Content: Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
advertisement

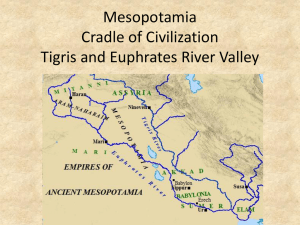
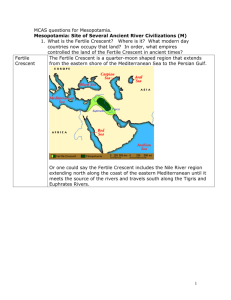
Content: Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization Villages in Mesopotamia grew into large cities . The people of Mesopotamia had to solve a series of problems in order to live successfully in their challenging environment. These cities eventually grew into civilized empires with stable food supplies, social structures, governments, religion, arts, technology and written languages. Sumerian Empire Akkadian Empire Babylonian Empire Assyrian Empire Neo -Babylonian Empire Ancient Civilizations Grade 7 Learning Standards: 7.6 Identify the characteristics of civilizations. (H,G,E) The presence of geographic boundaries and political institutions An economy that produces food surpluses A concentration of a population in distinct areas or cities The existence of social classes Developed systems of religion, learning, art, and architecture A system of record keeping 7.7 Locate the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria on a historical map and explain why this area is sometimes called the Fertile Crescent. On a modern map of western Asia, identify the modern countries of Iraq, Iran and Turkey. (H,G,E) 7.8 Identify polytheism as the religious belief of the people in Mesopotamian civilizations. (H) 7.9 Describe how irrigation, metalsmithing, slavery, the domestication of animals , and inventions such as the wheel, the sail, and the plow contributed to the growth of Mesopotamian civilizations. (H,E) 7.10 Describe important Mesopotamian achievements. (H,C,E) Its system of writing (and its importance in the record keeping and tax collection) Monumental architecture (the ziggurat) Art (large relief sculptures, mosaics, and cylinder seals) 7.11 Describe who Hammurabi was and explain the basic principle of justice in Hammurabi’s Code. (H,C,E) Pacing Guide: - 9/29-10/24 (18 days) Key Questions: How did physical geography affect the growth of ancient civilizations? Skills and Outcomes: When students have finished studying this topic, they will know and be able to: Formative/Summative Assessments: Students will complete the following products/other assessments to demonstrate the skills and understandings they have acquired. Why were other groups able to conquer the city-states of Sumer? What accomplishments is each empire known for? What were the features of some of the first Mesopotamian city-states? What do the Sumerian religious beliefs tell us? What technology did Assyrians use to conquer lands? What are the advantages of a written code of laws as opposed to a set of spoken laws? identify how the physical setting contributed to the development of Mesopotamian city-states describe the development of agricultural techniques- such as irrigation systems, that led to the emergence of city-states list the key features of a Sumerian citystate identify characteristics of a civilization identify the locations of the early Mesopotamian empires describe the major achievements of early Mesopotamian empires and their leaders explain the significance of Hammurabi’s Code What is the difference between polytheism and monotheism? What role did slaves play in the economy of empires? Analyze several Mesopotamian artifacts and explain how they are examples of civilization. Summarize your findings. Make up your own descriptive poem or song about life in your empire. Include at least five aspects of life. Perform the poem as a rap or read aloud to your classmates. Draw a stele to commemorate one of your empires greatest achievements. In a paragraph, explain why you chose that particular achievement. Choose one of the five empires we have studied. Create a museum display that accurately depicts several aspects of life in your chosen empires. These aspects should include government, geography, writing, art, agriculture, technology, social structure, and religion. In the classroom, debate the pros and cons of Hammurabi’s Code when given different scenarios. In a persuasive essay debate the pros or cons of Hammurabi’s Code.