Road to Revolution Timeline
advertisement

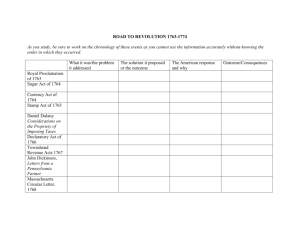
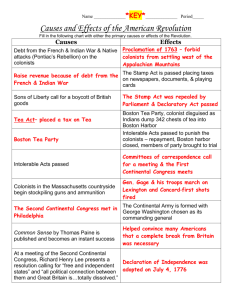
Road to Revolution Timeline French and Indian War – 1754-1763 Treaty of Paris – 1763 – Document which officially ended the French and Indian War. Proclamation of 1763 – Colonist cannot settle west of the Appalachian Mountains. Sugar Act – 1764 - Sugar Act of 1764, which increased duty on foreign sugar imported from the West Indies; after numerous protests from spoiled Americans, the duties were reduced. Stamp Act – 1765 - The Stamp Act mandated the use of stamped paper or the affixing of stamps, certifying payment of tax. Quartering Act – 1765 – The colonists had to provide housing and provisions for British soldiers. Townshend Act – 1767 - They put light taxes on lead, paper, paint, and tea, which were later repealed, except tea. Boston Massacre – 1770 – an incident in which British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists, killing five people. Tea Act – 1773 – a law passed by Parliament allowing the British EWast India Company to sell its low-cost tea directly to the colonies, undermining colonial tea merchants; led to the Boston Tea Party. Boston Tea Party – 1773 - On December 16, 1773, some Whites, led by patriot Samuel Adams, disguised themselves as Indians, opened 342 chests and dumped the tea into the ocean in this “Boston Tea Party.” Intolerable Acts – 1774 - The Acts passed in 1774, following the Boston Tea Party, that were considered unfair because they were designed to chastise Boston in particular, yet effected all the colonies by the Boston Port Act which closed Boston Harbor until damages were paid. First Continental Congress – 1774 - n Philadelphia, from September 5th to October 26th, 1774, the First Continental Congress met to discuss problems. While not wanting independence yet, it did come up with a list of grievances, which were ignored in Parliament. Lexington and Concord – 1775 - In April 1775, the British commander in Boston sent a detachment of troops to nearby Lexington and Concord to seize supplies and to capture Sam Adams and John Hancock. Minutemen, after having eight of their own killed at Lexington, fought back at Concord, pushing the Redcoats back, shooting them from behind rocks and trees, Indian style. Road to Revolution Timeline Second Continental Congress – 1775 - The Second Continental Congress met in Philadelphia on May 10, 1775, with no real intention of independence, but merely a desire to continue fighting in the hope that the king and Parliament would consent to a redress of grievances. Common Sense – 1776 - In 1776, Thomas Paine published the pamphlet Common Sense, which urged colonials to stop this war of inconsistency, stop pretending loyalty, and just fight. Declaration of Independence - 1776