Lecture 16
advertisement

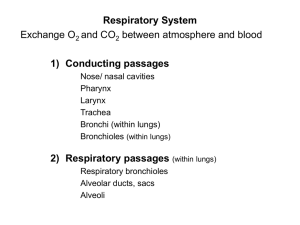
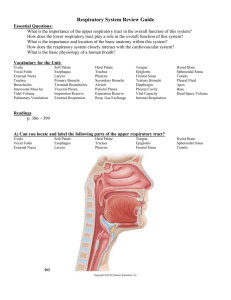
Lecture 16: The Respiratory System I. General Anatomy of Respiratory System A. Divisions 1. Upper Respiratory Tract a. nose and throat 2. Lower Respiratory Tract a. larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs B. Functions 1. pulmonary ventilation - inhaling and exhaling 2. external respiration - gas exchange lungs/blood 3. internal respiration - gas exchange blood/body II. Basic Structures A. Nose 1. external portion a. mainly cartilage attached to nasal bones b. external nares (nostrils) c. vestibules - just inside external nares 2. internal portion a. internal nares - connects nose to pharynx b. nasal septum - divides nasal cavity in two c. paranasal sinuses - cavities formed by cranium i. frontal, sphenoidal, maxillary, ethmoidal d. meatuses - passageways formed by conchae i. superior, middle, inferior e. olfactory region - above superior concha 3. FUNCTIONS a. warm and moisten air b. remove dust, debris, microbes c. assist in resonating sound from the larynx B. Pharynx (Throat) 1. nasopharynx - posterior to internal nasal cavity a. auditory (Eustachian) tubes - open here b. pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid) 2. oropharynx - posterior to oral cavity a. fauces - opening from the mouth b. palantine and lingual tonsils 3. laryngopharynx - most inferior portion a. larynx (voice box) located anteriorly b. esophagus located inferiorly C. Larynx (Voice Box) 1. 9 segments of cartilage a. unpaired - thyroid, epiglottic, cricoid b. paired - arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform 2. thyroid cartilage (Adam's apple) 3. epiglottis - covers larynx to route food a. glottis - vocal folds (cords) for sound 4. cricoid cartlage - attaches larynx to trachea 5. arytenoid cartilage - attached to vocal folds 6. Voice Production a. ventricular folds (false i. hold breath against b. vocal cords (true cords) ii. vibrate to produce c. pharynx, mouth, sinuses, iii. alter the sound cords) thoracic air pressure different frequencies nose, tongue, lips D. Trachea (Wind Pipe) 1. larynx -> T5 ; anterior to the esophagus 2. C-shaped hyaline cartilage along the esophagus 3. carina - ridge at the bifurcation to the bronchi 4. intubation - tube down collapsed trachea 5. tracheostomy - hole in trachea; bypass obstructions E. Bronchi 1. 2. 3. 4. primary bronchus -> secondary (lobar) bronchi secondary bronchi -> tertiary (segmental) bronchi tertiary bronchi -> bronchioles bronchioles -> terminal bronchioles F. Lungs 1. outer pleural membranes (remember balloon analogy) a. parietal pleura - on thoracic cavity wall b. visceral pleura - covers the lungs 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. apex (cupula) - 1 inch superior to the clavicle base - just above the diaphragm costal surfaces - against the ribs mediastinal surface - against the heart hilus - bronchi, vessels, nerves enter and exit cardiac notch - where heart lies near left lung 8. Right Lung a. 3 lobes - superior, middle, inferior b. 2 fissures - horizontal, oblique c. 3 sec. bronchi - superior, middle, inferior d. thicker and broader than left e. higher to accomodate the liver 9. Left a. b. c. Lung 2 lobes - superior, inferior 1 fissure - oblique 2 secondary bronchi - superior, inferior 10. Bronchopulmonary segments - sec. bronchi supply a. lobule - own vessels & terminal bronchiole b. terminal bronchioles -> respiratory bronchioles c. respiratory bronchioles -> alveolar ducts d. alveolar ducts -> alveoli & alveolar sacs e. alveolar sacs - alveoli with common opening 11. Alveoli - site of gas exchange with capillaries a. squamous pulmonary epithilial cells b. septal cells - secrete SURFACTANT 12. Layers of Alveolar - Capillary Membrane a. squamous pulmonary epithilium b. pulmonary basement membrane c. capillary basement membrane d. lining endothelium of capillary THE FINAL EXAM IS SOON!!!! START STUDYING NOW - IT IS COMPREHENSIVE!!!!