MCAS questions for Mesopotamia
advertisement

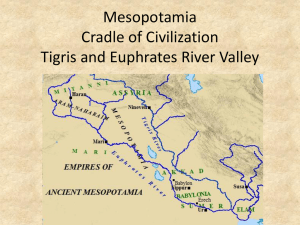
MCAS questions for Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia: Site of Several Ancient River Civilizations (M) 1. What is the Fertile Crescent? Where is it? What modern day countries now occupy that land? In order, what empires controlled the land of the Fertile Crescent in ancient times? Fertile The Fertile Crescent is a quarter-moon shaped region that extends Crescent from the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. Or one could say the Fertile Crescent includes the Nile River region extending north along the coast of the eastern Mediterranean until it meets the source of the rivers and travels south along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. 1 Mesopotamia Literally means “the land between two rivers”. Mesopotamia is the area of land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers The counties that now occupy the land include: Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, and Jordan. Empires of the Fertile Crescent An empire is many peoples and lands under the control of one ruler. Akkadian Sargon He was the first person to build an empire. Babylonian Empire Hammurabi He created the first code of law. Assyrian Empire Ashurbanipal He is credited with the construction of a library at Ninevah. Assyrians were known to be fierce fighters. Medes and Chaldeans joined forces to create the new empire. Nebeuchadnezzar built the Hanging Gardens of Babylon for his wife. Cyrus united the Persians and expanded the empire. New Babylonian empire Persian 2 2. Describe the religious beliefs of the people in Mesopotamian civilizations. Polytheistic Belief in many gods Many gods existed, each city state had their own gods People worshipped their own gods and the gods of other city states Sumerians thought of the gods as rich land owners Ziggurat Priests People Center of city life. Served as both a temple/church and the city hall. Usually three tiers tall, with the uppermost level reserved for religious purposes. Prominent in a city state. Were members of a high social class. Priests were thought to have contact with the gods Priests interpreted events for the populace Priests worked to satisfy the gods. Religious rituals and offerings were presented to gods by members of all social classes. Sumerians viewed events as rewards or punishments from the gods. The people worked hard to please the gods, offerings were presented to gods. 3 3. What three inventions contributed to the growth of the civilizations in Mesopotamia? Explain how each of them contributed to the growth of Mesopotamian civilizations. Wheel Major advancement Served 2 purposes Sail Plow Allowed for transportation over land of goods and people Used in making pottery “potter’s wheel” Used by potters to speed up the process of making clay pots Allowed the movement of heavy items via a boat without significant physical effort by people. Travel by boat was preferred to travel over land, it was safer and easier This device was being improved continuously Plows loosened soil allowing water to penetrate deeper into the soil Plows also reduced the effort required to yield crops 4 4. What four factors helped Mesopotamia to flourish? Explain how each factor contributed to the growth of the Mesopotamian civilizations. Irrigation Irrigation allowed man to settle further from the water source and still be able to water crops. Extended farmable land Increased farmable land meant even greater food production Water needed to grow crops could travel to the land via canals Metalsmithing Gradually over time tools were improved. With improved tools craftsmen and farmers were able to produce more products or products of improved quality The use of bronze made tools stronger Improved tools lasted longer Slavery Used to do the hard or dangerous work Free labor Obtained in wars and also sold into slavery by family Domestication of animals Animals were used to aid in farm labor. Animals were utilized for the products they produced, eggs, wool. Animals were used as a direct source of food. 5 5. Hammurabi developed a code explain the reasons why he developed the code and why the code was important. Basis “eye for an eye” Punishment is related to the crime Why is this important Goal How accomplished Example of a law This is the first set of laws Code established the idea that government should provide protection and justice for the people. Introduced the idea that the law should apply to all people “rule of law” Fair treatment (justice) for all people Hammurabi believed a code of law would help him control the empire Hammurabi sent representatives into the empire to gather existing laws Using the existing laws Hammurabi created a code for the empire. Code was posted prominently on pillars near a temple. 282 laws were created Law 197 - If a man break another man’s bone, his bone shall be broken. 6 6. Describe the THREE important achievements of Mesopotamian civilization. Achievements are the big ideas that mark a civilization. Writing A system of writing emerged from record keeping. Writing was first used to track food supplies. Over time writing was used for tax collection and the recording of other information. Cuneiform is the form of writing associated with the Mesopotamian area. Monumental The ability to construct multi story buildings and Architecture other large structures is an indicator of the success of the culture. Examples are the ziggurat, Ishtar’s Gate, Library at Ninevah, and Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Art Three forms of art are associated with Mesopotamia, relief sculptures, mosaics and cylinder seals. Relief sculptures are raised images on stone. Mosaics are small pieces of glass or stone assembled into an image. A cylinder seal is a cylinder engraved with a 'picture story', used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally wet clay. 7 8 7. Identify and explain the characteristics of a civilization. Advanced cities Specialized workers Complex Institutions Record keeping Advanced technology Places to store and trade surplus agricultural products and other resources. Many more skilled people existed in the cities, and there was a greater variety of skilled tradesmen in the cities. Food surpluses lead to specialized workers. For the first time in history everyone did not need to acquire food themselves. With surpluses, it became possible for people to specialize in a skill and trade for the necessary food or other new materials. Examples of specialized skills include: herdsman, potter, metal worker, scribe, boatman, trader, and weaver. Institutions are groups of people with a purpose; often the purpose was to help society meet its needs. Early examples are governmental and religious institutions. Maintaining proof of matters within the city. Record keeping was first used to keep track of the food supply. Over time more information was collected (taxes). Eventually keeping records led to the emergence of written language. Technology is the application of knowledge, tools, or inventions to better meet their needs. In cities technology continued to evolve. Cities were the places where new technology emerged. 9