what should i know about photosynthesis
advertisement
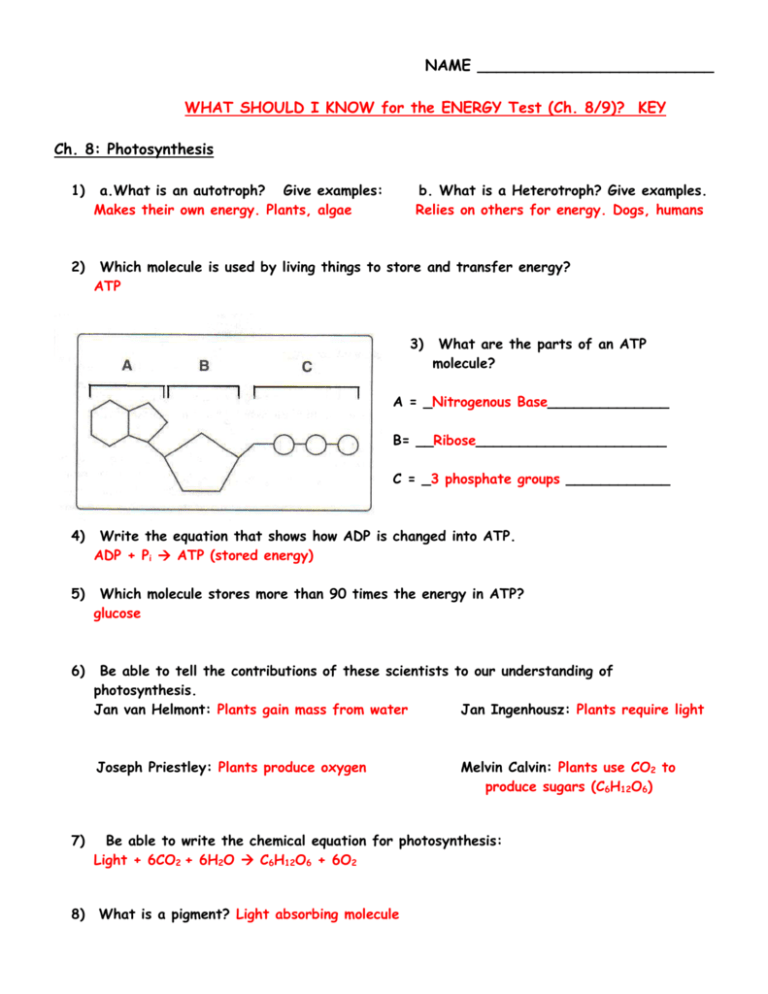
NAME _________________________ WHAT SHOULD I KNOW for the ENERGY Test (Ch. 8/9)? KEY Ch. 8: Photosynthesis 1) a.What is an autotroph? Give examples: Makes their own energy. Plants, algae b. What is a Heterotroph? Give examples. Relies on others for energy. Dogs, humans 2) Which molecule is used by living things to store and transfer energy? ATP 3) What are the parts of an ATP molecule? A = _Nitrogenous Base______________ B= __Ribose______________________ C = _3 phosphate groups ____________ 4) Write the equation that shows how ADP is changed into ATP. ADP + Pi ATP (stored energy) 5) Which molecule stores more than 90 times the energy in ATP? glucose 6) Be able to tell the contributions of these scientists to our understanding of photosynthesis. Jan van Helmont: Plants gain mass from water Jan Ingenhousz: Plants require light Joseph Priestley: Plants produce oxygen 7) 8) Melvin Calvin: Plants use CO2 to produce sugars (C6H12O6) Be able to write the chemical equation for photosynthesis: Light + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 What is a pigment? Light absorbing molecule 9) What is the main pigment used by green plants to absorb energy? chlorophyll 10) Which wavelengths of light are best absorbed by chlorophyll a & b? Chl a – blue-violet and red (450 and 700nm). Chl b – blue and red (500 and 700nm) 11) Why do plants look green? Reflect green Label the parts of a chloroplast and tell where the reactions for photosynthesis happen. A= _Thylakoid________________ B= __Stroma_________________ C= _Granum__________________ D= __Lumen__________________ E= __Cytoplam of Plant Cell ______ 12) Place where light dependent reactions happen = _A___ 13) Place where Calvin cycle happens = _B____ 14) What is NADP+ ? What does it do? Electron carrier, it shuttles electrons energized by sunlight to the dark reactions. 15) Where does the H that ends up in NADPH originally come from? Water (H2O gets split into Oxygen and Hydrogen) 16) Be able to describe the two sets of reactions involved in photosynthesis Light-dependent reactions, Calvin cycle. And Labe: Ch. 9: Cellular Respiration 17. Be able to label parts in a mitochondrion and tell where the different reactions happen. Intermembrane Space Inner Membrane (Cristae) Matrix 18. What is a calorie? Amount of energy needed to raise 1 g of water 1 deg Outer Membrane Celsius 19. What is a Calorie? Kilocalorie (1000 calories) – what’s on food labels 20. What is the chemical formula for cellular respiration? C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP 21. How does this equation compare to the equation for photosynthesis? It’s the exact reverse, except Light energy is replaced by cellular energy (ATP). 22. Be able to describe the steps of the pathways for: Glycolysis, alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, Krebs cycle, and Electron transport chain. Also, be able to label the summary diagram: 23. Does glycolysis require oxygen? NO 24. Which molecule forms when glucose is broken in half? pyruvate 25. What is the other name for Krebs cycle? Citric Acid Cycle 26. What happens to CO2, produced during the Krebs cycle? Gets released to the atmosphere. If an animal – breathes it out. 27. What is the final electron acceptor at the end of Electron Transport? Oxygen 28. What does anaerobic mean? What does aerobic mean? anaerobic – without oxygen aerobic – with oxygen 29. What are the two kinds of fermentation? Lactic acid and alcoholic 30. Why do cells use fermentation? (Hint: It’s NOT to make alcohol or lactic acid) To empty the electron carrier NADH created by glycolysis. It gives the electrons a place to go so that NAD+ is regenerated and glycolysis can continue thereby producing ATP for the organism. Remember – fermentation does NOT produce ATP for the organism, just allows glycolysis to continue repeating.









