Essential Questions, vocab, and practice quiz
advertisement

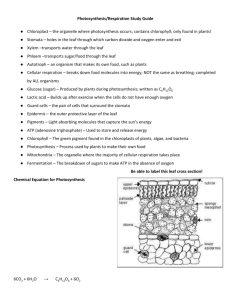
STANDARD 2 REVIEW MODULE 1 TEACHING TARGET Objective 1 a.) Recognize the importance of photosynthesis in using light energy as part of the chemical process that builds plant materials. Objective 1 b.) Explain how respiration in animals is a process that converts food energy into mechanical and heat energy. Learning Activities: Photosynthesis and Respiration SMARTNotes Differentiated Reading Activity VOCABULARY Photosynthesis: A process where autotrophs using solar energy to create glucose, cellulose or other sugar. The first step in most foodchains. Respiration: A process done by autotrophs and heterotrophs to get energy out of food Chemical potential energy: The energy stored in the tissues of plants and animals that can be used for energy when consumed. Referred to as biomass. Glucose: A form of sugar that is produced by photosynthesis. Yields/produces: Used in chemical equations to mean equals. Mechanical energy: Energy of motion. Examples include swimming, running, escaping Heat energy: Thermal energy usually in the form of body heat. Light/solar energy: Radiant energy emitted by the sun. Oxygen: A gas produced by photosynthesis and used by respiration. Carbon dioxide: A gas produced by respiration and used by photosynthesis. ATP: The energy molecule produced by respiration. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. Label each of the parts of the photosynthesis equation below. Use the following choices: carbon dioxide, water, water, chlorophyll, sunlight, sugar, oxygen 2. What energy conversion happens when plants do photosynthesis? Full sentence explanation. 3. An organism uses sunlight and carbon dioxide to form sugar. What kind of organism is this? Explain fully. 4. Explain the experiment we did with the Elodea plant and how it showed us that more light will cause a plant to do more photosynthesis. 5. Label each of the parts of the respiration equation below using the following choices: ATP, heat energy, mechanical energy, water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sugar ENERGY MOLECULE 6. Which process directly produces the energy needed to carry out life activities? EXPLAIN A. circulation B. digestion C. excretion D. respiration 7. What energy conversion happens when plants do respiration? Full sentence explanation. 8. An organism uses oxygen and sugar to get energy. What kind of organism is this? Explain fully. 9. An organism uses oxygen and sugar to get energy. What kinds of energy does this organism get? Explain fully there are two.. 10. How are respiration and photosynthesis related, similar, different? Explain in detail, answer your readers question. DIFFERENT SIMILAR RELATED STANDARD 1 FORMATIVE 1 PRACTICE CONTENT QUIZ 1. What energy conversion happens when animals use respiration? A. Nuclear energy is converted to chemical energy B. Chemical energy is converted to nuclear energy C. Chemical energy is converted to mechanical energy D. Heat energy is converted to chemical energy 2. Which substance do plants AND animals use for their energy and growth needs? A. carbon dioxide B. oxygen C. nitrogen D. water 3. What best explains photosynthesis? A. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and is usually the first step in food chains B. Photosynthesis produces carbon dioxide and is usually the last step in food chains C. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and is the last step in most food chains D. Photosynthesis produces carbon dioxide and is usually the first step in food chains 4. What best describes respiration? A. Respiration produces oxygen and ATP which makes sugar for animals B. Respiration produces carbon dioxide and ATP which allows animals to move and have a body temperature C. Respiration produces carbon dioxide and ATP which makes sugar for animals D. Respiration produces oxygen and ATP which allows animals to move and have a body temperature 5. Use the chemical equation below to answer the following question. sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 sunlight What does the mean in the equation above? A. Sunlight represents the raw materials needed. B. Sunlight must come from a specific direction. C. Sunlight is not a necessary part of this equation. D. Sunlight causes the change to occur. 