Definition Test
advertisement

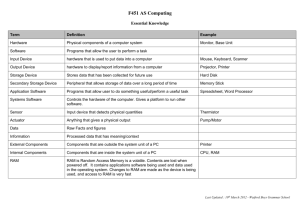
F451 Definition Jeopardy 1st Feb 2012 Programs that allow the user to perform a task SOFTWARE Data is transmitted. Received data is retransmitted back to sender. When received at source returned signal is compared to original. If there are any differences the data is retransmitted ECHOING Stores data that has been collected for future use STORAGE DEVICE Advanced piece of software used to provide an answer to a specific problem. Often used in medical diagnosis and fault repairs on hardware. EXPERT SYSTEM Programs that allow user to do something useful/perform a useful task APPLICATION SOFTWARE Controls the hardware of the computer. Gives a platform to run other software. SYSTEMS SOFTWARE Input device that detects physical quantities SENSOR Blocks of bytes are added before transmission to give a sum. The sum is transmitted with the block. The same calculation is done on the data blocks at the destination and result is compared with the transmitted value. If different, there is a transmission error CHECK SUM Peripheral that allows storage of data over a long period of time SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICE Often run during night time/weekends. No need for human to be present. No need for instant response to inputs. Processes large amounts of data in one go BATCH PROCESSING Network covering a single building or site. LAN Anything that gives a physical output ACTUATOR Hardware that is used to put data into a computer INPUT DEVICE Communication in both directions but one at a time HALF DUPLEX Raw Facts and figures DATA Interrogates the knowledge base to find an answer to a problem as part of an Expert System. INFERENCE ENGINE Processed data that has meaning/context INFORMATION Physical components of a computer system HARDWARE The user has to type in specific commands to operate the system. The user needs to be computer literate to use it as they have to remember all the commands and their syntax. Requires very little processing power. CLI Connects a LAN to a WAN ROUTER Hardware to display/report information from a computer OUTPUT DEVICE A list of on screen choices which leads to further menus which allows the user to choose an action from a set list of options. Does not allow user to access other parts of software. MENU DRIVEN INTERFACE Where the user communicates with the computer in a human conversation type way. Used with some internet search engines and expert systems. Requires no training or computer literacy. Very difficult to program due to the ambiguous nature of human speech. NATURAL LANGUAGE INTERFACE Used to control the hardware of the system/resource management through software like hardware drivers/system software. Provides platform on which applications can run. Handles storage/management of files. Provides a user interface. Allow communication between user & hardware. Has utility programs used to carry out housekeeping on system. OPERATING SYSTEM Housekeeping programs which perform a common task. Programs to help the running of the hardware and protect the system. UTILITY SOFTWARE Data is processed instantly. System responds instantly to changes in input REAL TIME OS Manual which explains how to use system. Contains FAQs. Installation guide. Index. Glossary. Contents. Written for future programmers. USER MANUAL Actions which are taken by the operating system without the user being aware of them. TRANSPARANCY Method of system lifecycle where each stage is fully completed before moving onto the next stage. WATERFALL Where analysis, design and implementation are done together and prototypes are produced by the programmer with the end user. This is iterative development. SPIRAL Looks at if creating a new system/software application is worthwhile. Examines Technical, Social and Economic factors. FEASABILITY STUDY Methods of finding out about current system. Questionnaire. Interviews. Observation. Collection and analysis of documentation. INFORMATION GATHERING Document which contains Variable Names, Data Structure, how the code works, Procedures names, DFDs, Flowcharts, Entity Relationship Diagrams. TECHINCAL DOCUMENTATION Data is put onto long term storage and kept offline so that it can be referred to if necessary. Data is still available without taking up space on working storage. ARCHIVING Carries out arithmetic instructions. Carries out logical instructions. Acts as a gateway to processor. ALU Controls fetch/execute cycle. Manages execution of instructions by using control signals to other parts of computer. Synchronises actions (using inbuilt clock). CONTROL UNIT Stores the OS/data currently in use and software currently in use MEMORY UNIT Stores the address of the next instruction and controls the sequence in which the instructions are executed. PROGRAM COUNTER Stores the address in memory currently being accessed MAR Stores the data being transferred to or from memory MDR Stores the instruction currently being executed CIR Stores results of calculations performed ACCUMULATOR Transmit data between areas of the processor DATA BUS Copy of files to backup medium – eg. Memory stick, CDRW, DVDRW (not CD-Rom). Frequency of backup, Time backup is performed. Storage of backup medium in safe location. BACKUP STRATEGY Send control signals from control unit to other parts of the processor CONTROL BUS Identification about where the data is being sent/coming from ADDRESS BUS The symbols that may be represented by a computer. Normally equates to the symbols on a keyboard. Each character on the keyboard has a binary code which is unique. ASCII has 1 byte per character. Unicode has 2 bytes. CHARACTER SET Network covers a wide geographical area crossing countries and continents. WAN A set of rules that governs communication between devices PROTOCOL A digit on the end of a string of numbers that has been calculated based on an algorithm performed on the string of numbers. Used in error checking. CHECK DIGIT Communication in one direction only SIMPLEX Communication in both directions simultaneously DUPLEX Total: / 52