Unit 1 SciRevision
advertisement
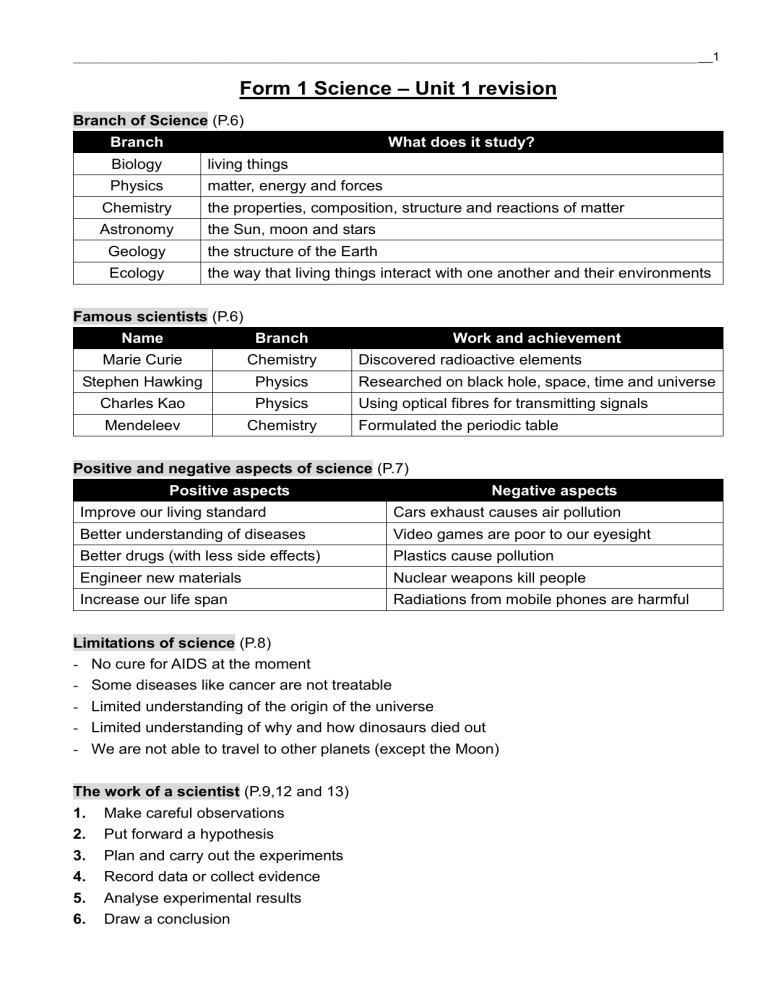
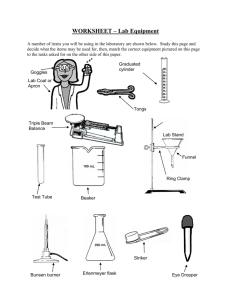
___________________________________________________________________________________________________1 Form 1 Science – Unit 1 revision Branch of Science (P.6) Branch What does it study? Biology living things Physics matter, energy and forces Chemistry the properties, composition, structure and reactions of matter Astronomy the Sun, moon and stars Geology the structure of the Earth Ecology the way that living things interact with one another and their environments Famous scientists (P.6) Name Branch Work and achievement Marie Curie Chemistry Stephen Hawking Physics Researched on black hole, space, time and universe Charles Kao Physics Using optical fibres for transmitting signals Mendeleev Chemistry Discovered radioactive elements Formulated the periodic table Positive and negative aspects of science (P.7) Positive aspects Negative aspects Improve our living standard Cars exhaust causes air pollution Better understanding of diseases Video games are poor to our eyesight Better drugs (with less side effects) Plastics cause pollution Engineer new materials Nuclear weapons kill people Increase our life span Radiations from mobile phones are harmful Limitations of science (P.8) - No cure for AIDS at the moment - Some diseases like cancer are not treatable - Limited understanding of the origin of the universe - Limited understanding of why and how dinosaurs died out - We are not able to travel to other planets (except the Moon) The work of a scientist (P.9,12 and 13) 1. Make careful observations 2. Put forward a hypothesis 3. Plan and carry out the experiments 4. Record data or collect evidence 5. Analyse experimental results 6. Draw a conclusion ___________________________________________________________________________________________________2 Laboratory equipment and apparatus (P. 14, 16 and 17) A Measuring cylinder M Heat-proof mat B Filter funnel N Test tube C Conical flask O Test tube rack D Dropper P Tongs E Glass rod Q Test tube holder F Reagent bottle R Sink and water tap G Gas tap S Watch glass H Thermometer T Evaporating dish I Beaker U Gas jar J Wire gauze V Safety spectacles K Tripod W First aid box L Bunsen burner X Fire extinguisher Laboratory safety (P.18-20) What you should do What you should NOT do Follow instructions given by the teacher Do not run and play in the laboratory Keep the laboratory clean and tidy Do not eat or drink in the laboratory Report all accidents to your teacher at once Do not throw waste into the sink Keep papers away from Bunsen burner Tie up long hair when using Bunsen burner Do not point test tubes towards anyone when heating chemicals Put the Bunsen burner on a heat proof mat Do not taste any chemicals ___________________________________________________________________________________________________3 Wear lab coat and safety spectacles Hold the test tube with a test tube holder Do not smell the chemicals directly, fan the gas to the nose instead Wait until hot apparatus has cooled before putting it away Do not enter the laboratory when teacher is not there Accidents and actions (P.21) Accidents What you should do Heat burns (Bunsen burner) Cool the affected area in slow running water Chemical burns Cool the affected area in slow running water Eye accidents Use eyewash bottle to wash the eyes Small cuts