6. Use the chemical equation for photosynthesis to answer the following. What is true of photosynthesis, based on this chemical equation? A. sunlight is not needed for photosynthesis B. glucose is produced by photosynthesis C. oxygen is needed for photosynthesis D. carbon dioxide is produced by photosynthesis sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 7. Use the chemical equation for respiration to answer the following. What is true of respiration, based on this chemical equation? A. oxygen is produced by respiration B. glucose is produced by photosynthesis C. oxygen is needed for respiration D. carbon dioxide is needed for respiration 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O+ ATP 8. Use the equations below. What best explains the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration. A. oxygen and carbon dioxide are produced by respiration and used for photosynthesis B. glucose and oxygen are produced by respiration and used for photosynthesis C. oxygen and glucose are produced by photosynthesis and is used for respiration D. glucose and carbon dioxide are produced by photosynthesis and used for respiration PHOTOSYNTHESIS sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O RESPIRATION 6O2 + C6H12O6 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O+ ATP STANDARD 1 FORMATIVE 1 PRACTICE VOCABULARY QUIZ 1. A process where autotrophs using solar energy to create glucose, cellulose or other sugar. The first step in most food chains. A. Photosynthesis C. Respiration B. Oxygen D. ATP 2. A process done by autotrophs and heterotrophs to get energy out of food A. Photosynthesis B. Oxygen C. Respiration D. ATP 3. The energy stored in the tissues of plants and animals that can be used for energy when consumed. Referred to as biomass. A. Heat energy B. Chemical potential energy: C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 4. The energy molecule produced by respiration A. Heat energy B. Chemical potential energy: C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 5. A form of sugar that is produced by photosynthesis. A. Heat energy B. Glucose C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 6. Thermal energy usually in the form of body heat. A. Heat energy B. Glucose C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 7. Radiant energy emitted by the sun. A. Heat energy C. Light/solar energy B. Mechanical Energy D. ATP 8. A gas produced by photosynthesis and used by respiration. A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 9. A gas produced by respiration and used by photosynthesis. A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 10. Energy of motion. Examples include swimming, running, escaping predators A. Heat energy B. Mechanical Energy C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 11. Used in chemical equations to mean equals. A. Yields/produces C. Light/solar energy B. Mechanical Energy D. ATP ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS KEY 1. Label each of the parts of the photosynthesis equation below. Use the following choices: carbon dioxide, water, water, chlorophyll, sunlight, sugar, oxygen 2. What energy conversion happens when plants do photosynthesis? Full sentence explanation. The sunlight energy, which is solar energy, gets converted to sugar which is chemical potential energy. 3. An organism uses sunlight and carbon dioxide to form sugar. What kind of organism is this? Explain fully. An autotroph or producer. Fancy name for plants. 4. Explain the experiment we did with the Elodea plant and how it showed us that more light will cause a plant to do more photosynthesis. The plant with more light did more photosynthesis and had more oxygen gas trapped in the top of the experiment set up. 5. Label each of the parts of the respiration equation below using the following choices: ATP, heat energy, mechanical energy, water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sugar ENERGY MOLECULE 6. Which process directly produces the energy needed to carry out life activities? EXPLAIN A. circulation B. digestion C. excretion D. respiration It is a process that releases energy from food energy so that organisms can do lifes activities. 7. What energy conversion happens when plants do respiration? Full sentence explanation. The sugar or food energy that is in the form of chemical potential energy gets converted to mechanical energy (running, flying, swimming, etc.) and heat energy in the form of maintaining body temperature. 8. An organism uses oxygen and sugar to get energy. What kind of organism is this? Explain fully. A heterotroph or consumer. Basically and animal or nonplant organism. 9. An organism uses oxygen and sugar to get energy. What kinds of energy does this organism get? Explain fully there are two. mechanical energy (running, flying, swimming, etc.) and heat energy in the form of maintaining body temperature. 