The Brain Stem
advertisement

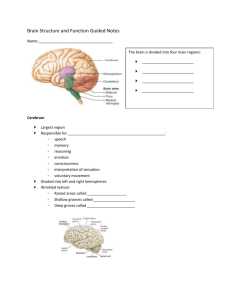
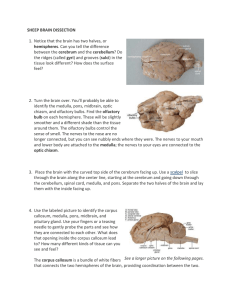
The Brain The Brain Weighs almost 3 lbs Consists of about 100 billion neurons and 10-50 trillion neuroglia Parts of the Brain The Brain Stem Continuous with the spinal cord Consists of medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain Diencephalon Above the brain stem Consists of the thalmus, hypothalmus and pineal gland Parts of the Brain Cerebrum Forms most of the brain Consists of a thin layer of gray matter, the cerebral cortex and white matter Cerebellum Posterior to the brain stem Means “little brain” Cranial Meninges Continuous with the spinal meninges Includes the Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater and Pia Mater Brain Blood Supply Oxygen – The brain requires 20% of the body’s oxygen supply. Neurons that are without oxygen for 4 or more minutes may be permanently damaged Glucose - the glucose in the blood is the source of energy for the brain’s cells. Very little glucose is stored in the brain, so if there isn’t enough glucose in the blood a person can experience confusion, dizziness, convulsions and loss of consciousness. The Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) Protects the brain from harmful substances and pathogens by blocking passage of many substances from the blood into brain tissue. Does NOT protect from lipid-soluble substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, alcohol, and most anesthetic agents. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) A clear, colorless liquid that carries oxygen, glucose, and other needed chemicals from the blood to the neurons. It removes wastes and toxic substances produced by the brain and spinal cord cells Brain Stem Medulla Oblongata a continuation of the spinal cord containing all the sensory and motor tracts extending between the spinal cord and other parts of the brain 1. Cardiovascular Center – regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of the blood vessels 2. Medullary Rhythmicity Area – adjusts the basic rhythm of breathing 3. Other areas also responsible for reflexes for swallowing, vomiting, coughing and sneezing 4. Receives input from or provides output to cranial nerves 8 – 12 Pons Above the medulla and anterior to the cerebellum 1. bridge that uses axons to connect parts of the brain with one another 2. helps to control breathing 3. associated with cranial nerves 5 – 8 Midbrain - connects the pons to the diencephalon 1. Cerebral Peduncles – conduct nerve impulses from the cerebrum to the spinal cord, medulla and pons 2. Substantia Nigra – large and darkly pigmented. Associated with Parkinson’s Disease 3. Red Nucleus – looks red due to rich blood supply. Helps to coordinate movement. Diencephalon Thalamus – paired oval masses of gray matter. Important relay stations for sensory impulses. Plays a role in acquisition of knowledge (cognition). Also contributes to motor function and regulation of autonomic activities Hypothalamus – small portion below the thalamus. Functions in control of the autonomic nervous system, pituitary gland, regulation of emotional and behavioral patterns, eating and drinking, body temperature and circadian rhythms. Pineal Gland – size of a small pea. Part of the endocrine system because it secretes the hormone melatonin which contributes to sleepiness. Cerebellum Compares intended movement with what is actually happening. Regulates posture and balance. Coordinates complex motor activities A. Cerebellar Hemispheres – located posterior to the medulla and pons and below the cerebrum. B. Cerebellar Cortex – Surface consisting of gray matter Cerebrum interprets sensory impulses, controls muscular movements and functions in emotional and intellectual processes A. Gyri – folds of brain tissue B. Fissures – deep groves between folds C. Sulci – shallow groves between folds D. Corpus Callosum – broad band of white matter containing axons that extend between the 2 hemispheres E. 4 Lobes (per hemisphere) – named by the bone that covers it 1. Frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital F. Basal Ganglia – coordinates automatic muscle movements and regulates muscles tone.