Cell Organelles Worksheet
advertisement

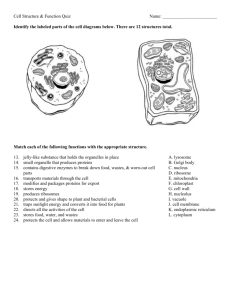
CELL ORGANELLE FEVER! Organelle CELL MEMBRANE or Description Function Animal, Plant, or Both Thin membrane that holds the cell together. It is a phospholipid bilayer that forms the barrier between the inside and outside of the cell. Protects the cell; controls what goes into and out of the cell. Both CYTOPLASM Jelly-like substance that contains and supports the organelles inside the cell. Pads and supports organelles inside the cell. Both NUCLEUS Dense, ball shaped structure that contains chromatin (DNA). Controls all of the cell’s activities. Both NUCLEAR MEMBRANE or Thin phospholipid bilayer that is the outer covering of the nucleus. Covers and protects the nucleus; Controls what goes into and out of the nucleus. Both NUCLELOUS Small dark area in the nucleus. Is not bound by a membrane. Makes ribosomes that get sent out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm or onto the RER. Both CHROMATIN Looks like a glob of strings inside the nucleus. It is all of the DNA in the nucleus. Provides instructions for the cells activities (growth, reproduction, production of proteins, etc.) Both SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Clear, tube-like membranes that are mainly round near the cell membrane. Makes lipids, including ones that make new cell membrane. Both PLASMA MEMBRANE NUCLEAR ENVELOPE 106757295 Organelle Appearance Function ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Clear, bumpy membranes that look like sheets or discs around the nucleus. The bumps are ribosomes. RIBOSOME Small specks made of Makes proteins by assembling RNA (ribonucleic acid). amino acids in a particular Found in cytoplasm or order. on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Made by the nucleolus. Animal, Plant, or Both Transports the proteins made by Both the ribosomes throughout the cell by pinching off sacs (vesicles) that are full of the protein. Most go to the golgi body for further processing. Both MITOCHONDRIA Located in the cytoplasm; bean shaped with wavy lines (crista) inside Supplies energy for the cell Both through the process called cellular respiration. Releasing energy stored in the bonds of molecules (glucose, for example), it recharges a batterylike molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). VACUOLE Storage sacs, smaller in animal cells than in plant cells. Storage tank for food, water, wastes or enzymes. Plants have a large central vacuole full of water that keeps plant cells plump. GOLGI BODY or Small bags with tubes Receives packaged proteins Both connecting them. Looks from the rough endoplasmic like a stack of pancakes. reticulum and assembles them into more complex proteins. Packages and ships those proteins for use inside and outside of the cell. Packaging = putting proteins in vesicles. GOLGI APPARATUS or GOLGI LYSOSOME Small, spherical sacs that contain enzymes (molecules that break down other molecules). Digests older cell parts, food or other objects Both Both Page 2 Organelle Appearance CYTOSKELETON Small fibers crisscrossing the cell. Function Provide support for the cell; help with movement of molecules around the cell Animal, Plant, or Both Both CILIA Small hairs coving a cell Used for movement and sensing Both that wave around. the environment FLAGELLA Whip-like single hair attached to the outside of a cell. Used for movement. Animals only CENTRIOLE 2 small cylinders that sit at right angles to each other. They look like churros stuck together in a cross formation. Centrioles make the spindle fibers that are used during cell division (mitosis) to pull apart chromosomes. Animals only CELL WALL Rigid, tough wall surrounding the cell that is made of cellulose. Protects and supports the cell and makes it rigid. Plants only CHLOROPLAST Green, bean-shaped structures that contain the pigment chlorophyll in stacks called grana. Captures sunlight and uses it to produce glucose/food through photosynthesis. Plants only CENTRAL VACUOLE Large balloon-like sac that fills most of the cell. Stores water and nutrients, Plants only keeps the plant cell plump when filled with water. Page 3 Cell Organelles Practice Use the information table on the previous pages to fill in the chart. Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function Cell Part Keeps plant cells plump when they have been watered Folded membranes that can be smooth or rough The sites of protein synthesis (site where proteins are made) Transports materials within the cell to the golgi body The jelly-like substance inside the cell Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective outer covering that is not found in animal cells Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for transport outside of the cell Source of the spindle fibers that help cells divide during cell division Site inside of the nucleus where ribosomes are made The membrane surrounding plant and animal cells that controls what goes into and out of the cell. Page 4 Network of tubes that provides internal support for the cell Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus Clear tunnels that make lipids and move them around the cell Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing things Composed of a phospholipid bilayer and controls what goes into and out of the cell Longer whip-like structures used for movement Animal Cells and Plant Cells are Different (but not by much!). Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both. Organelle Plant Cells Animal Cells Organelle Cell Wall Nucleolus Chloroplast Nucleus Chromatin Cell membrane Cytoplasm Central vacuole Cytoskeleton Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Golgi apparatus Central Vacuole Plant Cells Animal Cells Lysosome Mitochondria Page 5 Cell City Analogy Instructions: Write the name of the organelle associated with the city service in the parentheses. Read the paragraphs first before you attempt to fill in the blanks. This story is just an example of what you can do with your cell city. In a far away city called Kepler City, Thingamajigs of Science (___________________) are the main product of production and export. Anyone with any sense wants a Thingamajig of Science, therefore there is a high demand across the country. Everyone in the Kepler City has something to do with making Thingamajigs of Science, and the entire town is designed to build and export Thingamajigs of Science around the world. There are lots of kinds of Thingamajigs of Science: Physics Thingamajigs, Biology Thingamajigs, and Geology Thingamajigs, to name a few, so there are lots of factories that are located near the town hall. The town hall (_________________) of Kepler City has all the instructions (_______________________) for making the different types of Thingamajigs of Science, so it is a convenient location for the factories. Any citizen of Kepler City can make entire Thingamajigs of Science or parts of Thingamajigs and can get instructions from the town hall. Thingamajigs of Science are generally produced in small factories (________________) around the city. The Factory Union (_______________________) is responsible for building new factories if one goes out of business. After the Thingamajigs of Science or their parts are constructed, they are placed on special delivery trucks (___________________________), which can deliver the Thingamajig of Science anywhere in the city. However, in order for a Thingamajig of Science to be exported to other locations outside the city, the delivery trucks take the Thingamajig of Science or their parts to the post office (______________________), where the Thingamajigs of Science are packaged and labeled for export. The post office also takes Thingamajig parts and assembles them into entire Thingamajigs for export. Sometimes Thingamajigs of Science do not work properly, and the "rejects" are sent to the scrap yard (__________________) where they are broken down for parts or destroyed altogether. The town powers the Thingamajigs of Science factories and delivery trucks from a solar power plant (__________________________) that is in the city. A large wooden fence (______________________________) encloses the entire city, and only the postal trucks (and citizens with proper passports) are allowed inside and outside the city walls. A special fence repair team (___________________________) is always on call to repair the fence so that only postal trucks with the correct ID can enter or exit the city. Product quality is of highest importance in Kepler City, after all. Page 6 Make Your Own Cell City! Instructions: Create your own analogy of the cell that is original and different from the Kepler City analogy. You will build your city out of your choice of materials (a poster, a 3-D model, a Minecraft creation, a popsicle stick city, etc…). Your city will be displayed at Neighborhood Night in a few weeks, so keep in mind that everyone will see this. Use this page to brainstorm and to draw a rough sketch of what you will create. Use the CELL CITY PROJECT worksheet to help you organize your thoughts. Also, remember that it doesn’t have to be a “city.” It can be a kingdom, space station, alien planet, school, whatever else that you find exciting or interesting. Page 7 Name: ______________________________________ Date: __________________________ CELL ORGANELLES THINKING QUESTIONS Instructions: Use scientific writing and explain your answers. 1. If a person has a lack of energy, which organelle could be malfunctioning? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. If a cell is making proteins but the proteins are unable to get out of the cell, which organelle(s) could be malfunctioning? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. If a person has ribosomes that make proteins, but the proteins are unable to go to the golgi complex, what is wrong? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. A cell cannot make proteins. What could be wrong? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. A person’s cells are making proteins that are deformed. What could be wrong with the cells making the proteins? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 6. You see two cells under a microscope. Cell 1 has a cell wall and cell 2 does not. Which cell belongs to an animal? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 7. A plant cell wilts when it does not get watered. What organelle is causing the plant to wilt? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 8. A cell becomes toxic when it cannot get rid of waste. What organelle is malfunctioning? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Page 8