Answers-RespExcrReviewSheet
advertisement

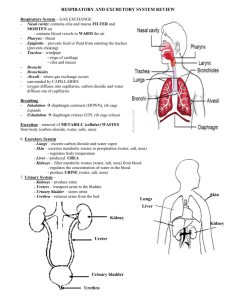
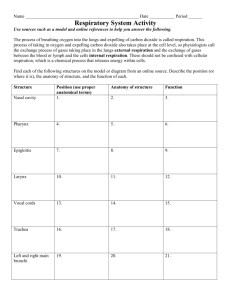
The Respiratory System Lungs and Breathing The following statements trace the path of oxygen from the atmosphere to a body cell. Label each statement from 1 – 6 in the correct sequence. Not all steps are listed here. _____ 1. Passes through the bronchi. _____ 2. Passes through the bronchioles. _____ 3. Enters the body through the mouth or nasal cavity. _____ 4. Blood in the capillaries of alveoli picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide _____ 5. Arrives at the alveolus and diffuses into the blood. _____ 6. Is carried by the blood to tissue cells. Gas Exchange Mark each statement below T if it is true and F if it is false. _____ 7. Gas exchange occurs when oxygen in the alveoli diffuses into the blood in the capillaries and carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the air of the alveoli. _____ 8. Carbon dioxide can be eliminated from cells by diffusion. _____ 9. Oxygen is transported in the blood by hemoglobin. Regulation of Breathing Complete each statement by underlining the correct word or phrase in the brackets. 10. Receptors in the (spinal cord and lymphatic system/brain and circulatory system) enable the body to automatically regulate oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations by sending signals to the brain. 11. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood has a (greater/lesser) effect on the regulation of breathing than does the concentration of oxygen. 12. Diffusion of gases between the blood or tissue fluids and cells is called (external respiration / internal respiration / cellular respiration). 13. Release of energy from the breakdown of glucose to form ATP is called (external respiration / internal respiration / cellular respiration). 14. Exchange of gases between the atmosphere and blood is called (external respiration / internal respiration / cellular respiration). Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 1 Place a check next to each statement that accurately describes the operation of the diaphragm and chest muscles. _____ 15. When the muscles of the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles contract, the chest cavity expands. _____ 16. When the diaphragm contracts, the lungs collapse. _____ 17. When the diaphragm relaxes, the pressure inside the chest cavity increases and air rushes out. Diseases of the Respiratory System Compare three diseases of the respiratory system by describing the disease. 18. Asthma ___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 19. Emphysema ________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 20. Lung Cancer _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM REVIEW 1. What is oxygen needed for? aerobic cellular respiration What is the function of this process? to make ATP 2. For animals, what gas needs to be taken in? oxygen What gas is a waste product? carbon dioxide 3. Where does air enter the body? mouth and nose Where does it travel to? alveoli 4. What is another name for the voice box? larynx 5. What is another name for the windpipe? trachea 6. What do the tissues that line the larynx and trachea do? trap unwanted particles in the respiratory tract 7. Explain what the bronchioles are. small branches from the bronchi 8. What are the bronchioles lined with? cilia Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 2 What do you suppose is the purpose of these? move trapped particles out of the respiratory of the respiratory tract 9. Define alveoli (include what gases do in them). small air sacs where gases are exchanged with capillaries 10. Describe the function of the capillaries around the alveolus. allow blood to exchange gases with alveoli 11. How many alveoli does each lung contain? about 300 million alveoli per lung What is the total surface area for each lung? about 70-90 square meters per lung; the surface area of both lungs together is almost the size of a tennis court! 12. When a person inhales, explain what happens to the diaphragm. it contracts and pulls down 13. When a person exhales, explain what happens to the diaphragm. it relaxes and goes up 14. How does the size of the chest cavity change when a person inhales? it gets bigger 15. How does the size of the chest cavity change when a person exhales? it’s smaller than on an inhale 16. What process is used for gas to go from the alveoli to the capillaries? diffusion!! 17. How does carbon dioxide get out of blood? it diffuses from a high concentration to a lower concentration 18. What does oxygen bind to in the blood? hemoglobin 19. What is hemoglobin? a protein found in red blood cells 20. Where does the oxygen go to from the red blood cells? into tissues that need oxygen (this could be muscle cells, brain cells, skin cells, etc. 21. What does your body’s tissues use oxygen for? to make ATP through cellular respiration 22. Explain the following respiratory diseases: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning - suffocation occurs when Carbon Monoxide gas blocks O2 from binding to hemoglobin; Carbon Monoxide is given off from natural gas (the stove), car fumes, etc. Tuberculosis – a contagious disease transmitted by airborne particles; most people are vaccinated against TB Cystic Fibrosis – a genetic disease that causes excess mucus to build up in respiratory passages and other organs; afflicted children often need a machine to help remove excess mucus from breathing passages Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 3 The Excretory System Kidney Form and Function On the line at the left, write the letter of the answer that best completes each sentence. ______ 1. Ammonia and other nitrogen-containing wastes are eliminated from the human body in the form of a. feces. b. uric acid. c. urea. d. purine. ______ 2. Each human kidney contains over 1 million ________ that serves as bloodcleaning units. a. stones b. microvillus c. enzymes d. nephrons Urine Formation Mark each statement below T if it is true and F if it is false. ______ 3. The first state of urine formation is called titration. ______ 4. About 1 L of urine is produced each day. ______ 5. During reabsorption, water and solutes moved out of the nephron and are sent back into the bloodstream. ______ 6. Urine exits the body through the ureter, a tube that leads outside the body. Kidney Disorders and Treatment Complete each statement by writing the correct word in each space provided. 