Particulate Inheritance Patterns Blended Inheritance Particulate
advertisement

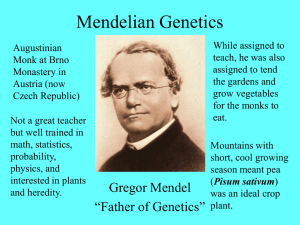
8/26/10 Particulate Inheritance Patterns Blended Inheritance • Articulated by Aristotle • Offspring result from the combination of parental “essences”. • Phenotypes of offspring should be intermediate to that of parents Particulate Inheritance • Theory proposed by Mendel • First articulated in 1865 • Result of work done with Pisum sativum – Established “pure strains” – Considered each character (trait) individually – Applied statistics to the data 1 8/26/10 Definitions • Dominant allele - an allele that expresses its phenotypic effect even when heterozygous with a recessive allele • Recessive allele - an allele whose phenotypic effect is not expressed in a heterozygote. Definitions • Parental generation (P1) - the original organisms under study • First filial generation - the offspring that results from a cross of the parental generation Reciprocal Cross • Organisms that have different sexes can be crossed in two different ways Phenotype A male X Phenotype B female Phenotype B male X Phenotype A female • Mendel concluded that reciprocal crosses are equal 2 8/26/10 Mendel’s Crosses Significance of 3:1 ratio Mendel’s Conclusions • Existence of particles of inheritance • These particles of inheritance are inherited in pairs • Members of of the pair segregate into gametes • Gametes carry only one set of chromosomes • Gametes combine without regard to the members of gene pair that are carried. 3 8/26/10 Mendel’s 5 points Mendel’s First Law The Law of Segregation The two members of a gene pair segregate from each other into the gametes; so half the gametes carry one member of the pair and the other half of the gametes carry the other member of the pair Definitions • Monohybrid - a heterozygote resulting from the cross of two pure parental strains. • Selfing- a cross in which individuals are allowed to self-fertilize (plants) or two phenotypically identical individuals from the same generation are allowed to mate. 4 8/26/10 Definitions • Dihybrid - a individual heterozygous at two gene loci. Results from the mating of two pure parental strains. • Dihybrid cross - the selfing of dihybrid individuals. 3/4 of these round seeds will be yellow 3/4 of the F2 will be round 1/4 of these round seeds will be green 3/4 of these wrinkled seeds will be yellow 1/4 of the F2 will be wrinkled 1/4 of these wrinkled seeds will be green 5 8/26/10 Mendel’s Second Law The Law of Independent Assortment During gamete formation, the segregation of the alleles of one gene is independent of the segregation of the alleles of another gene For genes whose loci are located on different chromosomes. Calculating Genetic Ratios • Punnett square • Forked line • Probabilities Punnett Square • For every loci that is heterozygous (n) • the number of gametes is 2n • the number of genotypes is 3n • the number of possible combinations is 4n 6 8/26/10 Forked Line 1/4CC 1/4BB 1/4 AA 1/2Bb 1/2Cc 1/4cc 1/4 bb Product Rule The probability of independent events occurring together is the product of the probabilities of the individual events Sum Rule The probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring together is the sum of their individual probabilities 7 8/26/10 Now Solve: For the cross: AaBbCcDdEe X AaBbCcDdEe What is the probability of getting an offspring with the genotype of aaBbCCDdee? (1/4)(1/2)(1/4)(1/2)(1/4) = 1/256 8