10. How are respiration and photosynthesis related, similar, different? Explain in detail, answer your readers question. DIFFERENT They are related as basically opposites that “feed” each other. SIMILAR The products of photosynthesis are the reactants for respiration. So they involve the same compounds and substances. RELATED They are different because what goes into one comes out of the other and vice a versa. STANDARD 1 FORMATIVE 1 PRACTICE CONTENT QUIZ KEY 1. What energy conversion happens when animals use respiration? A. Nuclear energy is converted to chemical energy B. Chemical energy is converted to nuclear energy C. Chemical energy is converted to mechanical energy D. Heat energy is converted to chemical energy 2. Which substance do plants AND animals use for their energy and growth needs? A. carbon dioxide B. oxygen C. sugar D. water 3. What best explains photosynthesis? A. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and is usually the first step in food chains B. Photosynthesis produces carbon dioxide and is usually the last step in food chains C. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and is the last step in most food chains D. Photosynthesis produces carbon dioxide and is usually the first step in food chains 4. What best describes respiration? A. Respiration produces oxygen and ATP which makes sugar for animals B. Respiration produces carbon dioxide and ATP which allows animals to move and have a body temperature C. Respiration produces carbon dioxide and ATP which makes sugar for animals D. Respiration produces oxygen and ATP which allows animals to move and have a body temperature 5. Use the chemical equation below to answer the following question. sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 sunlight What does the mean in the equation above? A. Sunlight represents the raw materials needed. B. Sunlight must come from a specific direction. C. Sunlight is not a necessary part of this equation. D. Sunlight causes the change to occur. 6. Use the chemical equation for photosynthesis to answer the following. What is true of photosynthesis, based on this chemical equation? A. sunlight is not needed for photosynthesis B. glucose is produced by photosynthesis C. oxygen is needed for photosynthesis D. carbon dioxide is produced by photosynthesis sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 7. Use the chemical equation for respiration to answer the following. What is true of respiration, based on this chemical equation? A. oxygen is produced by respiration B. glucose is produced by photosynthesis C. oxygen is needed for respiration D. carbon dioxide is needed for respiration 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O+ ATP 8. Use the equations below. What best explains the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration. A. oxygen and carbon dioxide are produced by respiration and used for photosynthesis B. glucose and oxygen are produced by respiration and used for photosynthesis C. oxygen and glucose are produced by photosynthesis and is used for respiration D. glucose and carbon dioxide are produced by photosynthesis and used for respiration PHOTOSYNTHESIS sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O RESPIRATION 6O2 + C6H12O6 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O+ ATP STANDARD 1 FORMATIVE 1 PRACTICE VOCABULARY QUIZ KEY 1. A process where autotrophs using solar energy to create glucose, cellulose or other sugar. The first step in most food chains. A. Photosynthesis C. Respiration B. Oxygen D. ATP 2. A process done by autotrophs and heterotrophs to get energy out of food A. Photosynthesis B. Oxygen C. Respiration D. ATP 3. The energy stored in the tissues of plants and animals that can be used for energy when consumed. Referred to as biomass. A. Heat energy B. Chemical potential energy: C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 4. The energy molecule produced by respiration A. Heat energy B. Chemical potential energy: C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 5. A form of sugar that is produced by photosynthesis. A. Heat energy B. Glucose C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 6. Thermal energy usually in the form of body heat. A. Heat energy B. Glucose C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 7. Radiant energy emitted by the sun. A. Heat energy C. Light/solar energy B. Mechanical Energy D. ATP 8. A gas produced by photosynthesis and used by respiration. A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 9. A gas produced by respiration and used by photosynthesis. A. Oxygen B. Carbon dioxide C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 10. Energy of motion. Examples include swimming, running, escaping predators A. Heat energy B. Mechanical Energy C. Light/solar energy D. ATP 11. Used in chemical equations to mean equals. A. Yields/produces C. Light/solar energy B. Mechanical Energy D. ATP