F451 AS Computing
advertisement
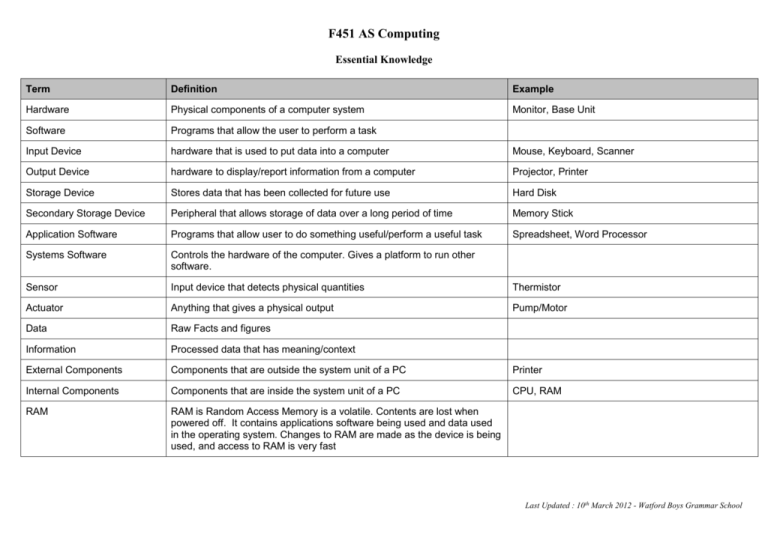
F451 AS Computing Essential Knowledge Term Definition Example Hardware Physical components of a computer system Monitor, Base Unit Software Programs that allow the user to perform a task Input Device hardware that is used to put data into a computer Mouse, Keyboard, Scanner Output Device hardware to display/report information from a computer Projector, Printer Storage Device Stores data that has been collected for future use Hard Disk Secondary Storage Device Peripheral that allows storage of data over a long period of time Memory Stick Application Software Programs that allow user to do something useful/perform a useful task Spreadsheet, Word Processor Systems Software Controls the hardware of the computer. Gives a platform to run other software. Sensor Input device that detects physical quantities Thermistor Actuator Anything that gives a physical output Pump/Motor Data Raw Facts and figures Information Processed data that has meaning/context External Components Components that are outside the system unit of a PC Printer Internal Components Components that are inside the system unit of a PC CPU, RAM RAM RAM is Random Access Memory is a volatile. Contents are lost when powered off. It contains applications software being used and data used in the operating system. Changes to RAM are made as the device is being used, and access to RAM is very fast Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School ROM ROM is Read Only Memory and is non-volatile. The contents are not erased when powered off. The ROM contains the start up program which allows a device to boot up the OS. The start up program is needed immediately when the device is powered on. The contents of ROM cannot be changed. IAS Immediate Access Store - RAM GUI A GUI is a graphical user interface which uses WIMP. A GUI is very processor intensive. WIMP Window Icons Menu Pointer. 4 components of a GUI. CLI A CLI is a command line interface. The user has to type in specific commands to operate the system. The user needs to be computer literate to use it as they have to remember all the commands and their syntax. CLI requires very little processing power. Menu Driven Interface A menu based interface is a list of on screen choices which leads to further menus which allows the user to choose an action from a set list of options. Does not allow user to access other parts of software. These are commonly used on a touch screen information terminal or a mobile phone. A menu based interface is easy and intuitive to use and requires little training or computer literacy. Mobile Phone. Touch screen information terminal. Natural Language Interface A natural language interface is where the user communicates with the computer in a human conversation type way. Used with some internet search engines and expert systems. Requires no training or computer literacy. Very difficult to program due to the ambiguous nature of human language. Expert System Expert System Advanced piece of software used to provide an answer to a specific problem. Often used in medical diagnosis and fault repairs on hardware. Consists of a Knowledge Base, Inference Engine and a HCI (usually a natural language interface) Inference Engine Interrogates the knowledge base to find an answer to a problem as part of an Expert System. Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Knowledge Base Experts in the field are interviewed to get information to create a knowledge base. The rules used to interrogate the knowledge base are collected in the rules base .The rules are used to interrogate the knowledge base using a set of algorithms stored in the inference engine Batch OS Often run during night time/weekends No need for human to be present Run in computer downtime when workers have gone home No need for instant response to inputs Processes large amounts of data in one go Similar data that requires similar processing Operating System Used to control the hardware of the system/resource management through software like hardware drivers/system software. Provides platform on which applications can run. Handles storage/management of files. Provides a user interface. Allow communication between user & hardware. Has utility programs used to carry out housekeeping on system. Utility Software Housekeeping programs which perform a common task. Programs to help the running of the hardware and protect the system. File handling Software Allows storage of files on secondary storage devices. Uses folders/directories/file extensions. Allows opening files/folders to retrieve data. Copying of files from. Deletion of files from storage. Allows security of files where needed. Real Time OS Data is processed instantly. System responds instantly to changes in input Multi user OS Allows more than 1 user to use the system simultaneously – e.g. a network operating system. One computer with many terminals allows more than one user at a time to access a central server. Each terminal given time slice... in turn - each time slice very small (1/100 of a second). Time slice cycles around each terminal at high speed allowing apparently simultaneous access to all users. Data is separated from terminals. Must have security provision/ individual user rights. Processing