Short Story Elements Analysis Template
advertisement

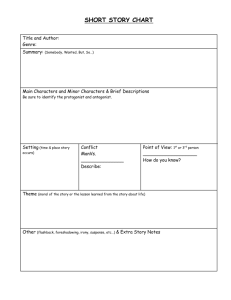
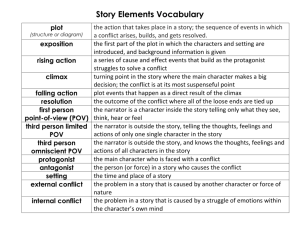
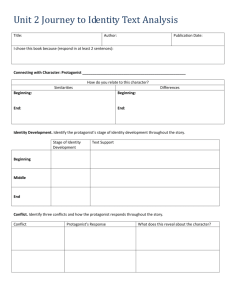
Short Story Elements Analysis Character: - Protagonist: - Antagonist: - Dynamitic Character: - Static Character: - Flat Character: - Round Character: Plot: - Exposition (Introduction): - Rising Action (includes conflict): - Climax (turning point) : - Falling Action: - Resolution: Conflict: - Man vs Man - Man vs Self: - External conflict: - Internal conflict: - Man vs Nature: - Man vs Society: Point of View: - First Person: - Third Person: Irony: Foreshadowing: Plot/Setting: Theme: Suspense: Short Story Elements – Vocabulary Character: Person in a story - Protagonist: Person who drives the action- main character - Antagonist: The opponent of the main character- causes the conflict Character Analysis: Static: stays the same Dynamic: Changes Flat: stereotyped/one sided Round: multi-faceted Plot: the events that make up a story - Exposition (Introduction): situation, setting, characters - Rising Action: conflicts and complicating events that lead up to the climax - Climax: Tense minute where the reader realizes the outcome - Falling action: results of the climax and previous decisions (very short in a short story) - Resolution/conclusion/denouement: all the problems are done (good or bad) Conflict: struggle or problem between opposing forces - External Conflict: - Man vs Man: A situation in which two characters have opposing desires or interests. The typical scenario is a conflict between the protagonist and antagonist. This is an external conflict. Most thrillers and mysteries have this type of conflict. - Man vs Nature: In this type of conflict, a character is tormented by natural forces such as storms or animals. - Man vs Society: struggle is with an outside force - Man vs Self ( Internal & External): - Internal conflict: struggle takes place within the character (greed, jealousy, etc…) this conflict develops from a protagonist’s inner struggles, and may depend on a character trying to decide between good and evil or overcome self-doubts. This conflict has both internal and external aspects, as obstacles outside the protagonist force the protagonist to deal with inner issues. Narrator: Person created by the author to tell you the story Point of View: vantage point from which the narrator tells the story - First Person: the narrator is in the story (uses I) - Third Person: narrator is not in the story but zooms in on ONE character who is (like a parrot on his shoulder – uses he, she, they) Foreshadowing: hints or clues about what is coming later Setting: time and place of a story Theme: the main idea of a story Suspense: anxiety about what will happen next in a story Connotation All the meanings associated with a word Denotation Literal meaning of the word The dictionary definition