Notes 3-1
advertisement

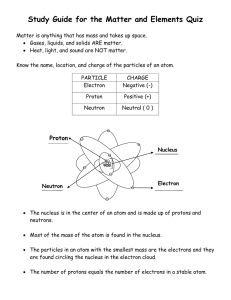
CHAPTER 3 Section 1 Dmitri Mendeleev A Russian scientist who was able to organize the elements in a pattern according to their properties. Atomic Mass – average mass of one atom of the element. Periodic Table – chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties. -Patterns appeared when arranged in order of increasing atomic mass Inside an Atom Nucleus – core of an atom containing protons and usually neutrons. -Protons – small positively charged particles. -Neutron – small particles with no charge. -Electrons – negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom. Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – unit used to measure the mass of particles in an atom. -Ex. Protons and Neutrons are 1 amu Atomic Number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Reading the Periodic Table Chemical Symbol – one or two letter representations of an element. Ex. C – Carbon, Na - Sodium Groups or Families – elements that are arranged in a column. Period – elements arranged in a horizontal row. Why the Table Works Valence Electrons – one of the electrons farthest away from the nucleus. These electrons are involved in a chemical reaction. -The elements in each group of the periodic table have the same number and arrangement of valence electrons.