Lecture Overheads for Monday, November 26
advertisement

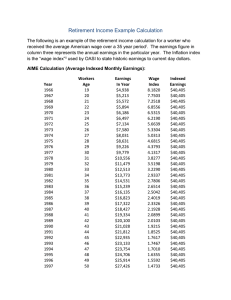
Announcements for Monday, November 26, 2001 For Wednesday 11/28: Read chapter 13 Reading quiz #14 over chapter 13 Submit stage III project paper Chapter 13 Lecture For Monday 12/3: Assignment 15/16 paper due Group Presentations Will distribute sheets to grade group members For Wednesday 12/5: Group Presentations Will distribute final exam review information For Today: Submit Reaction Paper, Assignment #13 Lecture Over Chapters 11 (welfare programs) and Chapter 12 (Social Insurance Programs) Social Insurance Programs I. Social Security II. Medicare III.Unemployment Insurance Event-conditioned income transfer programs designed to prevent people from falling into poverty due to retirement, disability, illness, old age, death of wage earner, and unemployment. Why have socially provided insurance? Paternalism Adverse selection Government can economize on costs of setting up insurance for individuals by handling many people as a large group. What programs together constitute social security? O.A.S.D.H.I. Programs 1935 Social Security Act created Old Age Insurance (OAI) - designed to provide an income floor when aged workers left the work force 1939 amended to include Survivor's Insurance for survivors and dependents of workers who die. (S) 1956 added coverage for disabled workers disability insurance (D) 1958 added benefits for dependents of disabled worker 1965 added Health Insurance (HI) creating Medicare Program How are the social security programs financed? Through a common payroll tax on wages and salaries. Pay-as-you-go basis - current contributions used to pay current benefits For us, in future, part financed pay as you go, part financed from trust fund being built up now. What is the FICA Payroll Tax and how does it work? FICA - Federal Insurance Contributions Act - that requires withholding of these contributions Employer must match the employee's contribution to social security FICA payroll tax is 7.65% (5.6% OASI, .6% disability insurance, 1.45% health insurance) For 2002 federal government has allotted 455 billion for OASDI for 46 million people. They expect to collect 539 billion through taxes for these programs. When collecting the FICA tax, what is the "wage base?" In 2000, earnings over $76,200 were not taxed for OASDI, but any earnings below that level taxed at 6.2% total. HI taxes of 1.45% are levied on all earnings (no cap) Why is social security financed through a specific payroll tax instead of from general government revenues? Read 184-185 of Rosen What does it mean to say that the tax for OSADI, with an income ceiling, is regressive? Someone earning $76,200 would be taxed at a rate of 7.65%, but someone earning twice that amount, pays no additional payroll tax. The effective tax rate is lower for the person earning more. How are social security benefits calculated: Size of benefit depends on employment history To earn benefits, worker must have equivalent of 10 years of work experience Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME): Average wages in covered employment for length of working life o Discard lowest five years of earnings o Adjusted for inflation o Wages over ceiling ($68,400 in ’98) Benefit Formula or Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) Calculation of PIA if 65 in 2001: o PIA is 90% of 1st $561+ o 32% of AIME between $561 – 3,381 + o 15% above $3,381 AIME $200 $1600 PIA $180 $837.38 Is this benefit structure progressive or regressive? Progressive - gives low-wage workers a higher wagereplacement rate Benefit maximum of $1,433 per month in 2000. What are replacement rates? Low earner has 57% of earnings replaced Average earner has 42% High earner has 26% Average benefit amount for workers retiring at 65 was $1,000 monthly. How does benefit differ if you retire at age 62 instead of 65? (Early Retirement) Can collect benefits starting at 62, but only 80% of benefit amount. Also, if you work any, the marginal tax rate on your benefit is 50%. Can a non-working spouse receive a benefit? Yes - 50% of spouse's benefit amount. So married couple - one worker 150% of workers benefit amount Other factors that affect Social Security benefits: Age at which benefit is drawn –at 62 instead of 65 receive a 20% reduction, each year past 65 adds 3% Earnings test for ages 65 – 70 earnings above $14,500 subject to tax of 33% 85% can be taxed if taxable income > 34,000 (single) or 44,000 (married) Distribution Issues: Women receive more benefits on age than men as they live longer Married receive more than single because spouse receives 50%. Surviving spouse receives entire benefit One-earner couples gain more than two-earner couples. The 50% bonus may be more than the benefit from the secondary worker Does social security help to prevent poverty among the elderly? Income dependence: 40% of income to aged households comes from social security as old people get older, % of total income coming from social security rises for 40% of elderly with lowest incomes, social security is 80% of income with S.S. 1 in 11 elderly Americans is poor without S.S. half of elderly Americans would be in poverty Does social security affect work incentives and retirement age? People can afford to retire early with S.S. income as an option Structure of S.S. payments distorts work incentives with a 50% marginal tax rate for workers from age 62-64.



![[Product Name]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005238235_1-ad193c18a3c3c1520cb3a408c054adb7-300x300.png)