Mesopotamia
advertisement
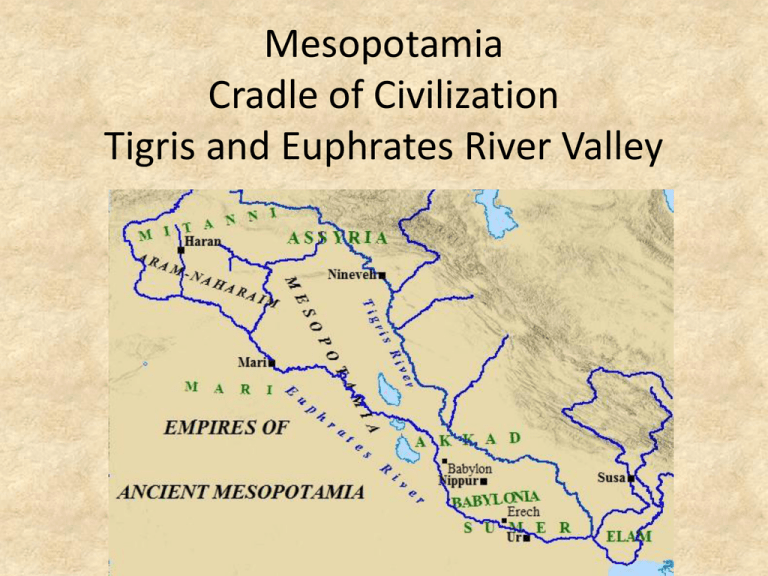
Mesopotamia Cradle of Civilization Tigris and Euphrates River Valley Geography • Fertile Crescent • Not many, if any natural barriers • Unpredictable flooding History • Over the course of several thousand years, several successive civilizations occupied the same general area • Mesopotamia literally means “Land between 2 rivers” Cultural Diffusion • With each passing civilization, ideas were shared (or taken when conquered), then modified and improved upon • Through this diffusion, a number of achievements were made Achievements (by ruling group) • Sumerians – City-State Political Organization • Similar cultures, but each ruled itself – Smelting of Metals (Bronze and Iron Age) • First to use bronze – – – – – Invented the Wheel, Sail, and Plow Ziggurats – enormous, religious pyramid type buildings Cuneiform writing Organized land development and irrigation canals Numerical system in base 60 • Ex. 60 minutes in an hour; 360 degrees in a circle Sumerians (continued) • 4500 B.C. people were settling in the region, then in 3500 B.C. the Sumerians settled there and became the dominant group Sumerian Literature • Epic of Gilgamesh – Early Literature – Story of a young ruler and his quest for immortality – Many note the similarities between this and Ecclesiastes in the Bible – Gilgamesh learns lessons similar to the ideals of Hammurabi’s Code Decline of Sumer • Sumerian city-states were weakened due to fighting one another • Conquered by Sargon the Akkadian from the North in 2350 B.C. • This created the first empire (more than one previously independent nation or people coming under the same control) Hammurabi’s Code • Around 2000 B.C. Amorites take over Mesopotamia, and set up at Babylon • Hammurabi rules from 1792 B.C. to 1750 B.C. (this is the height of their empire) • He created the code, which is the first set of laws to be written down – Uniform laws for all – Idea the government has duty to people Phoenicians begin c. 1200 BC – ends c. 146 BC • Alphabet – Developed writing system that had one character for one sound – Trading partners picked it up – The word alphabet comes from their first 2 letters (aleph and beth) – Makes learning easier for everyone around the world that encountered it • Trading Empire – Excellent ship builders and seafarers – Some evidence shows that they traded for tin with those on the southern coast of Britain – Other evidence suggests they may have traveled all the way around Africa Assyrians first established c. 2200 BC.c. 859 BC firmly established and thriving; ends c. 608 BC—had many different eras From the Tigris to Central Egypt • Communication – Multi-level to keep rulers informed of goings on • Chariots • Military Organization – Developed through constantly being attacked (no natural barriers) • Empire Building and Organization Persians begins c. 540 BC – ends c. 331BC • Tolerant Empire – did not destroy cities they conquered – Allowed local customs to remain in place – Allowed Jews to return to Jerusalem c. 538 BC (had been exiled earlier by Babylonians) • Roads (empire wide communication system) – Ran from Persia to Anatolia (1677 miles) • Structure of Government – Divided the vast empire into 20 provinces, governed by a satrap • Standing Army • Standardized coined money Hebrews • Monotheistic Religion • Torah/Law of Moses and the Prophets – Begins c. 2000-1500BC