I. write in an appropriate correction so that the statement now...

Biology 242 – Lecture Chapter 23 ( Respiratory System ) Practice Quiz
I.
Circle T (True) or F (False). If the statement is false, cross out the word(s) that make it false and
write in an appropriate correction so that the statement now becomes a true statement.
T F 1.
When chemoreceptors sense increase in p CO
2
or increase in acidity of blood (H + ), respiratory rate
normally is stimulated.
T F 2.
The cricoid cartilage is located inferior to the thyroid cartilage.
T F 3.
The pneumotaxic and apneustic areas controlling respiration are located in the pons.
T F 4.
Most CO
2 is carried in the blood in the form of bicarbonate ion (HCO
3
).
T F 5.
Vital capacity is normally larger than expiratory reserve volume.
T F 6.
The p O
2
and p CO
2
of blood leaving the lungs are normally about the same as p O
2
and p CO
2
of
alveolar air.
II.
Using the blanks provided, fill-in the word or phrase that best fits the description given:
_________________________ 7.
This is the term for the process of exchange of gases between alveolar air and
blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
_________________________ 8.
This is the amount of air left in your lungs after you take a normal breath in
and then force exhale as vigorously as possible.
_________________________ 9.
This is the normal (average) quantity of air of the above amount of air.
________________________ 10.
This is the term what means “difficult or labored breathing”.
________________________ 11.
This is the collective name for the structure to which the epiglottis, thyroid,
and cricoid cartilages belong.
________________________ 12.
This is a substance that increases inflatability (compliance) of the lungs.
III.
Circle the letter preceding the one best answer to each question:
13.
Which of these values (in mmHg) would be normal for p O
2 of blood in the femoral artery?
A. 40 B. 45 C. 100 D. 160 E. 760 F. 0
14.
Choose the correct formula for carbonic acid:
A. HCO
3
B. H
3
CO
2
C. H
2
CO
3
D. HO
3
C
2
E. H
2
C
3
O
15.
The chief muscles of inspiration are: 1 Diaphragm 2 External Intercostals 3 Internal Intercostals
A. 1 only B. 1 and 2 C. 1 and 3 D. 2 and 3 E. 1, 2, and 3
16.
A pattern of shallow breathing is referred to as__________(1)___________; whereas a pattern of deep
breathing is called __________(2)______________.
A. 1 – Chest; 2 – Stomach B. 1 - Rib; 2 – Abdominal C. 1 – Sternal; 2 - Gut
D. 1 – Costal; 2 – Diaphragmatic E. 1 – Diaphragmatic; 2 – Abdominal
Biology 250 – Lecture Chapter 23 Practice Quiz – continued
IV.
Match the answer on the right with the short definition of the left:
17.
_____ C-shaped structures
18.
_____ internal intercostals
19.
_____cricoid cartilage
20.
_____pleura
21.
_____elastic cartilage
22.
_____ larynx
23.
_____diaphragm
24.
_____cardiac notch
25.
_____external intercostals
26.
_____ has three lobes
A.
aka “voice box”
B.
tissue of which the epiglottis is composed
C.
serous membrane associated with each lung
D.
left lung
E.
contraction causes elevation of the rib cage
F.
tracheal cartilages
G.
right lung
H.
muscular floor of the thorax
I. contraction causes depression of the rib cage
J.
base of the larynx
Page Two
V.
Arrange the answers in correct sequence:
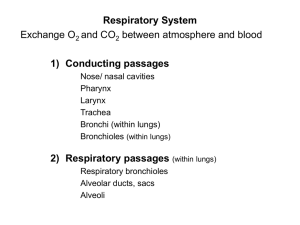
____, ____, ____, ____, ____ 27.
From superior to inferior: A.
Bronchioles B.
Bronchi C.
Larynx
D.
Pharynx E.
Trachea
___, ___, ___, ___, ___, ___ 28.
Pathway of inspired air: A.
Alveolar ducts B.
Bronchioles
C.
Secondary bronchi D.
Primary bronchi E.
Tertiary bronchi F.
Alveoli