7. The common kidney disorder _____________ ___________ are deposits of uric acid, calcium salts, and other substances. 8. Kidney stones may be eliminated naturally from the body or be removed by ____________________ procedures. 9. Patients with kidney disorders may have their blood artificially filtered by ______________. 10. Why does the liver convert ammonia into urea? ___________________________________. Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 4 Write the name of the structure in the excretory system next to its description. Bowman’s capsule Nephron Urethra Glomerulus Ureter Urinary bladder ________________________________ 11. Basic functional unit of work in the kidney. ________________________________ 12. Tube that connects the renal pelvis to the bladder. _________________________________ 13. Holds urine. _________________________________ 14. Tube from the bladder to the outside of the body. __________________________________ 15. Cup-shaped end of the renal tubule that surrounds the glomerulus. ___________________________________ 16. Mass of capillaries in the nephron through which blood flows at high pressure. 17. What type of environment are your respiratory and excretory system trying to create in your body? The body is trying to maintain a balanced internal environment (homeostasis) by eliminating waste products. 18. What are the waste products from human metabolism? The excretory system produces urea as a waste product. The respiratory system produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. 19. Ammonia is a poisonous waste product that is created from breaking down excess amino acids. What is ammonia converted to, to make it less toxic and where does this take place? It’s converted to urea in the liver. 20. How is urea eliminated from the body? It’s filtered out by the kidneys and eliminated from the body in urine. 21. Why does your perspiration have an odor? Because it may contain urea. 22. What organ is the main part of the excretory system? kidney 23. What material is filtered out of the capillaries (glomerulus) into the Bowman’s capsule and removed from the blood? Basically all small components of the blood are filtered out (water, glucose, amino acids, urea, etc.) The good stuff is reabsorbed and the bad stuff (urea) forms the urine. THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM REVIEW Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 5 1. What product is released from the breakdown of amino acids? ammonia 2. Why must ammonia be released from the body? it is toxic to cells 3. What makes urea? ammonia is combined with carbon dioxide in the liver 4. Is urea more or less toxic than ammonia? less 5. What does urea enter after it has been in the liver? the blood 6. How does some of the urea leave the body? sweat 7. What is perspiration made up of? water, urea, salts 8. How is most urea eliminated from the body? in the urine 9. How big are the kidneys and where are the kidneys located? about the size of your fists; they are located in your lower back 10. What are nephrons? tiny filtration units of the kidney 11. How many nephrons does each kidney have? about 1 million 12. What does the capsule of a nephron surround? blood vessels 13. What does the blood in the capillaries do? transport blood cells and other materials 14. After the substances twist and turn around in the nephron, what do they form? eventually urine is formed as a waste product 15. What does urine contain? mostly water and urine, some salts and hydrogen ions too 16. What is the first stage of urine formation called? filtration 17. What happens during filtration? all small substances are filtered out of the blood 18. What substances remain in the blood? large particles like blood cells and big proteins 19. What substances are filtered out of the blood? all small substances are filtered out of the blood 20. What makes the concentrations of urine vary? your level of hydration 21. What is the second stage of urine formation? reabsorption 22. What percentage of filtered blood is sent back into the bloodstream? 99% 23. Again, list the substances that are sent back to the bloodstream. glucose, amino acids, water, some salts and minerals Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 6 24. What controls water reabsorption? the hypothalamus 25. What hormone is involved in this process? ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) 26. When your body needs to save water, what happens to the amount of this hormone? the amount of ADH increases 27. What does ADH do to the ends of the nephron? it makes the ends of the nephrons more permeable to water so more water is reabsorbed and conserved in the body 28. Is urine more or less dilute with a decrease in ADH? more dilute 29. After reabsorption, where is the urine located? in the collecting ducts of the nephrons 30. What is the urine made up of? water, urea, salts 31. After the kidney, where does the urine flow? the ureter 32. After the above tube, where does the urine flow next? bladder 33. Through which tube does the urine leave the body? urethra 34. Where does this tube lead? out of the body Congratulations, you’ve made it to the end of this answer key. Science/The Respiratory System/revised 2007/Kimberly Kim/l.kairis 7