cheques/bills/pay rolls File handlers, Anti virus, Compression software Automatic Pilots on airplanes. Seat booking system – ensures 2 seats aren’t booked simultaneously Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Multi Tasking OS Allows more than one task to run apparently simultaneously. Each task is given an amount of processor time before going onto the next task. Processor is so fast that it seems as though the tasks are done simultaneously. Round robin system with each task allowed a small amount of time. User can switch between programs. Different programs available in different windows. Single user OS A single user OS allows one user at a time to use the system. It allocates each user with rights and keeps the user files separate Transparency Actions which are taken by the operating system without the user being aware of them. Waterfall Method Method of system lifecycle where each stage is fully completed before moving onto the next stage. Spiral Method Where analysis, design and implementation are done together and prototypes are produced by the programmer with the end user. This is iterative development. Feasibility Study Looks at if creating a new system/software application is worthwhile. Examines Technical, Social and Economic factors. Information Gathering Methods of finding out about current system. Questionnaire. Interviews. Observation. Collection and analysis of documentation. Installation Strategy Parallel/pilot/phased/direct installation. Devise training program. Purchase hardware. System must be tested with real data by end users. Write technical and user documentation. Software Maintenance Corrective. Adaptive. Perfective. User Guide/Documentation Manual which explains how to use system. Contains FAQs. Installation guide. Index. Glossary. Contents. Technical Documentation Written for future programmers. Contains Variable Names, Data Structure, how the code works, Procedures names, DFDs, Flowcharts, Entity Relationship Diagrams. Play a video or music track whilst using a word processor. Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Requirements Specification List of requirements of the client for who the new system is being produced. Consists of input, processing and output requirements. The client agrees to these so no confusion when program is finished. Design Specification Taking the requirements specification and designing the stages to produce the final system. Consists of input design (interface), output design, design of data structure, any diagrams such as Flowcharts, DFDs, ERDs. OCR Characters shapes are scanned and these shapes are turned into text e.g. scanning a printed page of text into a word processor document OMR Scanned page which reads the positions of marks on a document that are made in a specific place which denotes inputted data. Multiple choice tests or lottery tickets. Fast and accurate to process. Useful on multiple choice tests as answers are all objective – no area for debate. Can be processed in batches. Useful for partially sighted users to turn text into speech synthesis. Multiple Choice Test MICR Where special characters on document written using magnetisable ink which are both computer and human readable. Commonly used for printing account numbers on used on banking cheques Voice Recognition Computer system can interpret spoken word into commands appropriate for the application Useful for partially sighted/sight deficient users ALU Carries out arithmetic instructions. Carries out logical instructions. Acts as a gateway to processor. Control Unit Controls fetch/execute cycle. Manages execution of instructions by using control signals to other parts of computer. Synchronises actions (using inbuilt clock). Memory Unit Stores the OS/data currently in use and software currently in use Program Counter Stores the address of the next instruction and controls the sequence in which the instructions are executed. Memory Address Register Stores the address in memory currently being accessed Memory Data Register Stores the data being transferred to or from memory Current Instruction Register Stores the instruction currently being executed Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Accumulator Stores results of calculations performed Data Bus Transmit data between areas of the processor Control Bus Send control signals from control unit to other parts of the processor Address Bus Identification about where the data is being sent/coming from Buffer A small area of computer memory / temporary storage that holds data. Interrupt A signal or message sent to the processor that stops the current activity of the processor. Character Set The symbols that may be represented by a computer. Normally equates to the symbols on a keyboard. Each character on the keyboard has a binary code which is unique. ASCII has 1 byte per character. Unicode has 2 bytes. ASCII. Unicode Verification Checking input data with original data to ensure there have been no input errors Input same data twice and compare it Validation Validation ensures data meets certain rules. These are programmed in the software. Range Check A number between a maximum and minimum range >=1 and <=10 Format Check A field may required letters and numbers in a certain order Data entry for a NI number - LLNNNNNNL (L)etter, (N)umber. Presence Check Checks data has been entered into a field. Existence Check Barcode is read at supermarket till. That number is looked up on a database. If number is not on database then it must have been incorrectly inputted. Encoding Shortening a data input for faster and easier entry. Encryption Scrambled data to make it illegible to someone. Can be decrypted by using password. Helps make sensitive data more secure when transmitting it. (S)mall, (M)edium, (L)arge Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Backup A backup is a copy of a file and its structure on a portable medium kept away from originals so that if the original is corrupted it can be replaced. Important files needs be protected from deliberate or accidental data loss. Backup Strategy Copy of files to backup medium – eg. Memory stick, CDRW, DVDRW (not CD-Rom). Frequency of backup, Time backup is performed. Storage of backup medium in safe location. Archive Data is put onto long term storage and kept offline so that it can be referred to if necessary. Data is still available without taking up space on working storage. Disaster Recovery Procedures that ensure data and systems can be restored following a major disaster e.g. Fire in a building. LAN A local area network is a network covering a single building or site. WAN A WAN covers a wide geographical area crossing countries and continents. Handshake The exchange of signals between devices to signify that they are ready for communication. Rules/protocol will be agreed prior to the communication.. Without agreement on rules the two devices cannot understand each other’s signals. One device may not be ready for communication eg may be switched off Router Connects a LAN to a WAN Protocol A set of rules that governs communication between devices Logical Protocol The logical part of the protocol are things that are programmed in software such as baud rate the error correction used, and any compression techniques used. Physical Protocol The physical part of the protocol can be if data is transmitted wireless or hard-wired, Serial or parallel or the type of cabling used e.g. copper wire, or fibre optic, frequency of of wireless signal Baud Rate The speed in which data is transmitted between 2 devices or across a LAN/WAN. Small bit rate required for downloading text document. High bit rate required to watch video – time sensitive. Measured in bits per second. Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School http Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. Protocol which governs how web pages are displayed over the internet. Parallel Transmission Multiple bits transmitted at a time down many wires eg. transferring data from CPU to hard disk which has time sensitivity of data transfer. Serial Transmission One bit transmitted at a time down a single wire Parity Bit When using parity the total number of 1’s in a byte must be either an odd or even number depending on the parity bit. This is the last bit in the byte. Method of error detection. Check Digit A digit on the end of a string of numbers that has been calculated based on an algorithm performed on the string of numbers. Used in error checking. Check Sum Blocks of bytes are added before transmission to give a sum. The sum is transmitted with the block. The same calculation is done on the data blocks at the destination and result is compared with the transmitted value. If different, there is a transmission error Echoing Data is transmitted. Received data is retransmitted back to sender. When received at source returned signal is compared to original. If there are any differences the data is retransmitted Simplex Communication in one direction only Duplex Communication in both directions simultaneously Half Duplex Communication in both directions but one at a time NIC Network Interface Card – Required to connect a PC to a network. NOS Network Operating System – OS required to manage the facilities of a network/LAN. Barcodes have a check digit to validate scanning. ISBN – Mod 11. Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School Packet Switching Data split into packets sent onto network. Each packet finds the fastest route to destination. Packets must be reordered at destination/arrives in wrong order. Packets have identity on label. No established route for each packet. Doesn’t tie up parts of network. Maximises use of network. Data cannot be easily intercepted. Maximises use of network. Only as fast as its slowest packet! Circuit Switching Route reserved before transmission. Establishes a route along which to send data. Data sent down this route in its entirety. Can tie up large areas of network. Data Protection Act Data protection Act governs the storage of personal data electronically. It is required because Information is confidential and sensitive Information must be accurate Clients must have confidence that measures are taken to protect their data Ensure irrelevant data is not kept Concerns about identity theft/fraud Stops data being passed onto 3rd parties for marketing purposes. Computer Misuse Act Law that governs unauthorised access to data - Hacking Copyright Patents Act Law that governs pirating software/music/images. Last Updated : 10th March 2012 - Watford Boys Grammar School