Dihybrid Genetics Problems: Teacher Resource
advertisement

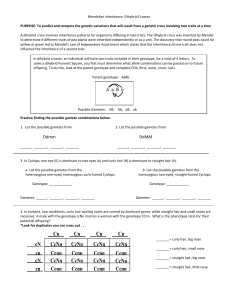
Biology TEACHER EQ: Do I carry deadly genes? Enduring Understanding Nucleic acids transfer genetic information from generation to generation. Broad Brush Knowledge Mendelian genetics, probability Dihybrid Genetics Problems Targeted Skills analysis, probability Target 3. Apply Punnett squares to determine the probability of two factor crosses Concepts Important to Know and Understand Heredity Core Objectives 7. Interpret the role of genetics in determining heredity as it applies to biotechnology. TEKS (6D) compare genetic variations observed in plants and animals TEACHER MANAGEMENT Estimated Time: 30 – 40 minutes (option - may start in class and finish for homework) Materials: handouts Teacher Prep: make copies of handouts A dihybrid cross involves inheritance patterns for organisms differing in two traits. The dihybrid cross was invented by Mendel to determine if different traits of pea plants were inherited independently or as a unit. The discovery that round peas could be yellow or green led to Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment which states that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of a second trait. The genotype alleles are shown by using two sets of letters, one set to represent each trait being studied. Each parent’s gametes must have two of each letter representing the traits, four letters in all. Parent: AaBb AaBb AaBb AaBb Gametes: AB Ab aB aa A a B b AB Ab aB ab KEY PRACTICE: 1. a. List the possible gametes from Parent A with DDMM. DM, DM, DM, DM (all DM) b. List the possible gametes from Parent B with DdMM. DM, DM, dM, dM c. List the possible gametes from Parent C with Ddmm. Dm, Dm, dm, dm If Parent A mates with Parent B, list the possible offspring genotypes. DDMM, DdMM If Parent B mates with Parent C, list the possible offspring. DDMm, DdMm, ddMm 2. In Cyclops, one eye (E) is dominant to two eyes (e) and curly hair (H) is dominant to straight hair (h). a. Write the cross between a homozygous one-eyed, curly-haired Cyclops and a homozygous two-eyed, straight-haired Cyclops. EEHH vs. eehh b. List the possible gametes from the homozygous one-eyed, curly-haired Cyclops. EH Dihybrid Genetics Problems- Biology - TEACHER (Revised June 26, 2008) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 1 c. List the possible gametes from the homozygous two-eyed, straight-haired Cyclops. eh d. Write the genotype of all individual produced in the above cross. EeHh e. Write the phenotype of all individuals produced in the above cross. One-eyed, Curlyhaired 3. In humans, two abnormal conditions, cataracts of the eyes and excessive fragility of the bones are carried by dominant genes. Below is the Punnett square showing their possible offspring. a. What are the genotypes of each parent? CCnn and ccNn b. What are the phenotypes of each parent? Cataracts and normal bones No cataracts and normal bones Cn Cn Cn Cn cN CcNn CcNn CcNn CcNn cn cN Ccnn Ccnn Ccnn Ccnn CcNn CcNn CcNn CcNn cn Ccnn Ccnn Ccnn Ccnn 4. In werewolves, sharp fangs are dominant (F) and round fangs are recessive (f). Long hair is dominant (H) and short hair is recessive (h). Cross a homozygous sharp fanged, heterozygous longhaired werewolf with a round fanged, shorthaired werewolf. FH a. Phenotypic ratio: 8:8:0:0 FH Fh Fh fh FfHh FfHh Ffhh Ffhh fh FfHh FfHh Ffhh Ffhh fh FfHh FfHh Ffhh Ffhh fh FfHh FfHh Ffhh Ffhh b. What is the probability of having a werewolf born with sharp fangs and long hair? 8/16 = ½ = .50 = 50% c. What is the probability of having a werewolf born with sharp fangs and short hair? 8/16 = ½ = .50 = 50% 5. In beauty queens, long legs (L) are dominant to short legs (l) and high cheekbones (B) are dominant to average cheek bones (b). A man with short legs and average cheekbones marries a woman who is heterozygous for both traits. lb lb lb lb a. Phenotypic ratio: 4:4:4:4 b. Based on known beauty queen characteristics, what is the probability of this couple having a future LB LlBb LlBb LlBb LlBb Lb Llbb Llbb Llbb Llbb lB llBb llBb llBb llBb llbb llbb llbb llbb lb Dihybrid Genetics Problems- Biology - TEACHER (Revised June 26, 2008) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 2 beauty queen? 4/16 = 1/4 = .25 = 25% 6. Pea plants can produce round (R) or wrinkled (r) peas as well as yellow (Y) or green (y) pea pods. A pea plant with the genotype RrYY is crossed with a pea plant with the genotype rrYy. a. How many different genotypes can be expressed in the offspring? List them below. Gametes A: RY and rY (1) RrYY (2) RrYy (3) rrYY (4) rrYy Gametes B: rY and ry b. How many different phenotypes can be expressed in the offspring? List them below. (1) Round and yellow (2) Wrinkled and yellow Dihybrid Genetics Problems- Biology - TEACHER (Revised June 26, 2008) (printed 3/9/2016) p. 3