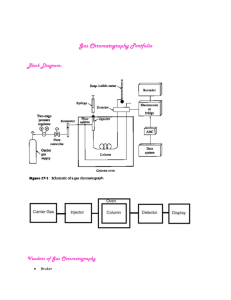
Worksheet - Cambridge Essentials
advertisement

9 Worksheet 3 Paper and thin-layer chromatography 1 a The table below shows the distances moved by the solvent and three substances undergoing paper chromatography. Distances are given to the nearest mm. Substance Distance moved (cm) solvent 10.0 A 4.0 B 5.0 C 6.0 Calculate the Rf values for the three substances. b The following chromatogram was obtained when using the same solvent and a mixture containing two of the substances. [3] i Using measurements from the diagram, calculate the Rf value for each spot. ii Which of the substances – A, B or C – are spot I and spot II? c Why should the same solvent be used for both experiments? d Use the diagram below to help explain the process of two-dimensional paper chromatography. [2] [1] [2] COAS Chemistry 2 Teacher Resources Original material © Cambridge University Press 2005, 2007, 2009 [3] 1 9 Worksheet 3 2 Thin-layer chromatography is used to separate substances and is an alternative to paper chromatography. a Name two substances that can be used as the stationary phase in thin-layer chromatography. b i Explain why dry thin-layer plates operate through adsorption. ii Explain why, if the same plates are only partially dried, the system operates through partition and adsorption. c Give three advantages of thin-layer chromatography over paper chromatography. Total: COAS Chemistry 2 Teacher Resources 22 Score: Original material © Cambridge University Press 2005, 2007, 2009 [2] [3] [3] [3] % 2