Anatomy of the Respiratory System
advertisement

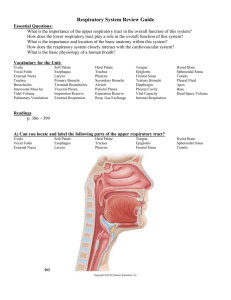
Anatomy of the Respiratory System I. A. B. C. D. E. F. Function air distributor gas exchange (O2 & CO2) filters, warms, and humidifies air sound production; phonation: speech olfaction; smell regulates pH II. Divisions A. upper respiratory system: 1. nose, pharynx (throat), and larynx (voice box) B. lower respiratory system 1. trachea (windpipe), lings, and bronchial tree C. accessory structures 1. diaphragm and thorax III. Upper Respiratory Tract A. nose 1. anatomy a. cleft palate: palatine bones do not fuse causing difficulty in swallowing and speech b. cribiform plate: separates nasal and cranial cavities c. septum: vomer; separates nose into right and left cavities d. anterior nares: external openings; nostrils e. vestibule: skin on inside of nose f. vibrissae: hair on vestibule g. posterior nares: openings that allow air into pharynx h. sinus: hollow cavities lined with mucus to lighten weight of skull i. epistaxis: nose bleed 2. function a. air distribution b. filters (vibrissae and mucous), warms (mucous), and moistens air (mucous) c. lightens weight of skull (sinuses) d. resonate speech (sinuses) e. olfaction: smell B. pharynx (throat) 1. divisions a. nasopharynx: posterior nares to soft palate b. oropharynx: soft palate to hyoid c. laryngopharynx: hyoid to esophagus 2. openings (7); into or out of the pharynx a. right and left eustachian (auditory) tubes into nasopharynx; 2 b. posterior nares into nasopharynx; 2 c. fauces (opening from mouth into oropharynx); 1 d. laryngopharynx into larynx (voice box); 1 e. laryngopharynx into esophagus; 1 3. tonsils a. pharyngeal tonsils: located in nasopharynx i. adenoids: enlarged; blocks air passage (sleep with mouth open) b. palatine tonsils: located in oropharynx; tonsillitis c. lingual tonsils: located in oropharynx 4. function a. air distribution b. pathway for digestive tract c. phonation: speech pronunciation (vowels) d. filter, warms, and humidify e. stops pathogens; disease causing agents C. larynx (voice box) 1. cartilage; 9 a. thyroid: Adam’s apple (larger in men and more fat padding); hyaline cartilage (support) b. epiglottis: made of elastic cartilage to blocks trachea during digestion; flexible c. cricoid; hyaline cartilage d. arytenoids (2) : attach vocal cords; hyaline cartilage e. corniculate (2); hyaline cartilage f. cuneiform (2); hyaline cartilage 2. function a. air distribution b. filters, warms, and humidifies: ciliated mucous to collect dust c. protects airway when swallowing; epiglottis d. voice production IV. Lower Respiratory Tract A. trachea (windpipe) 1. connection between larynx and primary bronchi 2. air distribution B. bronchial tree (inverted tree) 1. structure a. primary (1o) bronchi: left and right bronchi b. secondary (2o) bronchi c. tertiary (3o) bronchi d. bronchioles e. alveolar ducts: stem of grapes f. alveolar sacs: cluster of grapes g. alveoli: grape a. surrounded by capillaries; sight of gas exchange 2. function a. air distribution b. respiration: gas exchange c. filter, warms, and humidifies air C. lungs 1. structure a. apex: top b. base: bottom 2. lobes a. left lung: superior and inferior lobes j. oblique fissure separates lobes b. right lung: superior, middle, and inferior lobes i. oblique fissure separates inferior and middle lobe ii. horizontal fissure: separates middle and superior lobe 3. function a. air distribution: contains bronchial tree b. gas exchange: contains alveoli V. Accessory Structures A. thorax 1. cavities a. right pleural cavity: contains right lung b. mediastinum: contains heart c. left pleural cavity: contains left lung 2. function a. inspiration: increase size and raise chest b. expiration: decrease size and lower chest B. diaphragm: muscle 1. function a. inspiration: contracts; pulls thoracic cavity down b. expiration: relaxes VI. Diseases/Disorders A. upper respiratory infection (URI) 1. rhinitis: inflammation of the mucosa in the nasal cavity a. symptoms: can lead to sore throat, cough, upset stomach (excess mucus drips into esophagus and trachea) b. cause: bacteria, virus, allergic reaction, c. treatment: antibiotic, antihistamine, decongestant 2. pharyngitis: inflammation of the pharynx; sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes a. symptoms: redness and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) b. cause: bacteria c. treatment: lozenges, rest, fluid intake, antibiotics 3. laryngitis: inflammation of the larynx a. symptoms: edema (swelling) of vocal cords, dysphonia (hoarseness or loss of voice) b. cause: bacteria, inhale toxic substance (alcohol, smoke), intubations, vocal abuse c. treatment: limit speech B. lower respiratory tract 1. bronchitis: inflammation of the bronchi a. symptoms: nonproductive cough, malaise, fever, sore throat b. cause: bacteria, fatigue, malnutrition, exposure to air pollutants c. treatment: antibiotics, rest, cough suppressant 2. pneumonia: inflammation of the lower respiratory tract a. symptoms: high fever, chills, headache, cough , chest pain, (hypoxia) deficiency of oxygen in blood b. cause: bacteria, virus, fungi c. treatment: antibiotics, respiratory therapy 3. tuberculosis a. symptoms: nonproductive cough, fatigue, chest pain, weight loss, fever b. cause: bacteria c. treatment: antibiotics 4. emphysema a. symptoms: enlargement of air spaces to terminal bronchioles from tissue damage; alveoli enlarge: damage of gas exchange units b. cause: enzymes that destroy lung tissue that are triggered by smoking c. treatment: oxygen 5. asthma a. symptoms: muscle spasms in bronchi: narrows air passage b. cause: stress, exercise, infection, allergy c. treatment: steroids