Apply a dressing to it Thermometer broken Report to teacher and do NOT try to clean up yourself Solutions in test tube boils and overflows during heating Turn off the flame and inform your teacher immediately. Make sure you clean up the spillage Bunsen burner Using a Bunsen burner (P.23) 1. Put the Bunsen burner on a heat proof mat 2. Make sure the rubber tubing is properly connected to the gas tap 3. Close the air hole 4. Light a match and hold it over the top of the chimney 5. Turn on the gas tap, a yellow flame is observed 6. Open the air hole slowly to produce a blue flame ___________________________________________________________________________________________________4 Compare yellow and blue flames When the air hole is closed When the air hole is opened Shape of flame Irregular Regular Colour of flames Yellow Blue Temperature of the flame Lower Higher Luminosity of the flame Higher Lower Sound produced by the Bunsen burner Quiet Roaring/ noisy Diagram When the air hole is fully open, the Bunsen burner may strike back. The flame changes to a green colour and you can hear a loud noise. Please turn off the Bunsen burner immediately. Measurements How do we measure Units Length Ruler, metre rule km, m, cm, mm Volume Measuring cylinder L, ml, m3, cm3 Weight Balance, electronic balance, scale kg, g, lbs Temperature Thermometer °C, °F Time Stop-watch, clock, timer h, min, s Units Conversion 1 km = 1000 m 1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm 1 cm = 10 mm 1 L = 1000 mL 1 kg = 1000 g 1 hr = 60 min = 3600 s cm3 1 kg = 2.2 lbs 1 min = 60 s 1 mL = 1 1 L = 1000 cm3 How to do a simple scientific investigation (P.51, 53, 58) 1. Aim 2. Materials 3. Procedure 4. Record data/ measurements 5. Analysis 6. Fair test 7. Conclusion ___________________________________________________________________________________________________5 Questions : 1. Ans: What is Science ? < P.g.4> Science is the study of things and events around us. Besides finding out how and why things happen, science can also improve our living standard. (Short ans.!) In fact, many things we use in daily life are the products of scientific knowledge. They would not have been invented without the knowledge of science. 2. Is Science always good for us ? < P.g. 7> Ans: Science is not always good for mankind, especially when it is not used properly. (Short ans.!) For example, nuclear weapons can kill and injure many people. Cars and plastics can cause pollution of the environment. Therefore, we need to remind ourselves to use scientific inventions properly. 3. Ans: Name any four things that we should/ should not do in lab.! Four things we should do in lab. are: 1. 2. 3. 4. < P.g.20> Always follow instructions given by your teacher. Keep the laboratory clean and tidy. Report all accidents to your teacher at once. Keep books and papers away from the Bunsen burner. Four things that we should not do in lab. are : 1. 2. 3. 4. 4. Ans: Do not enter the laboratory unless your teacher is present. Do not run or play in the laboratory. Do not eat or drink in the laboratory. Do not throw solid wastes into the sink. Why do you think your heart beats/pulse rate increase after exercise ? The blood carries oxygen around the body. The harder you work, the more oxygen you need. Your heart has to pump faster so that more oxygen can be carried around the body. Important : Summing up Practice < P.g. 60 ~ 62 >