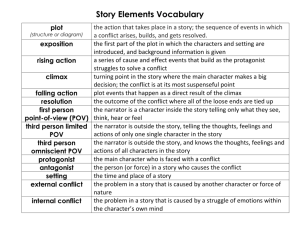
Literary Terms Definitions 1. plot the sequence of events in a story 2. exposition in the plot structure, sets the tone, establishes setting, introduces the characters, and gives the reader important background information 3. conflict a struggle between opposing forces (person vs. person, person vs. self, person vs. society, person vs. fate, person vs. nature, and person vs. technology) 4. internal conflict a struggle that occurs within a character 5. external conflict a character pitted against an outside force (person, society, fate, or nature) 6. rising action events in a story that move the plot along by adding complications or expanding the conflict 7. climax the turning point of the piece – the protagonist makes a key decision or revelation that changes the direction of the story. 8. falling action in the plot structure, the conflicts begin to be resolved. 9. resolution loose ends of story are tied up 10. theme the universal message in a work of literature – a perception about life or human nature 11. characterization 12. round character methods a writer uses to develop characters: describe a character’s physical appearance, character’s nature revealed through their own speech, thoughts, feelings, or actions, the speech, thoughts, feelings, or actions of other characters, or the narrator can make direct comments about aa character. more in depth representation of a character – multi-dimensional 13. flat character a character that we are only given a surface representation – one-dimensional 14. dynamic 15. character static character a character that undergoes changes as the plot unfolds 16. irony the difference between expectation and reality 17. dramatic irony a type of irony where the reader or viewer knows something that a character does not know. 18. situational irony the contrast between what a reader or character expects and what actually exists or happens 19. verbal irony when someone knowingly exaggerates or says one thing and means another rd a character who remains the same 20. 3 person omniscient POV the story is told by a narrative voice outside the action, not by one of the characters, and the narrator is all-knowing. Narrator uses: he, she, they, them, their, etc. 21. 3rd person limited POV the story is told by a narrative voice outside the action, not by one of the characters, and the narrator is able to see into the minds of one or more characters. Narrator uses: he, she, they, them, their, etc. the narrator is a character in the story – uses: I, me, we, us, our 22. 1st person POV 23. figurative 24. language metaphor language that communicates ideas beyond the ordinary, literal meanings of works. 25. personification a figure of speech in which human qualities are attributed to an object, animal, or idea 26. simile a figure of speech that makes a comparison between two things using like, as or resembles 27. symbolism a person, a place, an activity, or an object that stands for something beyond itself 28. mood the feeling or atmosphere that the writer creates for the reader 29. imagery consists of descriptive words and phrases that re-create sensory experiences for the reader – appeals to sight, hearing, smell, taste, and/or touch 30. foreshadowing the writer’s use of hints or clues to indicate events and situations that will occur later in the plot a figure of speech that makes a comparison between two things that are basically unlike but that have something in common