Cell Test Review Questions Answer Key

Your name:____________________________
The Date:_____________________________
Completed on time________
Review Questions Answer Key for Cell Test
Directions: Answer these in complete sentences
1.
read the directions
I. Cell concept and theory:
2.
Who is Robert Hooke and What did he look at?
He was an English scientist who used microscopes to look at cork cells
3.
What is in cells?
Primarily a complex liquid and organelles
4.
When would a scientific theory be discarded?
When evidence suggesting it needed fixing arose
5.
What tools do scientist use to discover cells. (There are two main kinds)
Dye, microscopes,
6.
What kind of microscope would some one use to look at endoplasmic reticulum
An electron microscope
7.
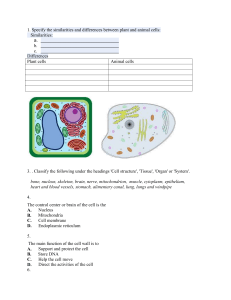
How are plant and animal cells similar?
They have most of the same organelles in common
II. Organelles
8.
What organelle is responsible for digestion of intracellular molecules lysosomes
1
9.
What does the nucleus contain?
DNA, chromosomes
10.
What are chromosomes composed of?
DNA
11.
What does the cell membrane function as, what does the cell membrane do in this capacity?
It is a barrier, it allows or commands the passage of things inside and outside the cell.
12.
What is the cell membrane composed of? phospholipids
13.
What organelle is involved in protein synthesis? ribosomes
14.
What are cell walls composed of, what does this contribute to in plants?
Cellulose, it gives rigidity
15.
What organelle generates ATP? mitochondria
16.
What do chloroplasts do?
Photosynthesis, make inorganic chemicals organic
III. Cell Functions
17.
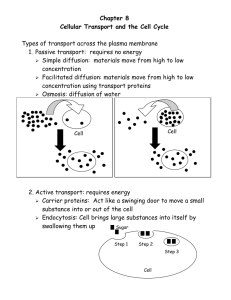
What is the relationship between osmosis and diffusion?
They both involve movement of material from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis is water, diffusion is not water.
18.
In what direction do molecules tend to move in diffusion?
From high concentration area to low concentration area or phrased another way -down its concentration gradient.
2
19.
What is the relationship between water and cell shape?
More water makes the cell swollen, less water makes it crenated
20.
What is the relationship between cell size and diffusion?
The smaller a cell is the higher the surface area to volume ratio is and the higher the diffusion factor.
IV. Cell Cycle
21.
What occurs during the G1 phase?
Primarily growth
22.
What occurs during the S phase?
DNA duplication
23.
What occurs during the G2 phase?
Final preparations, a few proteins and chemicals are made
24.
What occurs during Prophase?
Chromosomes condense and attach to the spindle fibers
25.
What occurs during Metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle
26.
What occurs during Anaphase?
Centromeres separate and chromatids move toward poles
27.
What occurs during Telophase?
Cell divides
28.
What is the relationship between the two cells resulting from mitosis?
They are genetically identical
29.
What is the spindle apparatus?
A protein structure that the chromosomes attach to and facilitates mitosis
3